SARS-CoV-2 Nsp16 protein drives inflammation by promoting IL-6 production via prevention of HIF-1alpha degradation
Sebastian Lavoie Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Sep 10, 2024 1 year, 3 months, 2 weeks, 1 day, 10 hours, 58 minutes ago
Medical News: A recent study sheds new light on how a specific protein of SARS-CoV-2, called nonstructural protein 16 (NSP16), plays a crucial role in the inflammatory response linked to severe cases of COVID-19. Conducted by researchers from Wuhan University-China, University of Helsinki-Finland, and Guangzhou Laboratory-China, the study provides valuable insights into how this viral protein promotes the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a molecule involved in the dangerous "cytokine storm" observed in severe COVID-19 patients. This
Medical News report explores the key findings and their implications for developing new treatments aimed at reducing the severity of COVID-19 infections.
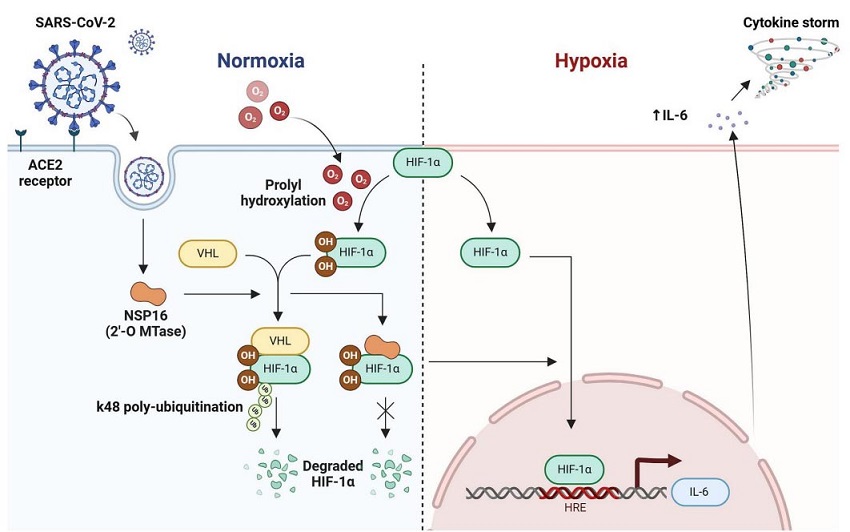 The proposed molecular mechanisms and implications of SARS-CoV-2 NSP16 regulates IL -6 production by targeting HIF-1α. Under normoxic condition, the 2′-O Mtase NSP16 of SARS-CoV-2 interacts with HIF-1α and impedes the association of VHL with HIF-1α, leading to inhibition of VHL mediated HIF-1α degradation by K-48 linked polyubiquitination. The stabilized HIF-1α can translocate to nucleus and bind with the HRE of IL-6 promoter to induce IL-6 production during hypoxia
The Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in COVID-19 Inflammation
The proposed molecular mechanisms and implications of SARS-CoV-2 NSP16 regulates IL -6 production by targeting HIF-1α. Under normoxic condition, the 2′-O Mtase NSP16 of SARS-CoV-2 interacts with HIF-1α and impedes the association of VHL with HIF-1α, leading to inhibition of VHL mediated HIF-1α degradation by K-48 linked polyubiquitination. The stabilized HIF-1α can translocate to nucleus and bind with the HRE of IL-6 promoter to induce IL-6 production during hypoxia
The Role of Hypoxia and HIF-1α in COVID-19 Inflammation
Severe COVID-19 cases are often characterized by excessive inflammation, leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and systemic hypoxia, where oxygen levels in the body drop significantly. Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) is a key player in the body’s response to low oxygen levels, regulating genes that control processes such as glucose metabolism and immune responses.
The research team focused on how SARS-CoV-2 manipulates HIF-1α to increase IL-6 production, a pro-inflammatory cytokine linked to the severity of COVID-19 symptoms. By using a variety of advanced laboratory techniques, including dual luciferase assays and immunoblotting, they discovered that NSP16 is the primary driver of this heightened inflammatory response.
How NSP16 Interacts with HIF-1α to Promote Inflammation
Researchers discovered that NSP16 enhances the activity of HIF-1α by preventing its degradation. Under normal circumstances, HIF-1α is broken down by a process called ubiquitination, which involves a protein known as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL). However, NSP16 interrupts this process, leading to increased levels of HIF-1α in cells. As a result, HIF-1α accumulates and activates a specific gene region known as the hypoxia-response element (HRE) within the IL-6 promoter, leading to increased production of IL-6.
The study reveals that this interaction could be responsible for the cytokine storms that wreak havoc in severe COVID-19 cases, as the elevated IL-6 levels trigger a chain reaction of inflammation and tissue damage, particularly in the lungs.
Why IL-6 Matters in COVID-19
IL-6 is a critical molecule in the body’s immune response, but too much of it can be harmful. In COVID-19 patients, elevated IL
-6 levels have been strongly associated with worse clinical outcomes, including respiratory failure and multi-organ dysfunction. This explains why some treatments for COVID-19 have focused on blocking IL-6 or its signaling pathways.
The study’s findings underscore the role of NSP16 in specifically regulating IL-6, without significantly affecting other pro-inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). This selective activation of IL-6 suggests that NSP16 could be a promising target for future therapeutic strategies aimed at controlling the immune response in COVID-19.
Implications for Treatment: Targeting HIF-1α and NSP16
One of the most significant findings of this study is the potential for targeting HIF-1α and its interaction with NSP16 to develop new treatments for COVID-19. Drugs that inhibit HIF-1α, such as BAY87-2243, have already shown promise in reducing IL-6 levels in cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to the research.
This approach could help control the overactive immune response seen in severe COVID-19 cases, potentially reducing the need for invasive treatments such as mechanical ventilation or intensive care. Additionally, the fact that NSP16 also interacts with another protein called HIF-2α, which has similar functions to HIF-1α, opens up even more possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
Future Research Directions
While the study has provided crucial insights into how SARS-CoV-2 manipulates the immune system to cause severe inflammation, there is still much to learn. For example, researchers are interested in further exploring the structural details of how NSP16 interacts with HIF-1α and HIF-2α. Understanding these interactions at a molecular level could pave the way for developing more precise and effective treatments.
Moreover, the study highlights the need for further investigation into how NSP16’s effects on IL-6 differ from its effects on other pro-inflammatory molecules. This could help scientists identify which COVID-19 patients are most at risk of experiencing a cytokine storm and guide the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, this groundbreaking study has revealed that SARS-CoV-2’s NSP16 protein plays a critical role in promoting IL-6 production by stabilizing HIF-1α, a key regulator of the body’s response to low oxygen levels. By interfering with the normal degradation of HIF-1α, NSP16 drives the inflammatory response that leads to severe COVID-19 symptoms. These findings point to HIF-1α and NSP16 as potential targets for new treatments aimed at reducing the severity of COVID-19 infections.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cellular Signalling.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0898656824003553
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-university-of-texas-study-shows-that-sars-cov-2-uses-nonstructural-protein-16-to-evade-restriction-by-ifit1-and-ifit3-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mutations-covid-19-study-shows-that-often-ignored-mutations-on-nsp4-and-nsp16-regions-of-sars-cov-2-genome-plays-critical-role-in-pathogenesis
