Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 09, 2024 9 months, 3 weeks, 1 day, 18 hours, 36 minutes ago
Medical News: Chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders might sound complex, but they fundamentally refer to persistent muscle inflammation that leads to long-lasting pain and impaired movement. Recent scientific breakthroughs have highlighted the central role of mitochondria - tiny powerhouses within our cells - in these conditions. This study review covered in this
Medical News report delves deeper into the fascinating world of mitochondria and understand their impact on chronic muscle inflammation and potential treatments.
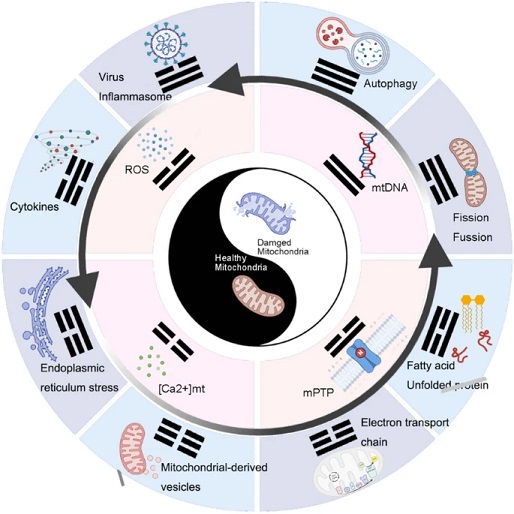 Graphical Abstract - Mitochondria and Muscle Health
What Are Mitochondria?
Graphical Abstract - Mitochondria and Muscle Health
What Are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are vital components of our cells, responsible for producing energy. They generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is crucial for muscle contraction and overall cellular function. In a state of chronic inflammation, the mitochondria's ability to produce energy is compromised, leading to muscle pain, fatigue, and weakness.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic Inflammation
When muscles are inflamed over extended periods, several issues arise at the mitochondrial level:
-Mitochondrial Dynamics: Mitochondria are dynamic structures that continuously undergo fission (splitting into smaller units) and fusion (joining together into larger structures). This balance is essential for their proper function. Chronic inflammation disrupts this balance, leading to an accumulation of damaged mitochondria.
-Calcium Regulation: Mitochondria play a critical role in regulating calcium levels within cells. During chronic inflammation, calcium regulation is disturbed, causing further mitochondrial dysfunction and contributing to muscle pain and weakness.
-Oxidative Stress: This occurs when there is an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS), harmful molecules that can damage cells. Under normal conditions, mitochondria help neutralize ROS. However, in chronic inflammation, the mitochondria are overwhelmed, leading to increased oxidative stress and further damage.
The Vicious Cycle of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is a key player in chronic muscle inflammation. Damaged mitochondria produce more ROS, which, in turn, causes more mitochondrial damage. This creates a vicious cycle of ongoing inflammation and muscle deterioration. High levels of ROS can lead to reduced ATP production, further impairing muscle function and increasing pain and fatigue.
Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Quality Control
Our bodies have built-in mechanisms to manage mitochondrial health:
-Mitochondrial Biogenesis: This process involves the creation of new mitochondria to replace damaged ones. It is regulated by various factors, including PGC-1α, a protein that stimulates the production of new mitochondria.
-Mitophagy: This is the
process of removing damaged mitochondria. It ensures that only healthy mitochondria remain in the cells, maintaining optimal cellular function.
In chronic inflammation, both mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy are impaired. This leads to the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria, exacerbating the symptoms of muscle inflammation.
Structural Differences in Mitochondria
Mitochondria within muscle cells are not all the same. There are two main types:
-Intramyofibrillar Mitochondria (IFM): Located between muscle fibers, these mitochondria are critical for muscle contraction and endurance. They are more susceptible to damage during chronic inflammation.
-Subsarcolemmal Mitochondria (SSM): These are found beneath the cell membrane and are involved in regulating cellular metabolism. SSM can also be significantly affected by chronic inflammation, leading to metabolic disturbances.
The Role of Mitochondria in Inflammation
Damaged mitochondria release signals known as mitochondrial-derived damage-associated molecular patterns (mito-DAMPs). These signals are similar to those released by pathogens and can trigger an immune response. In chronic inflammation, excessive mito-DAMPs lead to a sustained inflammatory state, further damaging muscle tissues.
Potential Treatments
Understanding the role of mitochondria in chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders offers new treatment avenues:
-Antioxidants: These substances can help manage oxidative stress by neutralizing ROS. Common antioxidants include vitamins C and E, and compounds like coenzyme Q10.
-Mitochondrial Enhancers: Compounds that support mitochondrial function and biogenesis can improve energy production and reduce inflammation. Examples include PGC-1α activators and AMPK activators.
-Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise is known to boost mitochondrial biogenesis and function. A balanced diet rich in nutrients can also support mitochondrial health. Avoiding excessive stress and managing body weight are additional lifestyle modifications that can help.
Conclusion
Mitochondria play a crucial role in maintaining muscle health. Their dysfunction is a significant factor in chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders. By targeting mitochondrial health through antioxidants, mitochondrial enhancers, and lifestyle changes, we can potentially alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. Understanding and maintaining mitochondrial health is essential for managing and treating chronic muscle inflammation.
The study review by researchers from The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University-China, National Defense Medical Center-Taiwan, The Chinese University of Hong Kong-China and The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University-China were published in the peer reviewed journal: cell and Bioscience.
https://cellandbioscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13578-024-01259-9
For more about chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mitochondrial-dysfunction-biomarkers-and-curcumin-new-hope-for-severe-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/philadelphia-study-validates-that-sars-cov-2-causes-mitochondrial-metabolic-and-epigenomic-reprogramming
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mitochondrial-respiratory-chain-component-ndufa4-identified-as-potential-therapeutic-target-for-gastrointestinal-cancer
