New Study Shows That Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Reduce Risk Of Severity, Hospitalizations And Mortality In COVID-19
Source: COVID-19 Supplements -Thailand Medical News Mar 31, 2022 3 years, 8 months, 3 weeks, 15 hours, 1 minute ago
A new study by researchers from Shiraz University of Medical Sciences-Iran And Birjand University of Medical Science-Iran has found that polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reduce risk of severity, hospitalizations and mortality in COVID-19.

PUFAs include omega-3 PUFA and omega-6 PUFA which the former acids originate from natural sources and include alpha linoleic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the latter one, mainly contain linoleic acid (LA) and arachidonic acid (AA).
Thailand Medical News had already reported since May 2020 that resolvins from Omega-3 fatty acids could help resolve SARS-CoV-2 induced cytokine storms and severe inflammatory condition.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-supplements-us-study-finds-that-resolvins-from-omega-3-fatty-acids-could-prevent-covid-19-cytokine-storms
COVID-19 mortality is largely associated with a severe increase in inflammatory cytokines and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play an important role in modulating immune pathways and inflammatory responses.
The study team conducted this meta-analysis cum review study to evaluate the effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on the prognosis of COVID-19 disease.
A detailed search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science. For systematic identification, the search was performed based on the following keywords COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, COVID, Coronavirus Disease 19, SARS COV- 2 Infection, SARS-CoV-2, COVID19, Coronavirus Disease, Fatty Acids, Omega-3, Omega-3 Fatty Acid, Omega-6, n 3 Fatty and Omega-9 in the mentioned databases, using OR, and AND.
The review was based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA). The inclusion criteria for the review were studies focusing on the evaluation of the impact of PUFAs on disease severity, ICU admission, hospital admission, and mortality among COVID-19 patients, articles in the English language, and all original research papers. Exclusion criteria for this review were articles written in other languages, reviews, case reports, and letters to the editors.
All searched articles were included in the study and retrieved, and End-Note X7 software was used to manage the studies.
The meta-analysis study found that the relationship between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and the risk of COVID-19 are various, but typically omega-3 supplements have been found to be 12 to 21% effective in reducing the risk of COVID-19.
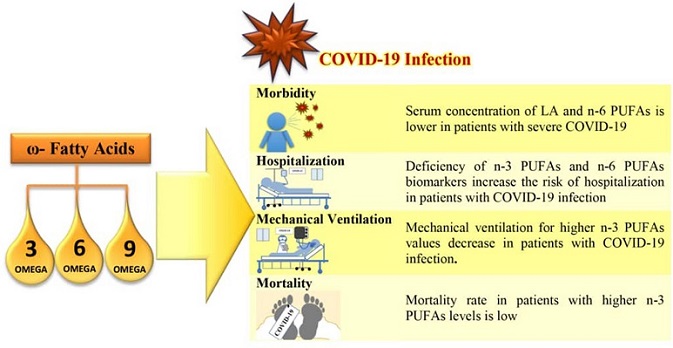
A large proportion of the studies emphasized the increasing severity of the disease and the need for mechanical ventilation and hospitalization due to polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency.
The COVID-19 Supplements study findings also demonstrated that omega-3 fatty acid deficiency increased mortality in patients with Covid-19.
However, there is also a warning that in criti
cal cases, elevated levels of fatty acids in patients' lungs and a cytokine storm are the main reasons for mortality in COVID-19 patients.
The study findings concluded that polyunsaturated fatty acids can reduce the risk of COVID-19 which could be considered as a preventative, inexpensive and safe method. However, the risk of taking high-dose omega-3 supplements before or during SARS-COV-2 infection needs to be investigated.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal:
Life Sciences.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024320522001898
Numerous studies have showed that COVID-19 mortality, from the causative organism severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is closely associated with a sizable increase in inflammatory cytokines, leading to a cytokine storm. PUFAs have been shown to play a crucial role in regulating immune pathways as well as inflammatory responses.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
As PUFAs are typically lipophilic in nature, they can also disrupt the viral envelope and change its dynamics, thus inactivating viruses. Hence the study evaluated the effect of PUFAs on COVID-19 prognosis.
The meta-analysis study revealed many several crucial findings on the relationship between the risk of COVID-19 and the levels of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
Mots importantly Omega-3 supplements were 12 to 21% effective in reducing COVID-19 risk.
Most of the studies highlighted the increasing disease severity and the need for hospitalization and mechanical ventilation in patients with a PUFA deficiency.
Interestingly however a Belgium-based study found that serum levels of PUFA were higher with lower COVID-19 severity and serum levels of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) were higher with higher disease severity.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.11.09.20228221v1
Most past studies found that the mean serum omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acid levels were significantly different in COVID-19 patients compared to healthy individuals.
A study conducted in China showed that patients with asymptomatic COVID-19 had decreased levels of omega-3 fatty acids, including oleic acid and omega-3 PUFAs. Also, compared to healthy controls, omega-3 fatty acids were decreased by 35% in asymptomatic COVID-19 patients.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004221009421
More importantly, the study findings showed that the deficiency of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFA biomarkers was found to increase the risk of severe disease and hospitalization by almost three times, and the consumption of omega-3 PUFA supplements seemed to reduce the risk of severe disease and hospitalization.
One study noted that the levels of fatty acids such as arachidonic acid and oleic acid were directly associated with COVID-19 severity and ICU admission.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/22/8623
Most of the studies reported that omega-3 fatty acid deficiency also increased mortality in COVID-19 patients.
However, the study warned that in critical cases, elevated fatty acid levels in the lungs of the patients and a cytokine storm were found to be the reasons for death in COVID-19 patients.
A study conducted in Chile observed that the COVID-19 mortality risk was over three times higher in patients who had low omega-3 PUFA levels, while the risk decreased in patients with high levels of omega-3 PUFA.
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/15/7722
Another study reported that the risk of COVID-19 mortality was reduced by 75% in patients with an omega-3 PUFA index above 5.7%.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952327821000132
The review and meta-analysis investigated the potential role played by omega PUFAs as an effective adjunct therapy in mitigating COVID-19-related inflammation and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) replication.
The study findings showed that omega-3 PUFAs and their metabolites can regulate COVID-19-related complications and enhance the immunological defense against SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication.
Most importantly, the evidence presented by this systematic review showed that PUFAs can be a preventative, safe, and inexpensive method to decrease COVID-19 risk.
The study team however stress that the possible risk of consuming high doses of omega-3 supplements prior to or during SARS-CoV-2 infection must be further investigated.
For more on
COVID-19 Supplements, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.

