Potential for TIM3 as a Biomarker in COVID-19 Severity and Long COVID Complications
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 14, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 3 weeks, 2 minutes ago
Medical News:
Unveiling TIM3 as An Immune Checkpoint Marker in Viral Response
Research institutions, including Charles University in Prague and the Czech Academy of Sciences-Czech Republic, have recently explored the role of TIM3, a unique immune checkpoint protein, in COVID-19 patients. While immune checkpoint proteins like PD-1 have been well-studied, TIM3’s implications, particularly in severe cases of COVID-19, bring new insights into immune system response and dysfunction under viral attacks. The recent findings present TIM3 as a possible biomarker, particularly in individuals with heightened disease severity or long-term symptoms, known as Long COVID.
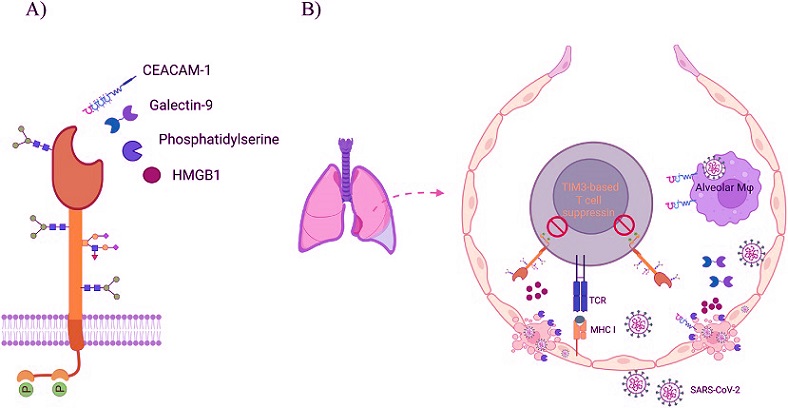 A) Schematic representation of TIM3 structure and its known ligands; Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1), Galectin-9 (Gal-9), Phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1). B) A potential scenario of immune suppression in SARS-CoV-2-infected lungs.
A) Schematic representation of TIM3 structure and its known ligands; Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1), Galectin-9 (Gal-9), Phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1). B) A potential scenario of immune suppression in SARS-CoV-2-infected lungs.
This
Medical News report delves into the mechanisms and implications of TIM3's involvement in COVID-19, providing a clearer picture of how immune responses might be redirected or weakened by the virus through TIM3 pathways.
The Role of TIM3 in Immune Response and Exhaustion
TIM3, part of the immune system’s regulatory framework, is primarily expressed on immune cells like T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. This checkpoint protein modulates immune responses, particularly under chronic infections, leading to “immune exhaustion.” In COVID-19, elevated TIM3 levels were noted across various studies, especially in severe cases, linking it directly with disease progression and poor outcomes.
One study highlighted how TIM3's upregulation correlated with more severe respiratory failure (RF) and higher rates of ICU admission. Researchers observed that TIM3 levels remained consistently high in patients undergoing extensive hospitalization, even persisting at three- and twelve-month post-discharge follow-ups.
TIM3’s Function in T Cell Regulation and Inflammation Suppression
The study findings suggest that TIM3, by binding with ligands such as Galectin-9 and CEACAM1, creates an inhibitory effect on T cell responses. This binding disrupts the signaling pathways crucial for T cell activation, thereby limiting cytokine production and cytotoxicity needed to target the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Interestingly, TIM3 inhibits the Akt-mTOR pathway, vital for T cell metabolism and survival, which could contribute to the extended immune dysfunction seen in severe COVID-19 cases.
In another study, researchers compared TIM3 expression among severe, moderate, and mild COVID-19 cases, revealing that TIM3 expression was notably higher in severe cases, contributing to worsened clinical symptoms. Additionally, this study emphasized that TIM3 levels not only remained high during hospitalization but were also linked with mortality rates among critically ill patients.
g>Persistent High Levels of TIM3 in Post-Acute COVID Syndrome (Long COVID)
Long COVID, a condition where symptoms persist for over twelve weeks post-infection, has been a mystery. The current research examined immune profiles of individuals with Long COVID and found that TIM3 levels stayed elevated months after initial infection. This trend was particularly significant in T cells, where immune system exhaustion markers continued to exhibit high TIM3 levels even eight months post-recovery, indicating prolonged immune dysregulation and potential susceptibility to secondary infections.
Potential of TIM3 as a Biomarker for COVID-19 Severity
A key finding in TIM3 studies is its association with soluble TIM3 (sTIM3) levels in the blood. Elevated sTIM3 levels are present in patients needing invasive ventilation, and, notably, a five-fold increase in sTIM3 levels was recorded in patients who developed severe symptoms compared to healthy controls. This makes sTIM3 a strong candidate for monitoring and predicting disease trajectory in COVID-19 cases.
TIM3 also showed promise in differentiating between severe and mild cases effectively, as sTIM3 levels could predict ICU admission requirements. One study noted that patients with higher TIM3 and sTIM3 levels experienced longer ICU stays and severe lung damage as evidenced by CT scans at three-month follow-ups.
Broader Implications: TIM3 in Viral Infections Beyond COVID-19
The role of TIM3 in immune regulation isn’t exclusive to COVID-19. Similar immune checkpoint behaviors are observed in other chronic viral infections, including HIV and hepatitis. In HIV patients, elevated TIM3 levels have been associated with disease progression, and blocking TIM3 has demonstrated potential in restoring immune responses. These findings emphasize the need for further exploration of TIM3 as a therapeutic target in viral infections where immune exhaustion plays a critical role.
Conclusion: A Pathway for Future Research and Therapeutic Development
The consistent link between TIM3 expression and COVID-19 severity has unveiled potential pathways for therapeutic interventions. Although more studies are needed, the upregulation of TIM3 could serve as a hallmark of immune dysfunction in COVID-19 and potentially in other viral infections. Current research advocates for anti-TIM3 therapies to potentially revive exhausted immune cells, thereby strengthening immune responses against SARS-CoV-2.
Future studies could focus on TIM3’s role across different stages of COVID-19 and include a variety of immune cell types. Additionally, examining the effects of different COVID-19 vaccines on TIM3 levels could reveal correlations between immune response durability and vaccination. The observed associations between TIM3, disease severity, and mortality also point to TIM3’s utility as a potential biomarker for monitoring patient health over the long term.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Heliyon.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844024164171
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/virus-news-university-of-alabama-study-alarmingly-shows-that-individuals-recovering-from-covid-19-exhibit-sustained-cellular-immune-dysregulation-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-indian-scientists-discover-four-major-phenotypes-of-immune-dysregulation-caused-by-sars-cov-2-in-covid-19-patients
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/persistent-heart-issues-in-post-covid-linked-to-immune-dysregulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-immune-dysfunction-altered-immune-metabolism-dysbiosis-neuroinflammation-and-viral-persistence-are-issues-causing-long-covid
