Protective Role of Vitamin K3 Supplements On SARS-CoV-2 Structural Protein-Induced Inflammation And Cell Death: A Potential Treatment For COVID-19
Thailand Medical News Team Aug 04, 2023 1 year, 8 months, 1 week, 2 days, 4 hours, 13 minutes ago
COVID-19 Supplements: In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, scientists and medical researchers continue to explore potential treatments and preventive measures to combat the devastating effects of the virus. Among the many avenues of research, a recent study conducted by the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang University, and Pingxiang Maternity and Child Care Hospital in China has shed light on the protective role of Vitamin K3 in countering the inflammatory response and cell damage triggered by SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins. This new research may offer a new strategy in the fight against COVID-19.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
COVID-19 is known for its wide range of symptoms, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress and organ failure. One of the key contributors to the worsening of the disease is the activation of the body's inflammatory response, particularly in the vascular endothelial cells. This inflammatory response is linked to increased vascular permeability, microvascular thrombosis, and eventual multi-organ dysfunction.
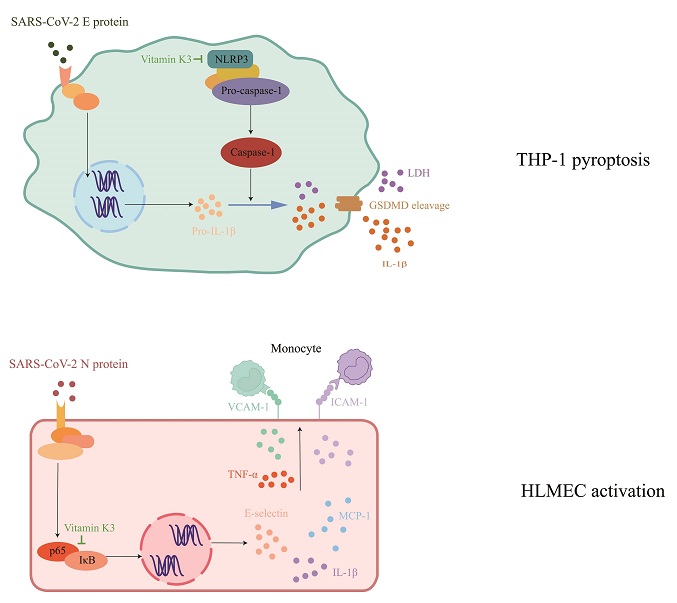
Structural proteins of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, such as the nucleocapsid protein (N protein) and the envelope protein (E protein), have been identified as major pro-inflammatory factors in COVID-19. The N protein is essential for protecting the viral genome, while the E protein is involved in mediating inflammatory processes and cell death.
Understanding how to mitigate the inflammatory effects of these structural proteins is crucial in developing effective treatments for COVID-19.
Vitamin K3, a member of the vitamin K family, has been recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties. Previous studies have shown that vitamin K3 and its analogs can reduce COVID-19 mortality and play a role in preventing lung injury and thromboembolism formation. Moreover, vitamin K3 has been found to inhibit the activity of a crucial enzyme (3-chymotrypsin-like protease) required for SARS-CoV-2 transcription and replication.
These findings have sparked interest in exploring the potential therapeutic benefits of vitamin K3 in COVID-19 treatment.
The current study investigated the effects of vitamin K3 on SARS-CoV-2 N protein-induced endothelial activation and SARS-CoV-2 E protein-induced cell death in human THP-1 cells.
The
COVID-19 Supplements study team observed that vitamin K3 significantly reduced N protein-induced monocyte adhesion and suppressed the expression of adhesion molecules.
Furthermore, the vitamin reduced the expression of pro-infl
ammatory cytokines in the endothelial cells, indicating its anti-inflammatory properties. The study also demonstrated that the protective effects of vitamin K3 on endothelial activation might be associated with the inhibition of the NF-κB signal pathway, a major pro-inflammatory pathway.
Another significant finding was related to the E protein-induced cell death, known as pyroptosis. Vitamin K3 was found to inhibit this process in THP-1 cells by suppressing the NLRP3/GSDMD signaling pathway, thereby reducing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This further reinforced the potential of vitamin K3 as an anti-inflammatory agent in response to SARS-CoV-2 proteins.
The protective role of vitamin K3 against both endothelial activation and pyroptosis suggests that it may serve as a potent suppressor of the inflammatory response in COVID-19 patients. By targeting the structural proteins of the virus, vitamin K3 could potentially alleviate endothelial dysfunction and mitigate the damaging effects of inflammation, thus improving patient outcomes.
In summary, the study findings found that:
-Vitamin K3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 N Protein-Induced Endothelial Cell Activation
-Vitamin K3 Reduced the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines after N Protein Exposure
-Vitamin K3 Prevents the Activation of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in HLMECs
-Vitamin K3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 E Protein-Induced Pyroptosis in Monocytes
Vitamin K3's beneficial effects go beyond its anti-inflammatory properties. It plays a vital role in maintaining normal blood coagulation, bone mineralization, soft tissue physiology, and neurological development.
The safety profile of vitamin K3 is well-established, with no reported cases of systemic toxicity. The potential for vitamin K3 to target SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins and reduce their activity adds to its potential as a preventive or therapeutic option for COVID-19 treatment.
While this study marks a significant step forward in understanding the protective effects of vitamin K3, there is still much to explore in terms of the mechanism of action and its efficacy in vivo. Future research will likely delve deeper into the post-transcriptional regulation of NLRP3 by vitamin K3 and may involve the development of animal models to validate the findings in human trials.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Pharmaceuticals.
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/16/8/1101
For more about
COVID-19 Supplements, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/researchers-in-netherlands-discover-that-lack-of-sufficient-vitamin-k-plays-a-role-in-covid-19-in-terms-of-lung-damage-and-thromboembolism
