Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 16, 2025 4 weeks, 1 day, 8 hours, 26 minutes ago
Medical News: Kidney stones are a common and painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These solid mineral deposits form in the kidneys and can cause severe discomfort when passing through the urinary tract. Researchers have long sought to understand the precise mechanisms behind kidney stone formation, and a recent study has provided significant insights into this complex process.
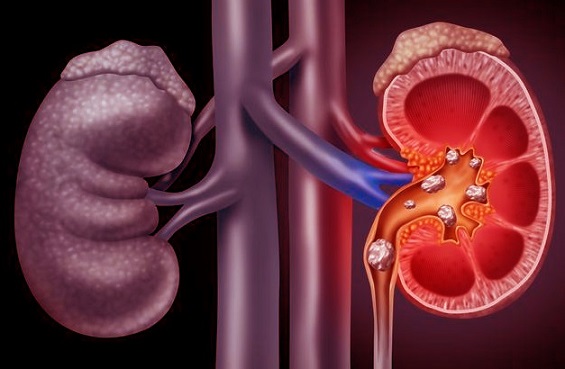 New Insights into the Formation of Kidney Stones and the Role of the Microbiome
How Kidney Stones Develop
New Insights into the Formation of Kidney Stones and the Role of the Microbiome
How Kidney Stones Develop
Scientists from multiple institutions have analyzed the various factors that contribute to kidney stone formation, particularly those made of calcium oxalate (CaOx), the most common type. Their findings highlight three major mechanisms:
-The Free-Particle Model - This occurs when small mineral particles form freely in the urine due to high concentrations of calcium and oxalate, eventually aggregating into larger stones.
-The Fixed-Particle Model - In this process, crystals attach themselves to the lining of the kidney’s inner walls, where they grow and become the nucleus of a kidney stone.
-The Randall’s Plaque Model - This occurs when calcium phosphate deposits form in the kidney tissue and gradually become exposed to urine, leading to the accumulation of calcium oxalate on their surface. Over time, this results in the formation of kidney stones.
This
Medical News report highlights that Randall’s plaques play a particularly important role, serving as the initial sites where kidney stones develop. These plaques are made up of calcium phosphate and originate in the renal papilla, a part of the kidney. When they come into contact with urine, they act as a base for further mineral buildup, eventually forming stones.
The Role of the Microbiome in Kidney Stone Formation
One of the most intriguing findings from the study is the potential role of the microbiome in kidney stone formation. Researchers identified bacterial and fungal DNA in the composition of kidney stones, suggesting that microbes might influence the crystallization process. Studies on stone samples revealed the presence of bacterial 16S rRNA and fungal DNA, indicating that these microorganisms may be actively involved in stone formation rather than being just incidental contaminants.
Some bacteria can alter the chemical balance of urine, making it either more or less conducive to stone formation. For instance, certain microbes produce molecules that can either promote or inhibit crystal growth. The presence of bacteria in kidney stones also raises questions about whether infections play a more significant role in stone formation than previously thought.
Inflammation and Stone Growth
Another key finding from the study is the link between inflammation and kidney stone formation. Researchers found that the body's immune response, includi
ng the release of inflammatory chemicals, could contribute to stone growth. When the kidney tissue is injured, immune cells release proteins and other substances that may accelerate the crystallization of minerals.
Additionally, kidney stones contain organic components such as proteins and cellular debris, which may act as scaffolding for mineral deposits. The study suggests that the body’s natural processes of healing and immune response could inadvertently promote stone development.
Potential Implications for Treatment and Prevention
Understanding these mechanisms could lead to new approaches for preventing and treating kidney stones. Future treatments may involve modifying the gut and urinary microbiome to reduce stone formation, targeting specific bacteria that influence urine chemistry. Additionally, researchers are exploring therapies that could block the formation of Randall’s plaques, potentially stopping stones before they develop.
Diet and lifestyle changes remain crucial in preventing kidney stones. Staying hydrated, reducing dietary oxalates (found in foods like spinach and nuts), and consuming adequate calcium may help prevent stones from forming. However, the new research suggests that addressing bacterial influences and inflammation could be equally important.
Conclusion
This study provides groundbreaking insights into the formation of kidney stones, highlighting the role of Randall’s plaques, the microbiome, and inflammation in their development. By understanding these complex interactions, researchers hope to develop more effective treatments and preventive strategies. Future studies will continue to explore the microbiome’s influence on kidney stone formation and investigate new ways to disrupt the crystallization process before stones can form.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Uro.
https://www.mdpi.com/2673-4397/5/1/6
For the latest on Kidney Stones, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/thailand-medical-researchers-discover-that-lactobacillus-acidophilus-can-prevent-kidney-stone-development
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/boosting-antioxidants-intake-can-help-prevent-kidney-stones
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/kidney-stones-new-faster-urine-diagnostics-for-kidney-stone-sufferers
https://www.thailandmedical.news/pages/thailand_doctors_listings
