Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jul 29, 2024 1 year, 4 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 2 hours, 15 minutes ago
Medical News - In a groundbreaking review, researchers from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf-Germany and the National Research Centre in Cairo-Egypt have highlighted the critical role of a protein known as Nucleophosmin (NPM1) in managing cellular stress. This
Medical News report delves into the fascinating ways NPM1 orchestrates stress responses within cells, maintaining cellular health and combating diseases such as cancer and viral infections.
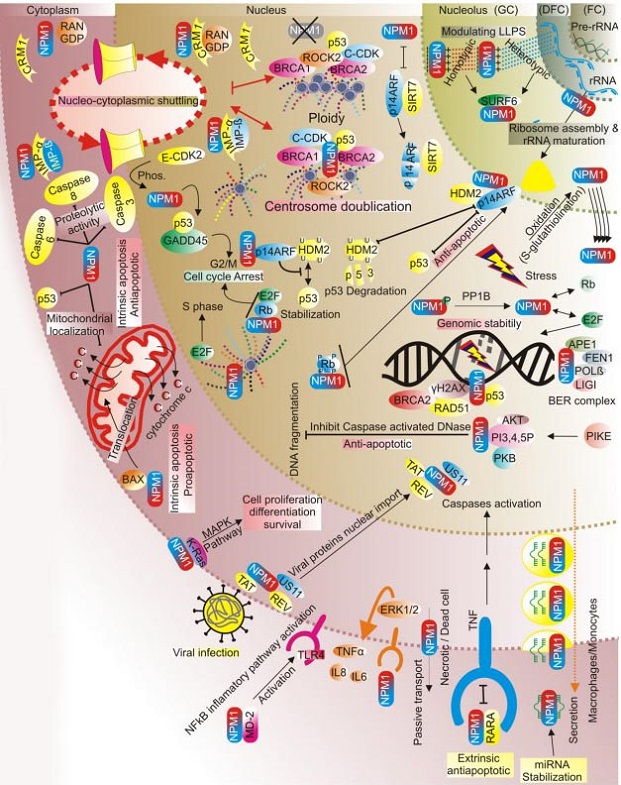 Nucleophosmin's Crucial Role in Cellular Health and Disease Management
Schematic representation of the subcellular localization, associated functions, and interaction networks of NPM1. The nucleolus (fibrillar center (FC), dense fibril compartment (DFC), and granular compartment (GC)), nucleus(nucleoplasm), cytoplasm (cytosol), and outer layer represent the plasma membrane and extracellular milieu.
What is Nucleophosmin?
Nucleophosmin's Crucial Role in Cellular Health and Disease Management
Schematic representation of the subcellular localization, associated functions, and interaction networks of NPM1. The nucleolus (fibrillar center (FC), dense fibril compartment (DFC), and granular compartment (GC)), nucleus(nucleoplasm), cytoplasm (cytosol), and outer layer represent the plasma membrane and extracellular milieu.
What is Nucleophosmin?
Nucleophosmin, also referred to as NPM1, is a nucleolar protein that rapidly moves between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in response to various stress stimuli. Found abundantly in tissues, it plays a central role in several biological processes, including ribosome biogenesis, cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and apoptosis. This article aims to shed light on the versatile functions and significance of NPM1 in cellular stress responses.
Structural Features and Functions of NPM1
NPM1 is a protein with 294 amino acids and a molecular weight of approximately 37 kDa. It comprises three key domains: the N-terminal oligomerization domain (OD), the central histone binding domain (HBD), and the C-terminal nucleic acid binding domain (NBD).
-N-terminal Oligomerization Domain (OD): This domain is crucial for NPM1's ability to form monomers, pentamers, and decamers. The pentameric form is typically localized in the nucleolus, involved in nucleosome formation and chromatin remodeling.
-Central Histone Binding Domain (HBD): The HBD facilitates binding to histones, crucial for nucleosome formation and chromatin decondensation. It also contains nuclear localization signals (NLS) that help in the nuclear import of NPM1.
-C-terminal Nucleic Acid Binding Domain (NBD): This domain preferentially binds RNA and double-stranded DNA, playing a role in ribosome maturation and export from the nucleolus.
NPM1 in Stress Responses
NPM1's role in cellular stress is multifaceted. It responds to various stress stimuli, including hypoxia, heat shock, oxidative stress, UV irradiation, and chemotherapeutic agents. By shuttling between the nucleus and cytoplasm, NPM1 helps in the regulation of numerous stress-related processes, ensuring cellular stability and survival.
NPM1 in Cancer
NPM1 is highly expressed in cancer cells and solid tumors. Mutations in NPM1 are a signifi
cant cause of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), making it a crucial target for cancer research. These mutations often result in the abnormal localization of NPM1 to the cytoplasm, disrupting its normal functions and contributing to tumorigenesis.
NPM1 in DNA Repair
NPM1 plays a pivotal role in maintaining genomic stability by participating in various DNA repair mechanisms. It interacts with several repair proteins, helping cells recover from damage and ensuring the integrity of genetic material. For instance, NPM1 forms complexes with proteins involved in base excision repair, facilitating the repair of damaged DNA.
NPM1 in Viral Infections
NPM1's interaction with viral proteins highlights its significance in viral infections. It is involved in various stages of the viral life cycle, including the nuclear import of viral proteins and final assembly. This interaction makes NPM1 a potential target for antiviral therapies, providing a new avenue for combating viral diseases.
NPM1 and Immune Response
Interestingly, NPM1 also plays a role in the immune response. It can be secreted by macrophages and monocytes, acting as an inflammatory stimulator. This function highlights NPM1's potential in treating inflammatory diseases and enhancing immune responses.
Future Directions
The diverse functions of NPM1 in stress responses, cancer, DNA repair, and viral infections make it a promising target for therapeutic interventions. Researchers are exploring gene therapy approaches to correct NPM1 mutations and develop small molecule inhibitors targeting its interactions. Such advancements could lead to significant breakthroughs in cancer treatment and the management of stress-related diseases.
Conclusion
Nucleophosmin is an essential multifunctional protein that plays a critical role in cellular stress responses. Its ability to regulate various biological processes, maintain genomic stability, and interact with viral proteins underscores its importance in cellular health and disease management. As research progresses, NPM1 holds promise as a therapeutic target for a range of conditions, from cancer to viral infections and inflammatory diseases.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cells.
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/15/1266
For the latest on Nucleophosmin, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-and-our-cells-powerhouses-mitochondria
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-immune-protein-ubxn3b-identified-as-playing-a-key-role-in-b-cell-development-and-immunity
