Researcher Proposes Using Aprepitant As A Drug To Target Neurokinin-1 Receptors To Prevent COVID-19 Cytokine Storms
Source: COVID-19-Drugs Sep 22, 2021 3 years, 6 months, 1 week, 3 days, 5 hours, 13 minutes ago
COVID-19 Drugs: A researcher from the University of Lahore Pakistan has proposed that the drug aprepitant could be used to target the neurokinin-1 receptors to prevent COVID-19 cytokine storms.
Aprepitant is a medication used in the management and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). It is in the neurokinin-1 antagonist class of medications.
The researcher hypothesized that the neuropeptide substance P (SP) as a possible cause of the initiation of cytokine storm developed in COVID-19 infection and to suggest Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) antagonist, Aprepitant, as a drug to be used for its treatment.
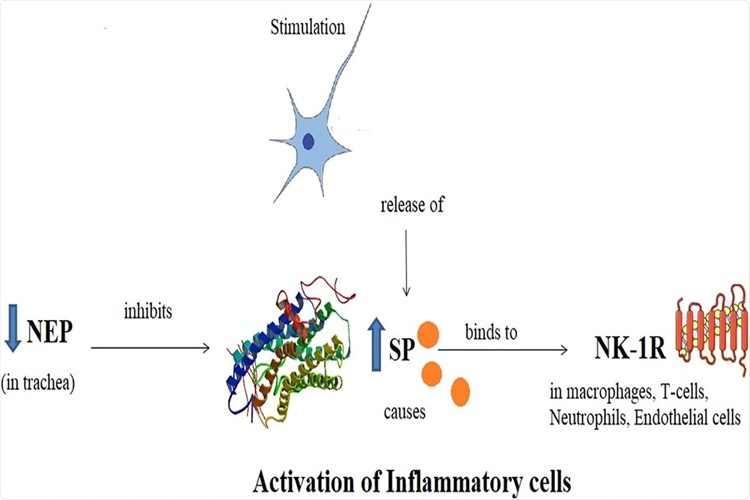 Schematic diagram showing Substance P, its receptor Neurokinin-1 and Neutral Endopeptidase. SP binds to NK-1R as a result of nociceptive stimulus and potentiates the inflammation. NEP acts as a regulatory mechanism by degrading the SP and hence, inflammation.
Schematic diagram showing Substance P, its receptor Neurokinin-1 and Neutral Endopeptidase. SP binds to NK-1R as a result of nociceptive stimulus and potentiates the inflammation. NEP acts as a regulatory mechanism by degrading the SP and hence, inflammation.
This proposed perspective will provide directions to the biomedical scientists to explore SP and NK-1R and prepare a drug to alleviate the symptoms and cure the disease. It is very important to work on this perspective at earliest to reach to some conclusion regarding the therapeutic intervention. Clinical studies may also be conducted if proven successful. SP is a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator, released from the trigeminal nerve of brainstem as a result of nociception. It is directly related to the respiratory illness as in COVID-19 infection. It is responsible for the increased inflammation and the signature symptoms associated with this disease. It is the main switch that needs to be switched off by administering Aprepitant along with glucocorticosteroid, dexamethasone.
The opinion article was published in the peer reviewed journal: Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy (Science Direct).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332221009434
The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus which cause the COVId-19 disease has a high transmission rate, and its symptoms may vary from being mild to severe pneumonia-like. Some individuals are also asymptomatically infected with the virus. Common clinical manifestations of mild COVID-19 include cough, fever, muscular pain, loss of smell and taste, shortness of breath, vomiting, and sore throat. Severe infection may lead to organ failure, respiratory failure, and eventually death.
Researchers say that the novel coronavirus alone does not cause mortalityby itself rather the cytokine storm is responsible for respiratory failure, multiple organ failure, or heart attack that leads to death.
Researchers and scientists worldwide have been developing effective COVID-19 treatments. Several clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate various drugs with antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects.
This new opinion article propose
s that Substance P (SP), via Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R), is responsible for the cytokine storm and inflammation in the case of severe COVID-19 infection.
The researcher aims to provide evidence that SP could be the possible factor for initiating the cytokine storm during severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. He has also proposed that such a condition could be effectively treated using Neurokinin-1 Receptor antagonist, aprepitant, as a potential therapeutic from the long list of prospective
COVID-19 Drugs.
In 1931, Euler and Gaddum first discovered SP as a brain-gut hormone.
https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002763
Subsequent extensive research revealed different roles of SP as a neuromodulator, neurotransmitter, and neurohormone, encoded by the gene named Tachykinin-1 (TAC-1).
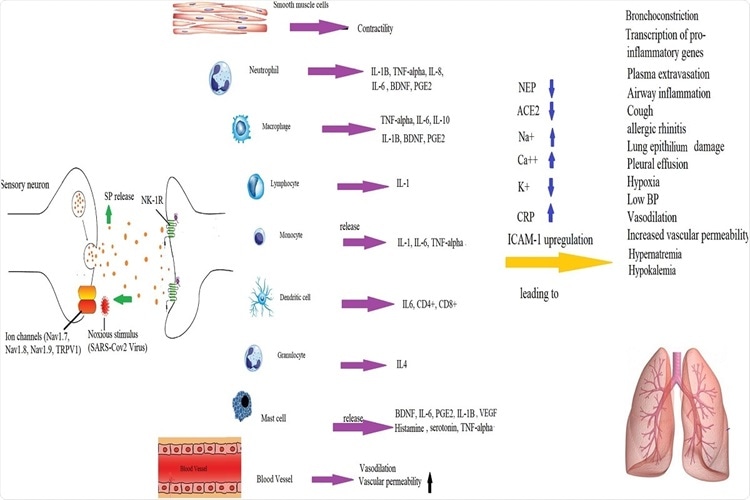 Mechanisms by which SP-induced inflammation is implicated in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 infection. SP binds to NK-1R on endothelial cells to increase BBB permeability and release of cytokines by immune cells.
Mechanisms by which SP-induced inflammation is implicated in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 infection. SP binds to NK-1R on endothelial cells to increase BBB permeability and release of cytokines by immune cells.
Furthermore it has been found that SP has many other functions, such as autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine functions. Scientists reported that SP and NK-1R are highly expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and the cardiovascular system. Immune cells such as leukocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages can also express SP.
Importantly SP is a chemokine that stimulates the cytokine release in respiratory tracts after attaching with NK-1R. These are also associated with various pathological conditions and inflammation.
Researchers have revealed that NK-1R is a 7-transmembrane domain, G-protein coupled receptor that possesses a high SP affinity.
Interestingly this receptor is also present in many cells such as white blood cells, lymphatics neurons, fibroblasts, vascular endothelium and, cardio-ventilatory regulatory centers. Previous research revealed that after the formation of the SP/NK1-R complex, a signaling cascade is responsible for the production of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
It has been found that some of the early symptoms associated with COVID-19, such as cough, loss of smell and taste, headache, sore throat, are linked with the release of SP from trigeminal ganglion via TrN. Also, the release of the SP in the vagal C fibers in the larynx and upper respiratory tracts causes a cough.
Researchers have found that NK-1R antagonists could reduce the refractory cough frequency.
It has been also found that differential severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection in varied age groups are linked with the expression of SP. Mostly, SARS-CoV-2 is found to severely affect older age groups, compared to younger people. Many studies have indicated that the elderly tend to have elevated SP levels and that a higher concentration of SP leads to death.
Past research have revealed that individuals with co-morbidities such as diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), hepatic renal and cardiovascular conditions are more vulnerable to severe COVID-19 infection. Generally, patients with DM and HTN are treated with Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) and Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. The spike proteins of the virus attach to the ACE2 of the host to establish infection.
Hence, ACE2 is the main receptor associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, which is abundantly present in the lung capillaries, renal and endothelial cells of humans. A high level of SP dilates vessels, resulting in more blood pumping in the heart, thereby increasing the risks of a heart attack. Increased levels of SP also lower the blood sugar level, causing multiple organ failure in severe COVID-19 cases.
Interestingly, previous research revealed that SP secretion by the immune cells is positively correlated with the viral load.
Numerous studies had indicated SP enhances inflammation via various mechanisms such as vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, leukocyte extravasation, and immune response activation in native cells and pathogens. In mice models, NK-1R deficient mice showed pulmonary inflammation as compared to controls.
Dr Riffat Mehboob, the author of this study strongly suggested that SP/NK-1R complex is associated with the pathogenesis of COVID-19 infection. A combined therapeutic approach including corticosteroids, antibiotics, purified intravenous immunoglobulins and anti-cytokinic therapy should be recommended .
A recent randomized clinical trial associated with the evaluation of NK-1R antagonists (Dexamethasone and Aprepitant) for treating COVID-19 infection revealed that both the drugs showed improved clinical outcomes. Also, patients who received the combination of these drugs reported improved clinical symptoms and reduced C-reactive protein.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.08.01.20166678v3
For the latest research on emerging
COVID-19-Drugs keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.


