Nitric Oxide-Powered Water Shows Promise as a Disinfectant in Fighting SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 14, 2024 1 year, 2 months, 4 weeks, 15 hours, 28 minutes ago
Medical News: New Hope Against COVID Variants: A Breakthrough Study on Nitric Oxide Plasma-Activated Water
Researchers from Kwangwoon University, University of Suwon in South Korea, KIIT University in India, and King Saud University in Saudi Arabia, have developed an innovative approach to combat COVID-19 variants using nitric oxide plasma-activated water (NOx-PAW). The D614G mutation, commonly found in various COVID-19 variants, increases the virus's ability to bind with human cells, enhancing its infectivity. In a recent study, scientists examined the impact of NOx-PAW on pseudoviruses carrying this mutation, revealing promising results for a novel antiviral treatment.
 Nitric Oxide-Powered Water Shows Promise as a Disinfectant in Fighting SARS-CoV-2 Variants
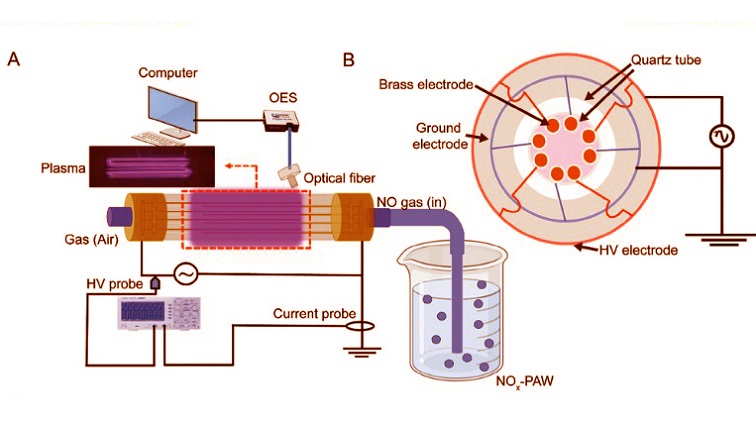
Plasma setup and diagnostic of cylindrical dielectric discharge plasma. (A) Diagram illustrating the configuration of the CDBDP setup, (B)electrode layout,
Nitric Oxide-Powered Water Shows Promise as a Disinfectant in Fighting SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Plasma setup and diagnostic of cylindrical dielectric discharge plasma. (A) Diagram illustrating the configuration of the CDBDP setup, (B)electrode layout,
This
Medical News report how NOx-PAW works against the D614G mutation. The plasma-activated water, enriched with nitric oxide (NOx), damages the virus's spike protein, weakening its ability to bind to the human ACE2 receptor - a vital step for the virus to enter cells. This breakthrough could offer a powerful new tool in the global fight against viral variants.
How Does Nitric Oxide Plasma-Activated Water Work?
NOx-PAW is created using a cylindrical dielectric barrier discharge plasma (CDBDP) device that produces nitric oxide-rich water. This water is infused with reactive nitrogen species, which are known for their antimicrobial properties. When exposed to NOx-PAW, the virus’s spike protein undergoes structural changes, resulting in decreased binding strength with the ACE2 receptors on human cells.
A notable finding was a 71% reduction in infectivity of the SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (a model of COVID-19) after treatment with NOx-PAW. Further in silico analysis showed that the reactive nitrogen species directly interacted with the spike protein, disrupting its structure. This chemical interaction helps prevent the virus from effectively latching onto human cells, thereby reducing its potential for infection.
Why Focus on the D614G Mutation?
The D614G mutation, located in the spike protein's S1-domain, enhances the virus's ability to maintain its structure and bind efficiently with human ACE2 receptors. Since the mutation promotes an “open” configuration of the spike protein, it makes the virus more infectious. By specifically targeting this mutation, researchers aim to curtail the transmissibility of COVID-19 variants carrying the D614G mutation.
Through extensive molecular modeling, the study identified how nitric oxide and other reactive nitrogen species in NOx-PAW interacted with amino acids in the D614G-mutated spike protein. The strongest interactions involved bonds with critical amino acids in the spike protein, which helped inactivate it, making it less capable of binding to ACE2 receptors.<
;br />
Key Findings and Impact of NOx-PAW
The study findings revealed that NOx-PAW significantly impaired the structural integrity of the D614G spike protein. Experiments with human cells expressing ACE2 receptors showed a marked reduction in infection rates among pseudoviruses treated with NOx-PAW compared to untreated controls. Specifically, the fluorescence intensity, indicative of virus-cell binding, was significantly lower in NOx-PAW treated cells, suggesting that the water treatment was effective in neutralizing the virus.
Additionally, the study noted that NOx-PAW exposure resulted in a 29% infectivity rate compared to untreated samples, underscoring its potential as a formidable tool for disinfection. Another vital outcome was the significant reduction in clathrin-mediated endocytosis-related gene expression, a pathway crucial for viral entry into cells.
Safety and Practicality of NOx-PAW
One of the most encouraging aspects of this research is the non-toxic nature of NOx-PAW. Unlike chemical disinfectants that often harm human tissues, NOx-PAW has demonstrated high cell compatibility in various dilutions. Tests showed no adverse morphological changes in human cells, suggesting that NOx-PAW can be safely applied to surfaces and environments without posing a risk to humans.
While UV light and ozone have been explored as antiviral agents, they either require prolonged exposure or carry potential risks with frequent use. In contrast, NOx-PAW offers a practical and safer approach, potentially extending the viability of disinfection practices in healthcare and public spaces.
Conclusions and Future Prospects
In conclusion, the nitric oxide plasma-activated water developed in this study provides a promising new approach to combating SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. By effectively inactivating the virus and disrupting its ability to bind to ACE2 receptors, NOx-PAW could play a significant role in preventing the spread of COVID-19 and possibly other airborne viruses.
As the world continues to grapple with COVID-19 variants, innovations like NOx-PAW offer renewed hope. Further studies will determine how this approach can be scaled and applied in real-world settings, but the potential of NOx-PAW as a fast, effective, and safe antiviral treatment is already clear.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Advanced Science.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202411515
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-liquid-hyperoxygen-found-to-be-a-new-and-effective-covid-19-disinfectant
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/how-nitric-oxide-could-help-macrophages-fight-covid-19-s-cytokine-storm
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid-19-disinfectants
