Scientists Discover That Combining IL-6 Inhibitors With Current Medications Is A Better Approach For Treating Pulmonary Hypertension
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 12, 2024 11 months, 1 week, 6 days, 2 hours, 35 minutes ago
Medical News: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a multifaceted condition characterized by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure due to narrowing or blockage of lung arteries. This leads to increased strain on the right side of the heart, potentially resulting in heart failure and life-threatening complications. Despite advancements in medical science, pulmonary hypertension remains a challenging disease to manage, often necessitating innovative approaches to treatment.
 Scientists Discover That Combining IL-6 Inhibitors With Current Medications Is A Better Approach For Treating Pulmonary Hypertension
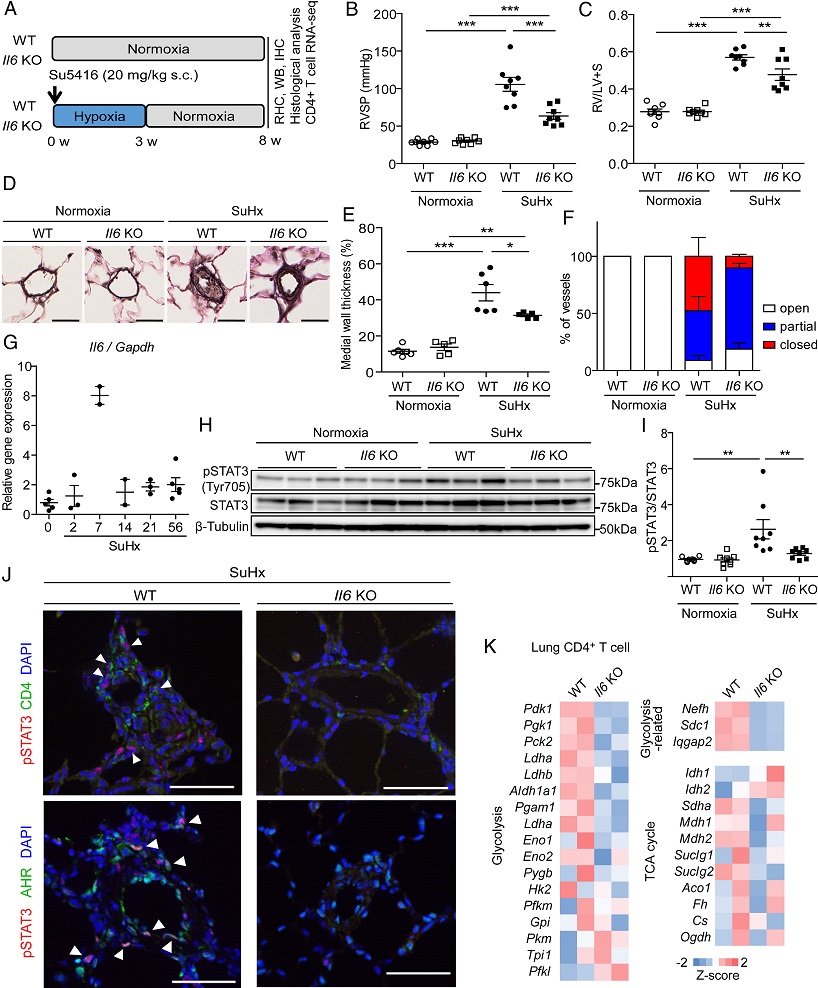
Il6 KO rats are resistant to PH in the SuHx rat model. (A) Experimental protocol for examining the effect of Il6 deletion on SuHx rats. (B and C) Assessment of the effect of Il6 deletion on the PH phenotype of SuHx rats in terms of RVSP (B) and Fulton’s index (C) (n = 8 in each group). (D) Representative images of the vascular remodeling of distal acinar arterioles in lung sections subjected to EVG staining. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (E) Medial wall thickness index of rats (normoxia WT: n = 6, normoxia Il6 KO: n = 5, SuHx WT: n = 6, SuHx Il6 KO: n = 5). (F) Pulmonary arterial occlusions were graded as open (no luminal occlusion; white), partial (<50% occlusion; blue), or closed (≥50% occlusion; red). Percentages of open, partial, and closed pulmonary arteries of outer diameter (OD) <100 μm in SuHx rats) (n = 4 in each group). (G) qRT-PCR analysis of Il6 mRNA expression in the lungs of WT rats after SuHx treatment. (H and I) Western blot analysis of STAT3 phosphorylation (Tyr705) and total STAT3 in lung homogenates from WT and Il6 KO rats 8 wk after normoxia or SuHx treatment (n = 8 in each group). (J) Representative immunofluorescence images of pulmonary arteries stained for pSTAT3 (red) and CD4 (green), and pSTAT3 (red) and Ahr (green) in the lung tissues of WT and Il6 KO rats 8 wk after SU5416 administration. Arrowheads indicate copositive cells. (K) Z-score of respiration-related genes in CD4+ cells. RHC: right heart catheterization, WB: western blotting, IHC: immunohistochemistry. Values are the means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05.
The Intricacies of Inflammatory Pathways in Pulmonary hypertension
Scientists Discover That Combining IL-6 Inhibitors With Current Medications Is A Better Approach For Treating Pulmonary Hypertension
Il6 KO rats are resistant to PH in the SuHx rat model. (A) Experimental protocol for examining the effect of Il6 deletion on SuHx rats. (B and C) Assessment of the effect of Il6 deletion on the PH phenotype of SuHx rats in terms of RVSP (B) and Fulton’s index (C) (n = 8 in each group). (D) Representative images of the vascular remodeling of distal acinar arterioles in lung sections subjected to EVG staining. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (E) Medial wall thickness index of rats (normoxia WT: n = 6, normoxia Il6 KO: n = 5, SuHx WT: n = 6, SuHx Il6 KO: n = 5). (F) Pulmonary arterial occlusions were graded as open (no luminal occlusion; white), partial (<50% occlusion; blue), or closed (≥50% occlusion; red). Percentages of open, partial, and closed pulmonary arteries of outer diameter (OD) <100 μm in SuHx rats) (n = 4 in each group). (G) qRT-PCR analysis of Il6 mRNA expression in the lungs of WT rats after SuHx treatment. (H and I) Western blot analysis of STAT3 phosphorylation (Tyr705) and total STAT3 in lung homogenates from WT and Il6 KO rats 8 wk after normoxia or SuHx treatment (n = 8 in each group). (J) Representative immunofluorescence images of pulmonary arteries stained for pSTAT3 (red) and CD4 (green), and pSTAT3 (red) and Ahr (green) in the lung tissues of WT and Il6 KO rats 8 wk after SU5416 administration. Arrowheads indicate copositive cells. (K) Z-score of respiration-related genes in CD4+ cells. RHC: right heart catheterization, WB: western blotting, IHC: immunohistochemistry. Values are the means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05.
The Intricacies of Inflammatory Pathways in Pulmonary hypertension
In recent years, researchers have delved into the intricate interplay between inflammation and PH pathogenesis. Inflammatory processes, orchestrated by various cytokines and immune cells, contribute significantly to vascular remodeling and dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Among these cytokines, interleukin-6 (IL-6) has emerged as a key player in driving inflammatory responses and promoting disease progression.
IL-6: A Critical Player in Immune Signaling
IL-6 is a multifunctional cytokine with diverse roles in immune regulation, cell proliferation, and tissue repair. Its dysregulation has been implicated in various autoimmune diseases and inflammatory disorders. In the context of pulmonary hypertension, elevated levels of IL-6 have been observed in both animal models and human patients, suggest
ing its involvement in disease pathophysiology.
Japanese Scientists' Groundbreaking Research
A significant breakthrough in understanding IL-6's role in PH came from researchers at the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center (NCVC) Research Institute in Japan. Their pioneering study, covered in this
Medical News sheds light on IL-6's specific impact on pulmonary hypertension and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Unraveling IL-6 Signaling Pathways
The NCVC researchers utilized advanced genetic techniques and animal models to dissect IL-6 signaling pathways in the context of PH. Their findings revealed that IL-6 activates specific immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells, contributing to vascular remodeling and elevated pulmonary arterial pressure.
Insights from Mouse and Rat Models
Through meticulously designed experiments in mice and rats, the researchers demonstrated the efficacy of targeting IL-6 signaling in ameliorating pulmonary hypertension pathology. By deleting genes encoding IL-6 or its receptor components, they observed significant improvements in vascular function, reduced pulmonary pressures, and enhanced survival rates in animal models of pulmonary hypertension.
Combination Therapy: A Promising Approach
One of the most striking findings from the study was the synergistic effect of combining IL-6 inhibitors with existing pulmonary hypertension medications. By augmenting conventional treatments with IL-6 blockade, researchers observed enhanced therapeutic outcomes, including symptom relief and reduced lung and heart damage in experimental models.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
While the preclinical findings are promising, translating these discoveries into clinical practice requires further validation through human studies. Several clinical trials investigating IL-6 inhibitors in pulmonary hypertension patients have yielded mixed results, highlighting the need for a nuanced understanding of IL-6's role in different disease subtypes and patient populations.
Personalized Medicine in PH: A Paradigm Shift
The emergence of IL-6 as a critical mediator in pulmonary hypertension opens avenues for personalized treatment strategies. Tailoring interventions based on individual immune profiles, disease severity, and genetic factors could lead to more targeted and effective therapies. Moreover, the integration of biomarkers and advanced imaging techniques may enable early detection and monitoring of pulmonary hypertension progression.
Collaborative Efforts and Global Impact
The collaborative nature of scientific research is instrumental in driving progress in pulmonary hypertension management. International collaborations, such as those between Japanese scientists and global research institutions, facilitate knowledge exchange, data sharing, and the development of standardized treatment protocols.
Ethical Considerations and Patient-Centered Care
Amidst scientific advancements, it is crucial to prioritize ethical considerations and patient-centered care. Ensuring equitable access to emerging therapies, promoting transparency in research practices, and prioritizing patient well-being are paramount in the journey towards combating pulmonary hypertension and improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion: Towards a Brighter Future for PH Patients
The discovery of IL-6's intricate involvement in pulmonary hypertension pathogenesis heralds a new era in disease understanding and treatment innovation. Collaborative efforts, cutting-edge research, and a patient-centered approach are pivotal in translating scientific discoveries into tangible benefits for individuals battling pulmonary hypertension. With continued advancements in immunotherapy, personalized medicine, and multidisciplinary care, the outlook for pulmonary hypertension patients is increasingly optimistic, offering hope for a brighter and healthier future.
The study findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2315123121
For the latest
Medical News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
