Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 23, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 4 weeks, 1 day, 22 hours, 44 minutes ago
Medical News: Heart failure (HF) is a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of people. One of the primary factors influencing the progression of heart failure is the disruption of the delicate sodium and water balance in the body. When sodium levels rise, it leads to water retention, causing swelling or edema, which worsens heart failure symptoms. Although controlling congestion is critical for improving patient outcomes, recent studies are challenging the effectiveness of traditional sodium-reducing interventions like strict dietary restrictions, saline solutions, and diuretics.
 New Approach to Managing Sodium Levels in Heart Failure Patients
Understanding the Role of Sodium in Heart Failure
New Approach to Managing Sodium Levels in Heart Failure Patients
Understanding the Role of Sodium in Heart Failure
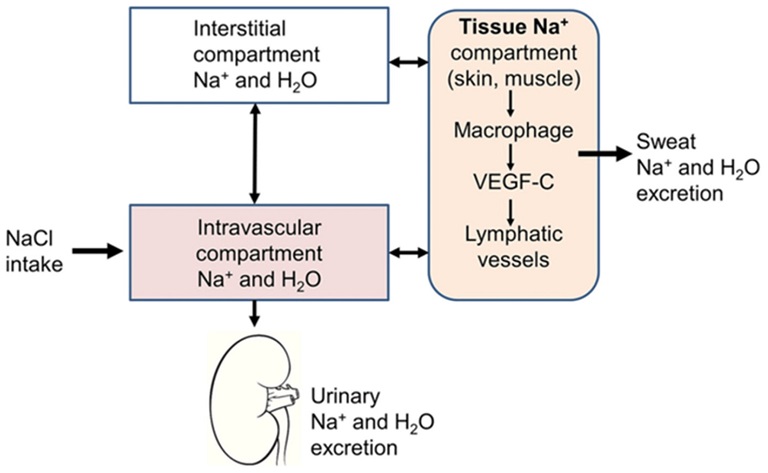
Sodium plays an essential role in the body by helping to maintain fluid balance. The extracellular fluid (ECF), which includes blood, lymph, and cerebrospinal fluid, contains most of the body's sodium. A rise in sodium levels, especially in heart failure patients, can lead to water retention, swelling, and increased pressure in the heart and blood vessels. This
Medical News report will explore the potential of new sodium-targeting treatments in improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
For decades, healthcare professionals have advised heart failure patients to limit their sodium intake to reduce the risk of water retention. Patients are also often treated with diuretics, which help the body eliminate excess sodium and fluid. However, the effectiveness of these strategies has been called into question by recent research. Researchers from the European University Cyprus and the University Hospital of Larissa in Greece suggest that sodium restriction alone may not be sufficient for managing heart failure in all patients. This has led to the exploration of more innovative and effective treatments.
Current Sodium-Targeting Interventions
Traditional sodium-targeting treatments, such as strict sodium-restricted diets, hypertonic saline solutions, and diuretics, have been used for years to manage heart failure symptoms. Diuretics are particularly common, helping to flush out excess sodium and water from the body. However, these interventions come with limitations. For example, strict sodium restrictions can be challenging for patients to adhere to, and long-term sodium restriction may even have adverse effects on health. Similarly, diuretics can cause side effects such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, while hypertonic saline is not always effective for every patient.
New Approaches to Sodium Management
Recent studies are shedding light on alternative methods for managing sodium levels in heart failure patients. One promising approach is the use of sodium magnetic resonance imaging (23Na-MRI) to measure sodium levels in body tissues. Traditionally, sodium levels have been assessed based on blood and urine tests. However, new evidence suggests that sodium can be stored in tissues like the skin, muscles, and blood vessel walls. By using 23Na-MRI, doctors can more accurately measure sodium levels in the body and tailor treatment plans a
ccordingly.
Another exciting development is the use of wearable devices that can monitor sodium levels in real time. These devices use sensors to detect sodium and chloride in sweat, offering a non-invasive way to track sodium levels in heart failure patients. This could be particularly useful for monitoring patients at home and adjusting their treatment plans as needed.
Studies have also shown that reducing tissue sodium content through interventions like diuretics or sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can improve patient outcomes. SGLT2 inhibitors are typically used to manage diabetes, but they have shown promise in helping to reduce sodium retention in heart failure patients.
What the Research Says
Researchers from the University Hospital of Larissa and the European University Cyprus conducted a review of recent studies on sodium management in heart failure patients. Their findings suggest that sodium-targeting interventions, including dietary restrictions, hypertonic saline, and diuretics, may have limited effectiveness for certain patients.
According to their research, sodium can be stored in a "third compartment" within the body, which includes tissues like the skin. This storage is not easily influenced by traditional sodium-reducing interventions. New technologies like 23Na-MRI can help doctors assess how much sodium is stored in tissues and adjust treatments accordingly. Furthermore, wearable devices that monitor sodium levels could allow for more personalized and effective treatment plans.
The review also highlights the potential benefits of combining sodium-targeting treatments with other heart failure therapies. For example, combining diuretics with SGLT2 inhibitors, beta-blockers, and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors may provide more comprehensive treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusions
In conclusion, heart failure is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. While sodium-targeting interventions have been a staple of heart failure management for many years, recent research suggests that they may not be sufficient on their own. Innovative technologies like 23Na-MRI and wearable sodium sensors could revolutionize the way doctors monitor and manage sodium levels in heart failure patients.
The key takeaway from this research is that sodium management should be personalized to each patient's needs. Traditional methods like strict dietary restrictions and diuretics may still play a role, but they should be combined with other treatments for optimal results. Moving forward, more research is needed to fully understand the role of sodium in heart failure and develop new strategies for managing it effectively.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Personalized Medicine.
https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4426/14/10/1064
For the latest about Heart Issues, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/taiwanese-study-reveals-heart-health-benefits-of-the-phytochemical-momordicine-i-from-bitter-melon
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/a-new-discovery-on-how-the-sars-cov-2-virus-affects-the-heart
