Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News May 21, 2024 10 months, 3 weeks, 3 days, 19 hours, 54 minutes ago
Cancer News: Glioblastoma (GBM) is a highly aggressive form of brain cancer that accounts for nearly half of all malignant brain tumors. Despite advances in medical science, treatment options for glioblastoma have remained largely unchanged over the past five decades. Standard treatments typically include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy with temozolomide (TMZ). Unfortunately, the effectiveness of TMZ is often short-lived, as glioblastoma cells rapidly develop resistance to this drug.
 Overcoming Drug Resistance In Glioblastoma: The Promise Of PI3K-Beta Inhibitors
The Role of Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Treatment
Overcoming Drug Resistance In Glioblastoma: The Promise Of PI3K-Beta Inhibitors
The Role of Temozolomide in Glioblastoma Treatment
Temozolomide is an alkylating agent that works by inducing DNA damage in cancer cells, leading to cell death. It can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, making it one of the few chemotherapeutic agents suitable for brain cancer treatment. Initially, TMZ can slow tumor progression, but its long-term efficacy is hindered by the cancer cells' ability to develop resistance. The underlying mechanisms of this resistance are complex and multifaceted, involving various genetic and molecular pathways.
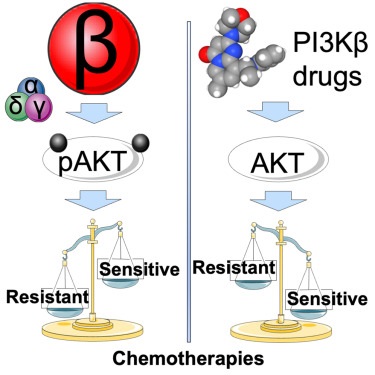
Discovering the PI3K Signaling Pathway
Researchers at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at Virginia Tech Carilion (VTC) have identified a critical molecular signaling pathway that could potentially be targeted to overcome chemotherapy resistance in glioblastoma. Their study findings are covered in this
Cancer News report. This pathway, known as the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K) pathway, plays a crucial role in cell growth, survival, and proliferation. The PI3K pathway's activation is associated with cancer growth, making it a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Specificity of PI3K-Beta in Glioblastoma
The PI3K pathway consists of several isoforms, including PI3K-alpha, PI3K-beta, PI3K-delta, and PI3K-gamma. Previous attempts to target the PI3K pathway in cancer treatment have been largely unsuccessful due to the non-selective inhibition of these isoforms, leading to undesired side effects. However, the new research focuses specifically on the PI3K-beta isoform, which has shown to be particularly significant in glioblastoma chemoresistance.
Research Findings
In their study, the Virginia Tech researchers analyzed glioblastoma cell cultures, including glioblastoma stem cells derived from patient specimens, and mouse models harboring human cancer cells. They discovered that glioblastoma patients who did not respond well to TMZ treatment had elevated levels of the PI3K-beta isoform. Blocking PI3K-beta in these cancer cells made them more sensitive to TMZ, significantly slowing their growth.
Implications for Treatment
The findings suggest that targeting PI3K-beta specifically, rather than the entire PI3K pathway, could be a more effective strategy in overcoming TMZ resistance in glioblastoma. This selective inhibition could potentially enhance the effectiveness of TMZ, providin
g a new avenue for treatment in patients with resistant glioblastoma.
The Challenge of the Blood-Brain Barrier
One of the significant challenges in translating these findings into clinical practice is overcoming the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The BBB is a selective permeability barrier that protects the brain from harmful substances in the blood but also makes it difficult for many drugs to reach brain tumors. Developing PI3K-beta inhibitors that can effectively cross the BBB is crucial for this treatment strategy to be viable in clinical settings.
The Role of Glioblastoma Stem Cells
Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) are a small population of cells within tumors that are particularly resistant to chemotherapy and radiation. These cells can self-renew and drive tumor growth and recurrence. The study found that PI3K-beta inhibition was effective in reducing the self-renewal capability of GSCs, making them more susceptible to TMZ. This finding is significant as it targets the root of tumor resistance and recurrence.
Highlights of the Research
-Targeting PI3K-beta: Researchers identified PI3K-beta as a critical factor in glioblastoma chemoresistance.
-Enhanced Chemosensitivity: Blocking PI3K-beta made glioblastoma cells more sensitive to TMZ.
-Stem Cell Impact: PI3K-beta inhibitors reduced the self-renewal ability of glioblastoma stem cells.
-Future Challenges: Overcoming the blood-brain barrier is crucial for clinical application.
The research highlights the importance of molecular specificity in cancer treatment and offers a new approach to overcoming drug resistance in one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer. By continuing to explore and refine these strategies, scientists hope to develop more effective treatments that can significantly improve the prognosis for glioblastoma patients.
Moving forward, researchers plan to address the challenge of drug delivery across the BBB and further explore the therapeutic potential of PI3K-beta inhibitors in combination with TMZ. This research represents a promising step towards developing more effective treatments for glioblastoma, a cancer that has long been considered difficult to treat.
Conclusion
The discovery of the role of PI3K-beta in glioblastoma chemoresistance opens up new possibilities for treatment strategies. By specifically targeting this isoform, researchers may enhance the effectiveness of TMZ and improve outcomes for patients with resistant glioblastoma. While challenges remain, particularly in drug delivery, the findings provide a hopeful direction for future research and potential clinical applications.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: iScience.
https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(24)01143-X
For the latest
Cancer News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
