SARS-CoV-2 Persistence In The Middle Ear Effusion Could Be The Cause Of Otitis Media
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 18, 2024 2 years, 3 weeks, 3 days, 13 hours, 14 minutes ago
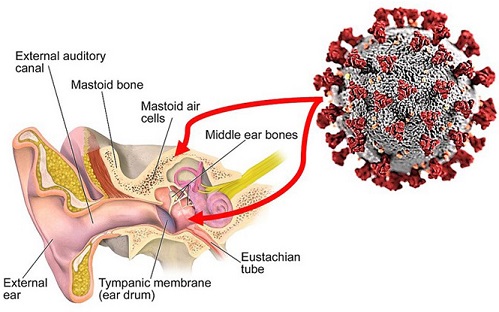
COVID-19 News: Otitis media, a prevalent middle ear condition characterized by inflammation or infection, has garnered increased attention in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. This
COVID-19 News report delves into a comprehensive analysis of the intricate relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and otitis media, focusing on the evolving landscape of otitis media during the pandemic, the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in middle ear effusion (MEE), and the therapeutic potential of tympanocentesis in managing COVID-19-associated otitis media. The study was conducted by researchers from the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China.
 SARS-CoV-2 Persistence In The Middle Ear Effusion Could Be The Cause Of Otitis Media
SARS-CoV-2 Persistence In The Middle Ear Effusion Could Be The Cause Of Otitis Media
Thailand
Medical News had also covered previous studies that also showed the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in the middle ear.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-finds-the-presence-of-sars-cov-2-in-middle-ear-fluid-implications-for-otitis-media-with-effusion-in-covid-19-patients
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sar-cov-2-virus-found-lingering-in-the-middle-ear-for-a-long-time-after-infection-chinese-researchers-warn-of-viral-persistence-in-the-ears
Understanding Otitis Media: A Common Middle Ear Disorder
Otitis media encompasses a spectrum of disorders, including acute otitis media (AOM), chronic otitis media (COM), and otitis media with effusion (OME). OME, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear without signs of active infection, is particularly prevalent and often encountered in clinical practice, especially among children and adults with predisposing factors such as allergies or upper respiratory tract infections.
The Emergence of a Potential Link Between SARS-CoV-2 and Otitis Media
As the COVID-19 pandemic unfolded, medical researchers began to explore its potential long-term effects, leading to the recognition of "long COVID" and its associated sequelae. Among these sequelae, reports emerged suggesting a possible association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and otitis media. Initial observations indicated a decrease in the incidence of otitis media during the pandemic's early phases, likely influenced by factors such as reduced healthcare-seeking behavior and stringent quarantine measures. However, as the pandemic progressed and restrictions eased, an uptick in otitis media cases was observed, prompting further investigation into the relationship between SARS-
CoV-2 and otitis media.
Investigating Viral Persistence in Middle Ear Effusion
Central to understanding the potential link between SARS-CoV-2 and otitis media is the investigation of viral persistence in middle ear effusion (MEE). Studies have demonstrated the presence of viral RNA, including SARS-CoV-2, in MEE samples of patients with COVID-19-associated otitis media. This persistence of viral RNA in MEE may be attributed to various factors, including the time interval between SARS-CoV-2 infection and tympanocentesis, as well as eustachian tube dysfunction. These findings underscore the need for further research into the dynamics of viral clearance and immune response in the middle ear, particularly in the context of COVID-19.
Evaluating Tympanocentesis as a Therapeutic Intervention
Tympanocentesis, a minor surgical procedure involving the aspiration of middle ear fluid, emerges as a valuable therapeutic intervention in the management of otitis media, particularly in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection. This procedure not only provides symptomatic relief but also facilitates the extraction of MEE for viral detection and culture. Studies have shown the efficacy of tympanocentesis in clearing viral RNA from MEE and improving clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19-associated otitis media. Moreover, the procedure offers insights into the pathophysiology of otitis media and its relationship to SARS-CoV-2 infection, paving the way for targeted therapeutic strategies.
Implications and Future Directions
The emerging evidence highlighting the potential link between SARS-CoV-2 and otitis media underscores the need for continued research in this field. Future studies should aim to elucidate the mechanisms underlying viral persistence in the middle ear, evaluate the long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 on auditory health, and explore novel therapeutic strategies for managing COVID-19-associated otitis media. Additionally, large-scale epidemiological studies are warranted to assess the true burden of otitis media during the pandemic and inform public health policies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolving landscape of the COVID-19 pandemic has brought attention to the potential association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and otitis media. While further research is needed to fully understand this relationship, current evidence suggests a plausible link between SARS-CoV-2 persistence in MEE and the development of otitis media. Tympanocentesis emerges as a promising therapeutic modality for managing COVID-19-associated otitis media, offering both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits. Moving forward, continued research efforts are essential to unraveling the complexities of this intriguing relationship and optimizing patient care in the midst of the pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Science Progress (Sage Journals).
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/00368504241231659
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
