SARS-CoV-2 News: Scientist From India Find That SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Protein Possesses Complement Inhibitory Properties
Thailand Medical News Team Aug 09, 2023 1 year, 8 months, 2 weeks, 22 hours, 46 minutes ago
SARS-CoV-2 News: In the ongoing battle against the SARS-CoV-2 virus, scientists continue to uncover the intricate mechanisms by which the virus evades the host's immune defenses. Recent research from the Neurobiology and Drug Discovery (NDD) Laboratory at Jamia Hamdard in New Delhi, India, has shed light on a remarkable discovery - the SARS-CoV-2-encoded ORF8 protein possesses unique properties that allow it to inhibit the complement system, a critical component of the body's innate immunity.
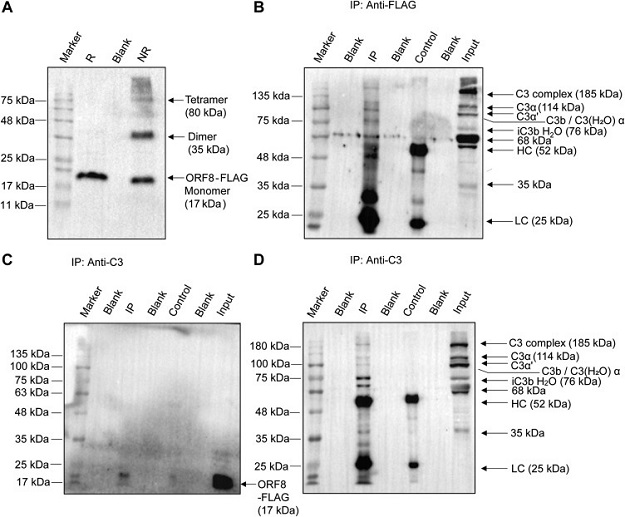 Expression of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 and interaction with complement C3 and its metabolites by Coimmunoprecipitation. A, multimeric forms of ORF8-FLAG–tagged protein, expressed in transfected HepG2 cells and immunoblotted using anti-FLAG antibody in lysates prepared under reduced (R) versus nonreduced (NR) condition. Monomers (17 kDa) in standard Laemmli buffer, oligomerizes in NR condition. Co-IP from FLAG-ORF8–transfected HepG2 cells as indicated in panels. B, IP with mouse-anti-FLAG antibody and detection on blot by rabbit anti-C3 antibody against C3dg/TED domain encompassing fragment (amino acid 1000–1326 of human C3); C, IP with rabbit anti-C3 antibody and detection on blot with anti-FLAG. D, reprobing of the stripped-blot in C panel with rabbit anti-C3. Anti-C3 recognizes epitopes in C3, C3b, iC3b, and C3c fragments, as indicated. Antibody light chain (LC) and heavy chain (HC) are also shown. For control lanes (anti-rabbit IgG antibody), IP lanes (target antibodies), and input lanes (lysate), 15% equivalent and 5% of total input samples were loaded, respectively. Data shown is representative image of three independent experiments.
Expression of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 and interaction with complement C3 and its metabolites by Coimmunoprecipitation. A, multimeric forms of ORF8-FLAG–tagged protein, expressed in transfected HepG2 cells and immunoblotted using anti-FLAG antibody in lysates prepared under reduced (R) versus nonreduced (NR) condition. Monomers (17 kDa) in standard Laemmli buffer, oligomerizes in NR condition. Co-IP from FLAG-ORF8–transfected HepG2 cells as indicated in panels. B, IP with mouse-anti-FLAG antibody and detection on blot by rabbit anti-C3 antibody against C3dg/TED domain encompassing fragment (amino acid 1000–1326 of human C3); C, IP with rabbit anti-C3 antibody and detection on blot with anti-FLAG. D, reprobing of the stripped-blot in C panel with rabbit anti-C3. Anti-C3 recognizes epitopes in C3, C3b, iC3b, and C3c fragments, as indicated. Antibody light chain (LC) and heavy chain (HC) are also shown. For control lanes (anti-rabbit IgG antibody), IP lanes (target antibodies), and input lanes (lysate), 15% equivalent and 5% of total input samples were loaded, respectively. Data shown is representative image of three independent experiments.
The complement system, a network of proteins, plays a pivotal role in detecting and eliminating viral pathogens. However, when hyperactivated, it can inadvertently cause harm to the host's own tissues. This hyperactivation has been linked to the severe clinical manifestations observed in COVID-19 patients.
Despite our understanding of the complement pathways' activation, the question of how the virus manages to escape the system's surveillance remained elusive until now.
The study team at the NDD Laboratory embarked on a mission to unravel this mystery. They focused their attention on the SARS-CoV-2-encoded ORF8 protein, which emerged as a major player in the virus's evasion strategy. By conducting a series of meticulous experiments, the researchers identified ORF8 as a key binding partner for human complement C3 and C3b components, critical pieces of the complement puzzle.
Their findings revealed that when ORF8 interacts with C3/C3b, a cascade of events occurs that effectively subverts the alternative pathway of the complement system. In this intricate interaction, ORF8 inhibits the proteolysis mediated by factor I, blocking the cleavage of C3b. Simultaneously, it prevents the activation of factor B zymogen into active Bb, an essential step in the formation of the C3-convertase complex. This remarkable process, driven by the ORF8 protein, leads to the seclusion of factor H and factor B from C3b, rendering the complexes impervious to factor I's proteolysis and inhibiting the inhibition of pro-C3-convertase formation.
The study team's discovery was further reinforced by a hemolysis-based assay, where ORF8 exhibit
ed potent complement inhibitory activity. It successfully prevented human serum-induced lysis of rabbit erythrocytes, showcasing its ability to hinder the complement system's destructive potential.
Additionally, in silico protein-protein docking analysis illuminated the intricate interactions between ORF8 and the β-chain of C3b. These interactions were akin to those of a peptidomimetic compound, obstructing the binding of essential cofactors crucial for complement amplification.
Historically, the concept of viruses evading the host's immune defenses is not new. Many viruses have evolved intricate strategies to manipulate the immune system for their own benefit as covered in past studies and
SARS-CoV-2 News reports.
However, the manner in which SARS-CoV-2 employs its evasion tactics remained elusive, particularly in the context of the complement system. While previous research hinted at complement activation and potential escape mechanisms, this study's uniqueness lies in its focus on ORF8-mediated evasion.
The study team provided a crucial piece of the puzzle by revealing that SARS-CoV-2's ORF8 protein operates as a master regulator of the alternative pathway of the complement system. By binding to C3/C3b, ORF8 effectively blinds the system's critical components, making them inaccessible to essential cofactors needed for activation and regulation. This orchestration ultimately allows the virus to slip through the immune system's net during the initial stages of infection, providing valuable insights into its survival strategy.
Furthermore, this study draws parallels between ORF8 and other viral evasion mechanisms. Viruses, such as herpes virus and Nipah virus, have employed distinct strategies to manipulate the complement system in their favor. ORF8's role in inhibiting the alternative pathway echoes the tactics employed by certain microbes, indicating that this protein has harnessed a well-documented evasion mechanism.
In conclusion, the groundbreaking research has unveiled a previously unknown facet of the SARS-CoV-2 virus's evasion strategy. The ORF8 protein's ability to inhibit the complement system's alternative pathway sheds light on the virus's sophisticated tactics to evade detection and clearance during the early stages of infection. While many questions remain unanswered, this study provides a critical foundation for future investigations into the physiological implications of ORF8-mediated complement regulation.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Biological Chemistry.
https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(23)00062-5/fulltext
For the latest
SARS-CoV-2 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-accessory-proteins-orf6,-orf8,-orf9b,-orf9c-have-the-ability-to-trigger-inflammatory-and-profibrotic-processes-through-il11-signaling
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/u-s-study-reveals-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-triggers-inflammatory-response-in-immune-cells-through-myd88-independently-of-the-il-17-receptor
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/unique-sites-of-immune-regulation-discovered-in-sars-cov-2-orf8
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-sublineages-lacking-orf8-protein-do-not-replicate-in-upper-respiratory-tract,-reducing-transmission-but-increasing-inflammation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-validates-that-sars-cov-2-accessory-proteins-orf6,-orf8,-orf9b-and-orf9c-involved-in-profibrotic-processes
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-orf8-protein-of-sars-cov-2-induces-endoplasmic-reticulum-stress-like-responses-and-facilitates-virus-replication-by-triggering-calnexin
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-exhibits-complement-inhibitory-properties-and-damages-innate-immunity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-yale-study-shows-that-omicron-subvariants-are-evolving-further-through-mutations-on-orf8-proteins-to-escape-from-mhc-i-recognition
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-french-scientists-uncover-how-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-causes-dysregulation-of-gene-expression-in-infected-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mayo-clinic-researchers-discover-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-is-the-key-factor-that-is-causing-covid-19-disease-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-encoded-protein-contains-a-histone-mimic-that-disrupts-human-host-cell-epigenetic-regulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-university-of-california-scientist-identify-rapidly-evolving-immune-evasion-protein-sars-cov-2-orf8-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-briefs-anti-androgens-and-covid-19,-possible-cytotoxic-t-cell-therapy-for-covid-19,-immune-evasion-by-evolving-orf8-protein-in-sars-
