Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Dec 31, 2024 4 months, 1 week, 2 days, 7 hours, 34 minutes ago
Medical News: Recent research delves into how mitochondrial flux - a term describing the dynamic balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission - plays a critical role in maintaining cellular health and immunity. The study, conducted by Charles Ward of the Department of Biochemistry at the Medical University of Gdańsk in Poland, emphasizes the intersection of mitochondrial behavior and the innate immune system. This
Medical News report explores these findings and their implications for understanding diseases like asthma, hepatitis, and COVID-19.
 Mitochondrial Flux and Its Disruption in Viral Infections Such as COVID-19
Mitochondrial Flux and Its Disruption in Viral Infections Such as COVID-19
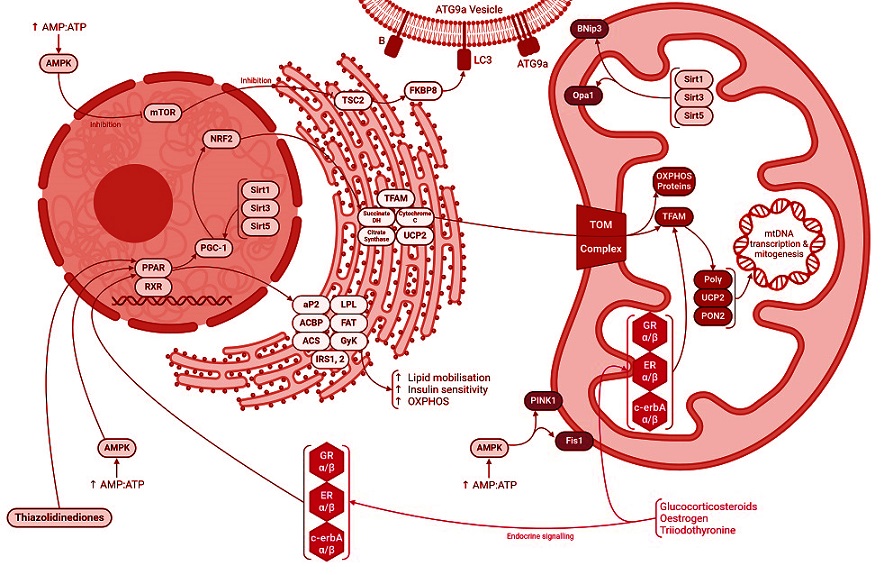
Mitochondria, often described as the cell's powerhouse, are more than energy generators. They engage in a continuous cycle of structural remodeling through fusion (joining) and fission (splitting). This dynamic process, referred to as flux, ensures proper energy distribution, cellular repair, and immune responses. Disruptions in this delicate balance are linked to various diseases, ranging from chronic respiratory conditions to viral infections.
Mechanisms of Flux Regulation
Mitochondrial flux involves two key processes: biogenesis and mitophagy. Biogenesis refers to the creation of new mitochondria, involving extensive communication between the cell's nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. The mitochondrial genome, though small, encodes essential proteins for the electron transport chain (ETC), crucial for cellular energy production. Complementary nuclear-encoded proteins ensure proper assembly and functionality.
Mitophagy, on the other hand, is the selective degradation of malfunctioning mitochondria. When mitochondria become damaged, they release signals like reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), triggering their removal. Proteins such as PINK1 (PTEN-induced kinase 1) and Parkin facilitate this process by marking defective mitochondria for degradation.
The balance between these processes is critical. As noted in the study, disruptions in flux mechanisms can lead to cellular dysfunction, heightened inflammation, and compromised immunity.
Mitochondria in Immune Responses
The study highlights how mitochondrial flux integrates with innate immunity. During infections, mitochondria serve as platforms for immune signaling. For instance, mtDNA leaks can activate pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which detect foreign or damaged cellular material. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), a key PRR, responds to mtDNA to initiate immune defenses.
Additionally, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) plays a pivotal role in defending against viruses. MAVS is activated when receptors like RIG-I detect viral RNA, initiating the production of interferons - proteins that suppress viral replication. However, many viruses, including hepatitis B and C, have evolved mechanisms to hijack mitochondrial processes, suppressing immune responses to sustain their survival.
Flux Disruption in Viral and Chronic Diseases
/>
Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in several diseases, as revealed by Ward’s research. In SARS-CoV-2 (the virus causing COVID-19), viral proteins interfere with mitochondrial flux, inhibiting mitophagy and disrupting energy metabolism. This contributes to severe inflammation and long-term complications seen in "long COVID."
Hepatitis B and C also exploit mitochondrial pathways. Hepatitis B virus enhances mitophagy to suppress immune defenses, while hepatitis C virus disables MAVS signaling, undermining interferon responses. Both strategies allow these viruses to persist in the host, leading to chronic inflammation and liver damage.
In asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), excessive autophagy (a related process to mitophagy) correlates with disease severity. Genetic studies show that mutations in autophagy-related genes increase susceptibility to these conditions. Targeting mitochondrial pathways, such as the mTOR signaling pathway, offers promising avenues for therapy.
Conclusions and Future Directions
Mitochondrial flux is not just a metabolic process but a cornerstone of cellular immunity. The study underscores its importance in maintaining immune balance and combating diseases. A deeper understanding of these mechanisms could pave the way for innovative treatments targeting mitochondrial dysfunction.
The findings illustrate that diseases such as asthma, hepatitis, and COVID-19 share a common thread: disruption of mitochondrial flux. Addressing these disruptions through therapeutic interventions, including modulating mitophagy and enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis, holds immense potential.
The study findings were published on preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202412.2275/v1
For the latest about Mitochondrial Flux, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mitochondrial-dysfunction-and-metabolic-chaos-in-viral-infections
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-insights-into-mitochondrial-role-in-post-covid-recovery-and-long-covid-progression
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-causes-skeletal-muscle-and-mitochondrial-damage-that-contributes-to-myalgic-encephalomyelitis-chronic-fatigue-syndrome
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-causes-disruptions-in-blood-brain-barrier-via-mitochondria-impairment-and-endothelial-dysfunction
