Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 23, 2025 3 months, 3 days, 1 hour, 3 minutes ago
Medical News: Understanding Pancreatic Cancer and the Role of KIFC1
Pancreatic cancer (PC) remains one of the most deadly forms of cancer worldwide, claiming the lives of thousands each year. With a five-year survival rate lingering at a mere 13%, the disease’s prognosis remains grim for most patients. The aggressive nature of pancreatic cancer, characterized by early metastasis and resistance to treatment, underscores the urgent need for new therapeutic targets.
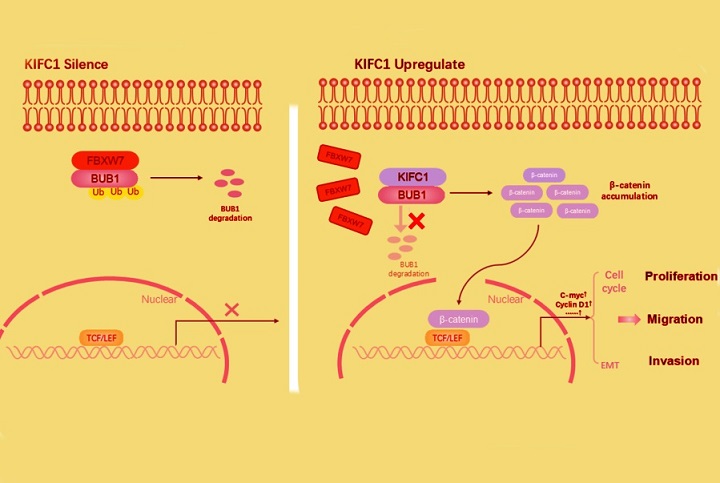 Schematic illustration of the potential molecular mechanism of KIFC1 as a key regulator in Pancreatic Cancer progression. KIFC1 overexpression promotes Pancreatic Cancer progression via the BUB1/WNT/β-catenin pathway
Schematic illustration of the potential molecular mechanism of KIFC1 as a key regulator in Pancreatic Cancer progression. KIFC1 overexpression promotes Pancreatic Cancer progression via the BUB1/WNT/β-catenin pathway
Recent groundbreaking research conducted by scientists from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi Medical College at Nanchang University has identified a key molecular player in pancreatic cancer progression: Kinesin family member C1 (KIFC1). This
Medical News report delves into the critical findings of the study, shedding light on how KIFC1 promotes cancer growth by stabilizing a protein called BUB1, thus activating a well-known cancer signaling pathway.
Key Findings of the Study
The researchers embarked on a comprehensive investigation to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying pancreatic cancer. They began by analyzing tissue samples from 62 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer between 2016 and 2023. Using advanced techniques such as immunohistochemistry and bioinformatics analysis, they observed a significant overexpression of KIFC1 in tumor tissues compared to normal pancreatic tissues.
KIFC1’s Function in Pancreatic Cancer
KIFC1, part of the kinesin-14 family of proteins, plays a critical role in cellular processes such as centrosome clustering and chromosomal transport during cell division. Overexpression of KIFC1 has previously been implicated in other cancers, including breast, lung, and gastric cancers. In pancreatic cancer, researchers demonstrated that high levels of KIFC1 are closely associated with advanced clinical stages, increased tumor aggressiveness, and poor patient survival.
By silencing KIFC1 in pancreatic cancer cell lines using specific RNA interference techniques, the scientists observed a marked reduction in cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion. Conversely, overexpression of KIFC1 enhanced these malignant behaviors, establishing its role as a driver of pancreatic cancer progression.
The Link Between KIFC1 and BUB1
BUB1, a protein involved in regulating cell division, emerged as a critical partner of KIFC1 in this study. Using protein interaction assays, the researchers showed that KIFC1 binds to BUB1 and stabilizes it by preventing its degradation through the ubiquitination pathway. This stabilization of BUB1 amplifies its role in activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, a well-known driver of cancer progression.
Further analysis revealed that high levels of both KIFC1 and BUB1 in pancre
atic cancer tissues are associated with poor patient outcomes. When BUB1 expression was reduced, the ability of KIFC1 to promote cancer cell growth and activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was significantly diminished. This finding underscores the pivotal role of the KIFC1-BUB1 axis in pancreatic cancer.
Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin Pathway
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is a central signaling pathway in cancer biology. It regulates critical processes such as cell proliferation, migration, and survival. The study revealed that KIFC1 overexpression leads to the accumulation of β-catenin in the nucleus, where it interacts with transcription factors to drive the expression of cancer-promoting genes, including c-Myc and cyclin D1. These changes enhance the ability of pancreatic cancer cells to grow uncontrollably and invade surrounding tissues.
In Vivo Validation
The researchers validated their findings through animal experiments. They created mouse models with pancreatic cancer cells that either overexpressed or lacked KIFC1. Tumors in mice with reduced KIFC1 expression showed significantly slower growth, smaller size, and lower levels of Wnt/β-catenin activation compared to controls. This in vivo evidence strongly supports the therapeutic potential of targeting KIFC1 in pancreatic cancer.
Implications for Future Therapies
This study highlights the potential of KIFC1 as a promising therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. By disrupting the KIFC1-BUB1 interaction or inhibiting KIFC1’s ability to stabilize BUB1, it may be possible to suppress cancer progression and improve patient outcomes. Additionally, the role of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in this process provides further avenues for developing targeted therapies.
Conclusion
The findings from this study offer a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms driving pancreatic cancer. KIFC1’s overexpression and its interaction with BUB1 play a critical role in promoting the growth, migration, and invasion of cancer cells. By stabilizing BUB1 and activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, KIFC1 emerges as a key player in pancreatic cancer progression.
Therapeutic strategies targeting the KIFC1-BUB1 axis or the downstream Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway could pave the way for more effective treatments. As researchers continue to explore these molecular pathways, there is hope for improved outcomes for pancreatic cancer patients.
The study findings were published on a preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-5746431/v1
For the latest Cancer News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/hoxa11as-and-its-role-in-pancreatic-cancer-progression
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/targeting-glutathione-peroxidase-as-a-game-changer-in-pancreatic-cancer-treatment
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-study-finds-link-between-high-hba1c-levels-and-pancreatic-cancer-risk
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/the-unexpected-connection-between-covid-19-and-pancreatic-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-hope-for-pancreatic-cancer-treatment-fungi-derived-bioactive-compounds
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/aronia-berry-extract-overcomes-pancreatic-cancer-drug-resistance-via-myd88-nf-kb-p-glycoprotein-modulation
