SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts the Hemostatic System and the Complement System in a Complex Interplay
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 14, 2025 11 months, 3 weeks, 1 day, 6 hours, 59 minutes ago
Medical News: A groundbreaking study conducted by researchers from the National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, Pakistan, explores the intricate ways in which SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, disrupts two critical systems of the human body - the hemostatic system and the complement system. This investigation not only sheds light on the biological chaos induced by the virus but also opens avenues for targeted treatments. This
Medical News report delves into the study’s key findings and their potential implications for managing severe COVID-19 cases.
 SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts the Hemostatic System and the Complement System in a Complex Interplay
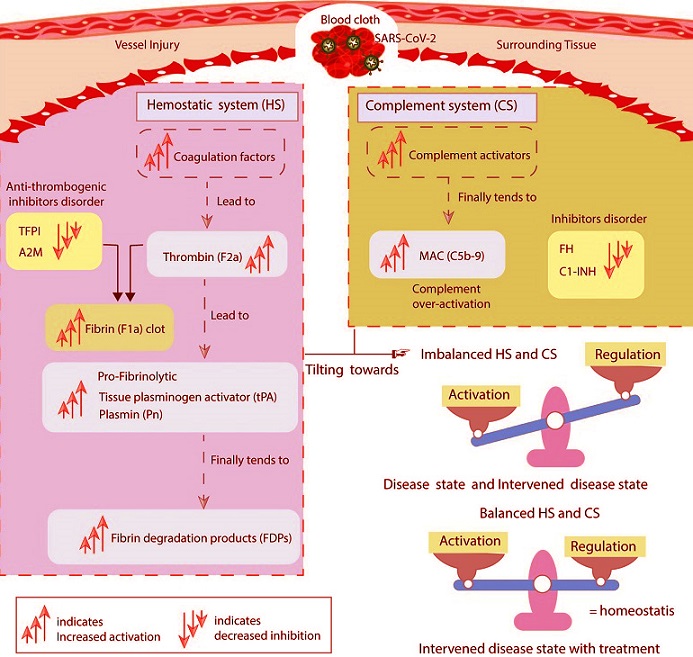
The study’s implications. The disordered inhibitors in the hemostatic and complement systems increased the activation of hemostatic factors. The activation of components of the complement system also increases. The main highly activated entities of both systems include F2a, thrombin; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; Pn, plasmin; FDPs, fibrin degradation products; and C5b-9, terminal complement complex. The suppressed inhibitors comprise TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; A2M, alpha-2-macroglobulin; FH, complement factor H; and C1INH, C1-inhibitor. In the state of unhealthy symptomatic COVID-19 patients, referred to as the disease state, and during decreased levels of the inhibitors termed as the intervened disease state, there is an imbalanced activation and regulation of HS and CS entities. Meanwhile, drug intervention tends to regulate these behaviors towards homeostasis.
Hemostatic and Complement Systems Unveiled
SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts the Hemostatic System and the Complement System in a Complex Interplay
The study’s implications. The disordered inhibitors in the hemostatic and complement systems increased the activation of hemostatic factors. The activation of components of the complement system also increases. The main highly activated entities of both systems include F2a, thrombin; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; Pn, plasmin; FDPs, fibrin degradation products; and C5b-9, terminal complement complex. The suppressed inhibitors comprise TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; A2M, alpha-2-macroglobulin; FH, complement factor H; and C1INH, C1-inhibitor. In the state of unhealthy symptomatic COVID-19 patients, referred to as the disease state, and during decreased levels of the inhibitors termed as the intervened disease state, there is an imbalanced activation and regulation of HS and CS entities. Meanwhile, drug intervention tends to regulate these behaviors towards homeostasis.
Hemostatic and Complement Systems Unveiled
The hemostatic system, responsible for preventing and stopping bleeding, works in tandem with the complement system, a critical component of the body’s innate immune response. Together, these systems maintain a delicate balance between clot formation and immune activation. However, in the context of COVID-19, this harmony is severely disrupted.
Researchers Didar Murad, Rehan Zafar Paracha, and Maryum Nisar have used a quantitative systems immunology model to examine how these disruptions occur. The dynamics of key components were analyzed under three conditions: the natural disease state, a perturbed state marked by reduced regulatory proteins, and a treatment state where therapeutic interventions were applied.
The study highlights that such detailed systems-level understanding is pivotal to designing effective therapies for the multifaceted complications caused by SARS-CoV-2.
Key Findings of the Study:
Impact on Critical Biomolecules
The study identified several molecules that are significantly impacted during a COVID-19 infection, including thrombin, plasmin, fibrin degradation products (FDPs), and the membrane attack complex (MAC or C5b-9). Key regulators such as complement factor H (FH) and C1-inhibitor (C1INH) were found to play critical roles in controlling these components. Wh
en their levels were reduced, as observed in severe cases of COVID-19, there was an alarming increase in thrombotic and inflammatory markers.
Drug Interventions and Their Effects
To counter these disruptions, the study tested several drugs, including:
-Heparin: Widely known as an anticoagulant, heparin was effective in controlling thrombin levels. However, its administration requires careful dosing to avoid excessive bleeding.
-Tranexamic Acid (TXA): Used to inhibit plasmin, TXA showed promise in reducing fibrinolytic activity and FDPs.
-Avdoralimab and Garadacimab: These drugs target complement components like C5aR1 and Factor XIIa, respectively, helping to regulate the inflammatory response and clot formation.
-Tocilizumab (TCZ): An anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, TCZ demonstrated efficacy in mitigating the cytokine storm - a hallmark of severe COVID-19 cases.
The restorative impact of these interventions underscores their potential to manage complications in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
Dynamic Responses Under Disease and Treatment States
-Thrombin Levels
Thrombin, a central player in clot formation, showed a rapid increase in the disease state, leading to hypercoagulation. The regulatory roles of FH and C1INH were highlighted, as their depletion exacerbated thrombin activity. In the treatment state, heparin demonstrated a dose-dependent ability to restore thrombin levels to normal.
-Plasmin and FDPs
Plasmin, an enzyme involved in breaking down clots, and its byproducts, FDPs, were elevated during the disease state. This increase contributed to hyperfibrinolysis and potential bleeding risks. The administration of TXA effectively reduced these levels, showcasing its role in balancing coagulation and fibrinolysis.
-Inflammatory Markers
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and its complex with its receptor were found to be elevated in the disease state, fueling the hyperinflammatory response known as the cytokine storm. Avdoralimab and TCZ emerged as effective agents in curbing this excessive immune reaction.
Complement Activation
The study observed an overactivation of the complement system, particularly the terminal complement complex (C5b-9). This overactivation contributed to inflammation and tissue damage. Heparin and other complement-targeting therapies demonstrated potential in modulating this response.
Implications for COVID-19 Treatment
The study’s findings have profound implications for clinical practice. They suggest that early intervention with targeted therapies can mitigate the severe complications of COVID-19, such as clot formation, hyperinflammation, and organ damage. However, the potential side effects of these treatments, such as bleeding risks with heparin or immune dysregulation with complement inhibitors, highlight the need for personalized treatment strategies.
A Vision for Future Therapies
The comprehensive systems immunology approach adopted by the researchers provides a detailed roadmap for understanding the interplay between the hemostatic and complement systems during SARS-CoV-2 infection. By simulating different disease and treatment states, the study offers valuable insights into how these systems can be modulated to improve patient outcomes.
The findings also emphasize the importance of regulatory proteins like FH and C1INH in maintaining systemic balance. Therapies aimed at enhancing these regulators could serve as a new frontier in managing not just COVID-19 but other diseases involving similar immune and coagulation pathways.
Conclusion
This study represents a significant step forward in unraveling the complex mechanisms underlying COVID-19’s impact on the human body. By highlighting the critical roles of the hemostatic and complement systems, it opens the door to more effective and targeted treatments for the severe complications associated with the disease.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Frontiers in Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457324/full
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-uses-heme-and-complement-factor-h-for-immune-evasion
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/the-covid-19-virus-exploits-host-cd55-cd59-and-factor-h-to-evade-antibody-dependent-complement-mediated-lysis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/post-covid-19-individuals-with-iga-nephropathy-found-to-have-overactivated-complement-system
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/coronavirus
