Neural Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise in Brain Restoration and Alzheimer’s Disease
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 08, 2024 4 months, 3 weeks, 3 days, 23 hours, 48 minutes ago
Medical News: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most challenging neurodegenerative conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people, particularly the elderly. The disease leads to a gradual decline in cognitive functions, memory, and daily functioning. Researchers globally have been exploring various treatments, yet effective options remain limited, often focusing on alleviating symptoms rather than curing or reversing the disease.
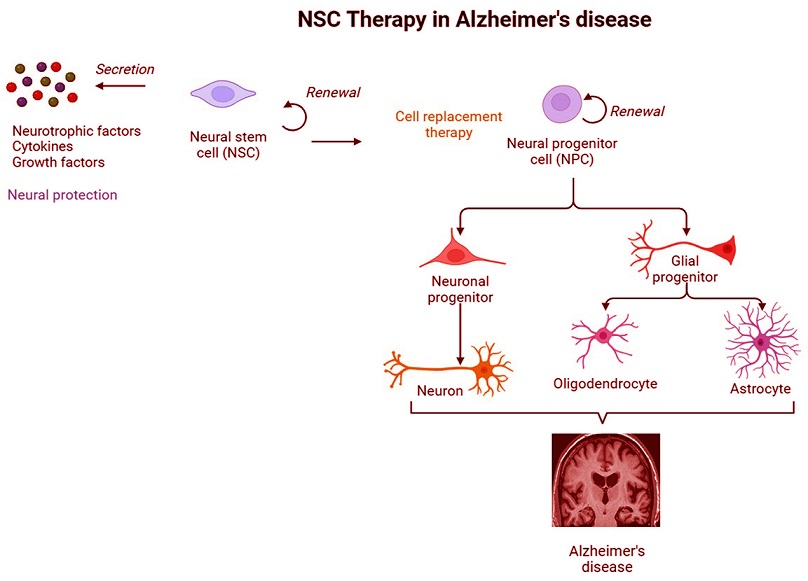 Graphical Abstract - Neural Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise in Brain Restoration and Alzheimer’s Disease
Stem Cells: The Next Frontier
Graphical Abstract - Neural Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise in Brain Restoration and Alzheimer’s Disease
Stem Cells: The Next Frontier
Recent advancements suggest that human neural stem cells (hNSCs) might hold the key to effective Alzheimer's treatments. This
Medical News report will delve into the science behind using stem cells to restore brain function and slow down AD progression. Researchers believe that stem cells can replace lost neurons, restore damaged networks, and improve brain health in patients. In essence, neural stem cells act as a repair system, potentially revolutionizing how we treat Alzheimer’s.
The Institutions Behind This Research
The groundbreaking research featured in this study was led by Indian scientists from the University of Kashmir in Srinagar, India, Khalsa College of Pharmacy in Amritsar, and the Central Council for Research in Unani Medicine in New Delhi.
How Neural Stem Cells Work in Alzheimer’s
Neural stem cells are unique because they have the ability to regenerate and transform into different types of brain cells, including neurons, which are often damaged in AD. They can integrate into the brain's complex architecture, connect with existing cells, and release substances that support neuron survival and growth.
Key Findings of the Study
Researchers have discovered that when neural stem cells are introduced into the brain, they can reduce symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s. Several important mechanisms were highlighted:
-Replacement of Lost Neurons: One of the critical aspects of AD is the loss of neurons responsible for cognitive functions. The stem cells replace these damaged neurons, restoring brain regions essential for memory and learning.
-Enhanced Brain Connectivity: Neural stem cells improve brain connectivity by forming new synaptic connections. This effect has been linked to the secretion of neurotrophic factors, which are proteins that help neurons grow and connect.
-Reduction of Inflammation: AD is characterized by inflammation in the brain, which accelerates neuron death. Stem cells release anti-inflammatory chemicals that help create a healthier environment for brain cells, reducing further damage.
-Removal of Toxic Proteins: Alzheimer’s is associated with toxic prot
ein buildup, such as amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which cause neuron death. Studies indicate that neural stem cells aid in the removal of these harmful proteins, enhancing overall brain health.
-Activation of Endogenous Repair Mechanisms: Neural stem cells may also activate dormant brain repair mechanisms, encouraging the brain to self-repair.
Challenges in Clinical Application
While the findings are promising, translating stem cell therapy from the lab to the clinic faces some hurdles. One significant challenge is ensuring the safe and effective delivery of stem cells to targeted brain areas without surgery.
Additionally, creating enough high-quality stem cells that are immune-compatible with each patient is essential to avoid rejection.
Looking Forward: Potential of Stem Cells in Other Brain Disorders
Neural stem cells are not limited to Alzheimer’s disease; they could be used to treat other neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases. Scientists are optimistic that the success seen in Alzheimer’s studies can also lead to advancements in treating these disorders.
Study Conclusion
This research highlights neural stem cell therapy as a revolutionary treatment path for Alzheimer's disease. Although more clinical trials are needed to confirm efficacy in human subjects, the approach holds the potential to restore brain function and improve quality of life for millions of Alzheimer’s patients. Scientists hope that, as this therapy progresses, it could serve as a multi-faceted approach, tackling Alzheimer’s from several fronts to slow or even halt its progression.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease.
https://www.mdpi.com/3042-4518/1/2/8
For the latest on Alzheimer research, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/thyroid-hormone-shows-promise-in-reversing-alzheime-s-like-symptoms
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/singapore-researchers-discover-how-to-activate-dormant-brain-stem-cells-to-treat-neurodevelopmental-disorders
