Study Finds ORF8 Protein Of SARS-CoV-2 Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-like Responses And Facilitates Virus Replication by Triggering Calnexin
SARS-CoV-2- ORF8 - Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-like Responses Mar 08, 2023 2 years, 9 months, 6 days, 18 hours, 52 minutes ago
The
SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus which is the viral pathogen responsible for the worldwide coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, contains a 30 kb positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome that encodes 29 proteins, including structural, non-structural, and accessory proteins.
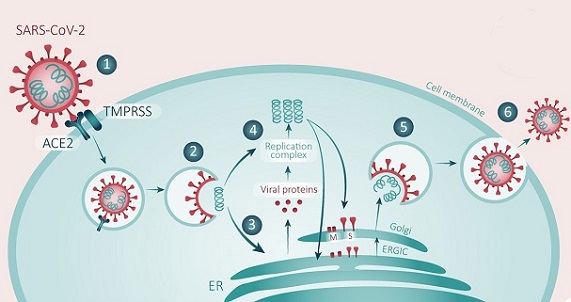
Similar to that of other coronaviruses (CoVs), the
SARS-CoV-2 genome is composed of 9 open reading frames (ORFs), including ORF1, spike, ORF3, envelope, membrane, ORF6, ORF7, ORF8, and nucleocapsid. ORF1 is directly translated by genomic positive RNA to form polyprotein 1a (pp1a) and pp1ab, which are post-translationally processed into individual nonstructural proteins (NSPs). The latter 8 ORFs encoding 4 structural proteins (spike, envelope, membrane, and nucleocapsid proteins), which are indispensable for viral capsid and nucleic acid packaging, and 4 accessory proteins, which are not commonly regarded to be independently critical for virus replication, are translated from a 3′-nested set of subgenomic mRNA (sgmRNA) species.
The novel SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein is not highly homologous with known proteins, including accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. ORF8 contains a 15-amino-acid signal peptide in the N terminus that localizes the mature protein to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Oligomannose-type glycosylation has been identified at the N78 site.
Although SARS-CoV-2 is basically regarded as a homolog of SARS-CoV, with their genomic structure and the majority of their genes being highly homologous, the ORF8 genes of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 are distinct.
With only 121 amino acids, the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein also shows little homology with other viral or host proteins and is regarded as a novel special virulence gene of SARS-CoV-2. The molecular function of ORF8 has not been clearly known until now.
This new study by researchers from Changchun Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun-China provides new insights into the molecular functions of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein.
The study used an unbiased approach to identify the molecular targets of ORF8 and to investigate its effects on host cells.
The study findings showed that ORF8 interacts with human Calnexin and HSPA5 via an immunoglobulin-like fold in a glycan-independent manner. The key ORF8-binding sites of Calnexin and HSPA5 are indicated on the globular domain and the core substrate-binding domain, respectively.
The research findings also demonstrated that ORF8 induces species-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-like responses in human cells exclusively via the IRE1 branch, including intensive HSPA5 and PDIA4 upregulation, with increases in other stress-responding effectors, including CHOP, EDEM, and DERL3.
Importantly, this clearly indicates that ORF8 is involved in modulating the host's response to ER stress, which is a critical component of the unfolded protein response (UPR).
Furthermore, the study showed that ORF8 overexpression facilitates SARS-CoV-2 replication.
The study findings correspond well with published results indicating the attenuation of vi
ral replication induced by genomic deletion of ORF8.
Considering that Calnexin universally coordinates the processing of newly synthesized viral glycoproteins by facilitating their folding and on the basis of the ORF8-Calnexin interaction revealed in the study, ORF8 is considered to induce stress-like responses and accelerate the proper folding of glycoproteins, probably by stimulating molecular chaperone upregulation (such as HSPA5 and PDIA4 identified here), which ultimately promotes the secretion of mature progeny virus.
The study team stresses that the detailed machinery of spike glycoprotein turnover mediated by the Calnexin-ORF8 interaction needs to be elucidated further.
ORF8-induced stress-like responses and virus replication are highly dependent on normal Calnexin expression. Therefore, Calnexin behaves as a molecular switch to control host functions induced by ORF8.
Interestingly, the study also explained the in vivo virulence discrepancy of ORF8 between SARS-CoV-2-infected patients and mice. Previous studies on mouse infection models have indicated that ORF8 is hardly considered to enhance virulence, while human clinical data have showed otherwise!
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Virology.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jvi.00011-23
An important note is that this Calnexin-ORF8 interaction could possibly lead to neuronal injury and also trigger neurodegenerative diseases! Urgent research is warranted on this area.
For the latest
SARS-CoV-2 Research, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-exhibits-complement-inhibitory-properties-and-damages-innate-immunity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-yale-study-shows-that-omicron-subvariants-are-evolving-further-through-mutations-on-orf8-proteins-to-escape-from-mhc-i-recognition
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-french-scientists-uncover-how-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-causes-dysregulation-of-gene-expression-in-infected-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-pennsylvania-study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-uses-histone-mimicry-to-disrupt-host-epigenetic-regulation-for-disarming-host-immune-responses
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mayo-clinic-researchers-discover-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-is-the-key-factor-that-is-causing-covid-19-disease-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-encoded-protein-contains-a-histone-mimic-that-disrupts-human-host-cell-epigenetic-regulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-university-of-california-scientist-identify-rapidly-evolving-immune-evasion-protein-sars-cov-2-orf8-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-briefs-anti-androgens-and-covid-19,-possible-cytotoxic-t-cell-therapy-for-covid-19,-immune-evasion-by-evolving-orf8-protein-in-sars-
