Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Component NDUFA4 Identified As Potential Therapeutic Target For Gastrointestinal Cancer
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 10, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 2 weeks, 2 days, 10 hours, 42 minutes ago
Cancer News: Gastrointestinal cancer stands as a formidable adversary in the realm of oncology, exacting a heavy toll on global health. Comprising a diverse array of malignancies such as colorectal, liver, gastric, and esophageal cancers, these diseases collectively contribute a significant portion of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. Despite advancements in diagnostic modalities and treatment strategies, the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and metabolic factors underlying gastrointestinal cancers continues to challenge clinicians and researchers alike. Among the myriad players in cancer biology, mitochondrial energy metabolism has emerged as a focal point for investigation, offering tantalizing prospects for targeted therapeutic interventions. Within this intricate landscape, NADH dehydrogenase 1 alpha subcomplex 4 (NDUFA4) has recently garnered attention as a potential linchpin in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal cancer. This
Cancer News report embarks on an in-depth exploration of NDUFA4, elucidating its structural, regulatory, and functional intricacies, while delving into its implications across various gastrointestinal malignancies. The study was conducted by researchers from Zunyi Medical University, Guizhou-China.
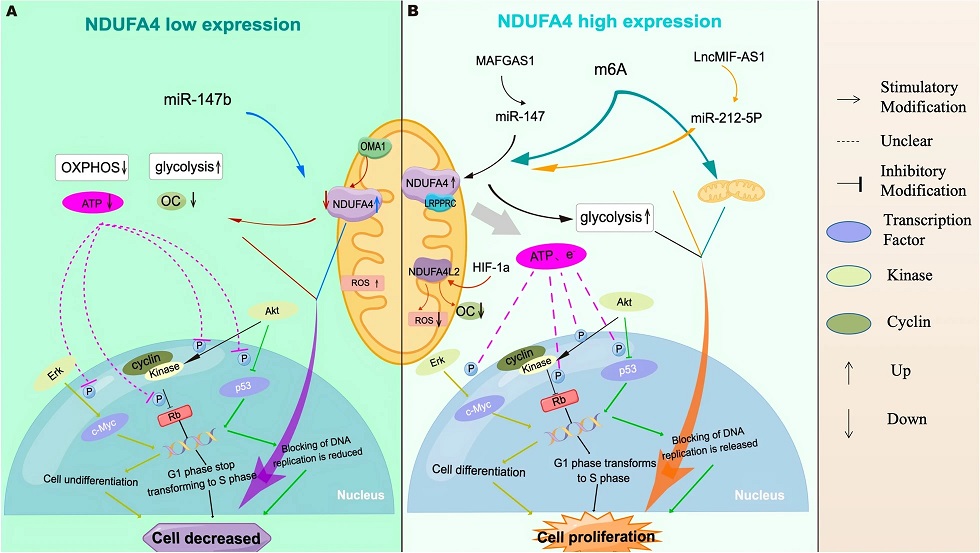 Schematic map of the mechanisms by which NDUFA4 regulates the proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. A Low NDUFA4 or downregulated expression leads to decreased cell number. B High expression of NDUFA4 or its regulated expression leads to cell proliferation.
Unraveling the Nexus of Energy Metabolism and Cancer
Schematic map of the mechanisms by which NDUFA4 regulates the proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. A Low NDUFA4 or downregulated expression leads to decreased cell number. B High expression of NDUFA4 or its regulated expression leads to cell proliferation.
Unraveling the Nexus of Energy Metabolism and Cancer
Energy metabolism lies at the heart of cellular physiology, dictating fundamental processes essential for growth and survival. In the context of cancer, dysregulation of energy metabolism manifests as a hallmark feature, driving aberrant cellular proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Central to this metabolic rewiring is the phenomenon known as the Warburg effect, wherein cancer cells favor glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation even in the presence of oxygen, thereby facilitating rapid biomass accumulation and tumor progression. Against this backdrop, understanding the intricate nuances of mitochondrial energy metabolism assumes paramount importance, with NDUFA4 emerging as a pivotal player in this dynamic interplay.
Structural Insights into NDUFA4
NDUFA4, encoded by the NDUFA4 gene on human chromosome 7p21.3, represents a critical component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex IV. Structurally, NDUFA4 comprises 81 amino acids and plays a multifaceted role in electron transport, redox processes, and ATP generation. Despite its ubiquitous expression across various tissues, the precise regulation of NDUFA4 expression remains a subject of intense scrutiny, with post-translational modifications and miRNA-mediated mechanisms exerting intricate control over its abundance.
Regulatory Mechanisms Governing NDUFA4 Expression
The expression of NDUFA4 is subject to a complex regulatory framework, encompassing transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational control me
chanisms. Transcriptional regulation of NDUFA4 involves the orchestration of transcription factors and co-regulators that modulate its promoter activity. Furthermore, post-transcriptional modifications, including miRNA-mediated regulation and mRNA stability, finely tune the abundance of NDUFA4 within the cellular milieu. Notably, post-translational modifications such as ubiquitination exert additional layers of control over NDUFA4 stability and function, highlighting the intricate regulatory networks that govern its expression.
Functional Implications of NDUFA4
NDUFA4's functional repertoire extends beyond its canonical role in mitochondrial respiration, encompassing diverse cellular processes ranging from stress response modulation to signaling pathway regulation. Aberrant expression of NDUFA4 has been implicated in a spectrum of clinical disorders, underscoring its significance in cellular homeostasis and disease pathogenesis. Notably, recent studies have unveiled NDUFA4's involvement in the modulation of signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt, implicating its role in cancer cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis.
NDUFA4 in Gastrointestinal Cancer
-Colorectal Cancer (CRC): In CRC, dysregulation of NDUFA4 expression has been associated with altered mitochondrial energy metabolism, culminating in enhanced cancer cell growth and metastasis. Mechanistically, NDUFA4 collaborates with regulatory proteins such as LRPPRC to modulate signaling pathways crucial for cancer progression.
-Liver Cancer (LC): Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exhibits aberrant upregulation of NDUFA4L2, a molecule related to NDUFA4, under hypoxic conditions. This heightened expression promotes cancer cell survival and metastasis by modulating mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
-Gastric Cancer (GC): Elevated expression of NDUFA4 in GC fosters glycolysis and oxidative metabolism, fueling cancer cell growth and invasiveness. Regulatory mechanisms involving RNA modifications and interactions with long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) further underscore NDUFA4's role in GC pathogenesis.
-Other Cancers: NDUFA4 has been implicated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, verrucous epidermal nevus, and head and neck paragangliomas, suggesting a broad impact on cancer development and progression.
Future Perspectives
As research endeavors continue to unravel the intricacies of NDUFA4 biology, several avenues beckon for further exploration. Elucidating tissue-specific expression patterns, deciphering transcriptional regulatory networks, and delineating NDUFA4's impact on mitochondrial dynamics represent critical priorities. Furthermore, harnessing the therapeutic potential of NDUFA4-based interventions demands meticulous investigation, emphasizing precision and efficacy in clinical translation.
Conclusion
In the burgeoning landscape of cancer biology, NDUFA4 stands as a beacon of hope, offering insights into the intricate nexus between energy metabolism and cancer pathogenesis. Across various gastrointestinal malignancies, NDUFA4's multifaceted roles underscore its potential as a therapeutic target, beckoning researchers to unravel its complexities further. As the quest for precision oncology gains momentum, NDUFA4 emerges as a promising candidate, heralding a new era of targeted therapies for gastrointestinal cancer.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Cancer Cell International.
https://cancerci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12935-024-03283-8
For the latest
Cancer News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
