Source : Thailand Medical News Dec 11, 2019 5 years, 4 months, 1 week, 2 days, 13 hours, 12 minutes ago
There are currently more than 180 clinical trials ongoing in various countries with regards to using stem cells in treating diabetes. One biotech company, Global Institute of Stem Cell Therapy and Research (GIOSTAR), a leader in regenerative technologies, has announced that they are in the process of approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to conduct type 2 diabetes clinical trials focused on development of stem cell-based treatment.
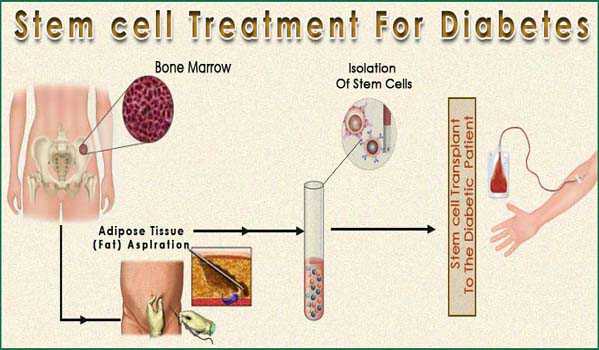
The new clinical trial to be led by GIOSTAR Chairman and Co-Founder Dr. Anand Srivastava, a team of scientists is further investigating a new potential approach to combat this disease, achieved through differentiation of
stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. The company had already previously tested on animal models with extremely positive results.
About one in 10 individuals suffers from
diabetes globally with nearly 1.4 million cases impacting individuals under the age of 20. Several factors have contributed to this
metabolic syndrome, including excessive consumption of high-calorie foods, an overly sedentary lifestyle, and other unhealthy habits. Given the staggering increase in the incidence of the disorder, the related cost of patient care has skyrocketed in recent years. A 2017 assessment by the American Association of
Diabetes estimated the figure to be roughly $327 billion for just America alone, which represents both direct medical costs and reduced productivity.
Dr Srivastava told
Thailand Medical News, "The conventional approach to this epidemic has primarily involved pharmaceutical products, which have several limitations. GIOSTAR's research into
stem cells may provide an alternative that addresses these concerns. In contrast to the adverse side effects seen with these drugs, for instance, post-procedure symptoms of
stem cell therapy are limited largely to mild fever, nausea, and headache. Furthermore, rather than simply ‘masking’ the symptoms of
diabetes,
stem cells have the potential to provide a lasting cure.”
About 150 past clinical trials listed on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Website have revealed several potential benefits of
stem cell implantation or infusion for the treatment of
diabetes. Clinical parameters such as Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), for instance, decreased considerably after
stem cell administration, as did the required amounts of insulin needed to manage blood glucose. Further, patients who received the treatments showed improved responsiveness to insulin. In most cases, patients continued to enjoy these benefits several months after follow up.
GIOSTAR studies focus on the therapeutic benefits of mesenchymal
stem cells (MSCs). Isolated from visceral fatty tissues of adults, MSCs are known to improve pancreatic function, prevent cell death, decrease systemic oxidative stress, and reduce insulin resistanc
e through the secretion of paracrine factors. Additionally, after exposure to interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, MSCs may become a source of anti-inflammatory cytokines which may generate new insulin-producing cells. Finally, intravenous infusion of
stem cells has been shown to regenerate beta cells of pancreatic islets and promote insulin sensitivity by decreasing systemic inflammation, the root cause of insulin resistance
Dr. Srivastava added, "
Stem cell therapy may offer a long-lasting therapeutic alternative for treating type 2
diabetes. However, additional research is needed, and we must remember that this is not a permanent cure yet. However, this groundbreaking study by pioneer in
stem cell research may potentially save millions of lives.”
