Purine Protein's Role in Prostate Cancer: New Hope for Understanding and Treatment
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 26, 2024 9 months, 4 weeks, 1 day, 23 hours, 49 minutes ago
Cancer News: A Key Discovery in Cancer Research
Researchers at Mie University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan and Nova Southeastern University in the USA have made a groundbreaking discovery in prostate cancer research. They identified a crucial protein called purine-rich element binding protein alpha (PURα) that plays a significant role in the progression of prostate cancer. This discovery covered in this
Cancer News report, could pave the way for new treatments and better understanding of how prostate cancer develops and becomes resistant to current therapies.
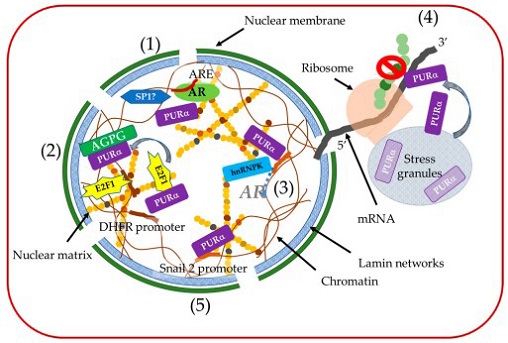 Diagram of the suspected role of PURα in cancer cells. (1) PURα upregulates or downregulates the androgen response element (ARE) together with other transcriptional factors such as Sp1 depending on the androgen concentration. (2) PURα interferes with the transcriptional activation of the S-phase-specific gene dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) by interacting with E2F1and preventing its associaion with the E2F1 elements located wihin the DHFR promoter. Acting gamma 1 pseudogene 25 (AGPG) disrupts the PURα/E2F1 interaction, activating E2F1 signaling pathways. (3) PURα and hnRNP K bind to the 5′-untranslated regions of the AR gene as a novel transcriptional repressor complex. (4) PURα directly binds mRNA with a strong preference for the UG-/U-rich motifs of 3′-UTRs and inhibits IGFBP3 protein expression (stop mark). (5) PURα binds to the Snail2 promoter, resulting in the downregulation of E-cadherin and accelerating cell proliferation and migration.
What is PURα?
Diagram of the suspected role of PURα in cancer cells. (1) PURα upregulates or downregulates the androgen response element (ARE) together with other transcriptional factors such as Sp1 depending on the androgen concentration. (2) PURα interferes with the transcriptional activation of the S-phase-specific gene dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) by interacting with E2F1and preventing its associaion with the E2F1 elements located wihin the DHFR promoter. Acting gamma 1 pseudogene 25 (AGPG) disrupts the PURα/E2F1 interaction, activating E2F1 signaling pathways. (3) PURα and hnRNP K bind to the 5′-untranslated regions of the AR gene as a novel transcriptional repressor complex. (4) PURα directly binds mRNA with a strong preference for the UG-/U-rich motifs of 3′-UTRs and inhibits IGFBP3 protein expression (stop mark). (5) PURα binds to the Snail2 promoter, resulting in the downregulation of E-cadherin and accelerating cell proliferation and migration.
What is PURα?
PURα is a protein found in the nucleus of cells. It's part of the nuclear matrix, which is a network of fibers that provide structure and support to the nucleus. This protein has various functions, including regulating gene expression, DNA replication, and RNA processing. In cancer cells, the nuclear matrix undergoes significant changes, and these changes can affect the behavior and characteristics of the cancer.
The Role of the Nuclear Matrix in Cancer
The nuclear matrix is more than just a structural component; it interacts with many different proteins and plays a vital role in the functioning of the cell. Changes in the nuclear matrix can lead to alterations in DNA structure and gene interactions, contributing to cancer progression. In prostate cancer, these changes are particularly pronounced, and studying the nuclear matrix can provide valuable insights into the disease.
Discovering PURα's Role in Prostate Cancer
Using prostate cancer cell lines, the researchers conducted a detailed analysis of the proteins in the nuclear matrix. They found that PURα was present in both androgen-sensitive and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells, but its levels were different. In androgen-independent cells, which are a model for advanced, treatment-resistant prostate cancer, PURα levels were sig
nificantly lower.
This finding suggests that PURα might play a role in the transition from hormone-sensitive to hormone-resistant prostate cancer, a critical step in the progression of the disease.
Androgen Receptors and Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer growth is often driven by androgens, male hormones like testosterone. Androgen receptors in prostate cells bind to these hormones and trigger cell growth. In advanced prostate cancer, the cancer cells can continue to grow even when androgen levels are reduced through treatment, leading to what is known as castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
The researchers found that PURα interacts with androgen receptors and can influence their activity. In cells with low androgen levels, PURα reduces androgen receptor activity, which in turn slows down cell growth. However, when androgen levels are high, PURα's effect is less pronounced or even reversed.
Potential for New Treatments
The study suggests that increasing PURα levels in prostate cancer cells might be a way to slow down or stop the progression of the disease, especially in cases where the cancer has become resistant to hormone therapy. This could be achieved through gene therapy or drugs that boost PURα production.
Moreover, understanding the exact mechanisms by which PURα affects androgen receptors and other cellular processes could lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies. For example, targeting the pathways that regulate PURα levels or its interaction with androgen receptors might offer new ways to combat prostate cancer.
Broader Implications
The discovery of PURα's role in prostate cancer also has broader implications for cancer research. The nuclear matrix and its associated proteins are involved in many types of cancer, not just prostate cancer. Studying these components can reveal new targets for treatment and improve our understanding of how cancers develop and spread.
Future Research Directions
Future research will focus on understanding exactly how PURα interacts with androgen receptors and other proteins in the nuclear matrix. Researchers will also explore ways to manipulate PURα levels in cancer cells and test the effectiveness of these approaches in animal models and eventually in clinical trials.
The research team is also interested in studying PURα in other types of cancer to see if similar mechanisms are at play. This could potentially lead to new treatments for a variety of cancers.
Conclusion
The discovery of PURα's role in prostate cancer is a significant step forward in cancer research. It opens up new avenues for treatment and enhances our understanding of how prostate cancer progresses and becomes resistant to current therapies. By continuing to explore the functions of PURα and the nuclear matrix, scientists hope to develop more effective treatments and improve outcomes for patients with prostate cancer and other types of cancer.
This exciting research highlights the importance of basic scientific discoveries in the fight against cancer and underscores the potential for new therapies that target the fundamental processes driving cancer progression.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/13/6911
For the latest
Cancer News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/cholesterol-intake-might-influence-early-prostate-cancer-development
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/wisconsin-researchers-pioneer-new-treatment-protocol-for-prostate-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-michigan-develops-new-urine-test-that-detects-high-grade-prostate-cancer-as-an-alternative-to-biopsies
