Study Finds That COVID-19 Induces Oxidative Stress That Contributes To Neuronal Dysfunction!
COVID-19 News - Oxidative Stress - Neuronal Dysfunction Jun 28, 2023 1 year, 9 months, 2 weeks, 5 days, 17 hours, 52 minutes ago
Phytochemicals Like Apigenin, Catechin, Hesperidin, Kaempferol, Luteolin, Myricetin, Naringenin And Quercetin Can Help
COVID-19 News: A new study conducted jointly by researchers from Auburn University (USA), Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University (China), and the University of Washington (USA) has shed light on a significant discovery: COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, induces oxidative stress that contributes to neuronal dysfunction. The implications of this finding are profound, as it provides a potential explanation for the thrombosis and other neurological complications observed in COVID-19 patients.
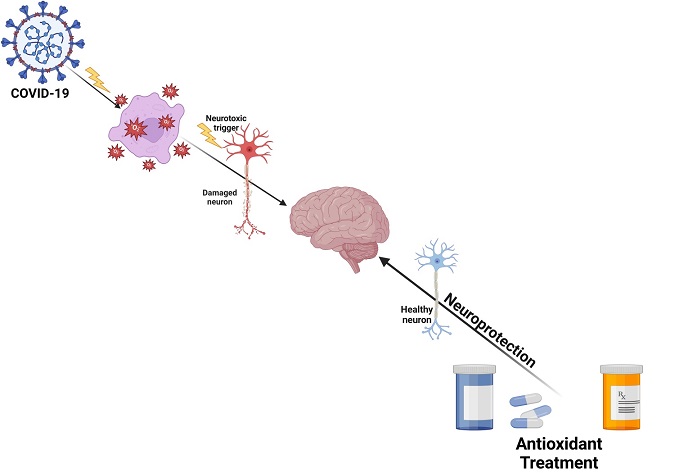 COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and oxidative stress plays a role in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders linked to COVID-19.Increased oxidative stress could well have caused the thrombosis and other neural dysfunction seen in COVID-19.
The Role of Oxidative Stress
COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and oxidative stress plays a role in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders linked to COVID-19.Increased oxidative stress could well have caused the thrombosis and other neural dysfunction seen in COVID-19.
The Role of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between antioxidants and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) in the body. While RONS have essential functions, excessive production can lead to cellular and tissue damage. Commonly generated RONS include superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, hypothiocyanite, and hypochlorous acid. Both endogenous factors, such as mitochondrial activity and enzymatic reactions, and exogenous factors, including environmental pollutants, certain foods, and heavy metals, contribute to RONS production.
Oxidative Stress and COVID-19
The study reveals that SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers oxidative stress through various pathways. Mitochondria, xanthine oxidoreductase, NADPH oxidases, peroxidases, and nitric oxide synthases are major contributors to RONS generation. This oxidative stress is implicated in the development and progression of age-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, kidney disease, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cancer.
COVID-19 and the Cytokine Storm
One of the severe manifestations of COVID-19 is the cytokine storm, characterized by an excessive immune response. The study identifies toll-like receptors (TLRs) as key players in sensing the SARS-CoV-2 virus. TLR4, TLR7, and TLR8 recognize specific viral components and initiate signaling cascades that result in the dysregulated production of proinflammatory cytokines. Notably, elevated levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been observed in COVID-19 patients and are associated with the inhibition of immune cells and increased inflammation as covered in various studies and
COVID-19 News reports.
Linking Oxidative Stress and Signal Transduction Pathways
The SARS-CoV-2 virus exploits the ACE2 receptor and the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) for cellular entry. Activation of toll-like receptors, such as TLR4, TLR1/2, TLR2/6, TLR7/8, and TLR3, triggers the NF-κB pathway, leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines. The excessive ac
tivation of NF-κB and interferon pathways contributes to the cytokine storm observed in severe COVID-19 cases.
Implications and Future Directions
Understanding the role of oxidative stress in COVID-19-induced neuronal dysfunction opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Targeting oxidative stress pathways and mitigating the cytokine storm could potentially alleviate neurological complications associated with the disease. However, further research is essential to unravel the precise mechanisms and clinical effects of oxidative stress in COVID-19. This knowledge will pave the way for the development of effective treatments and preventive strategies to minimize the neurological impact of COVID-19.
Conclusion
The study's findings highlight the detrimental impact of oxidative stress in COVID-19, specifically in relation to neuronal dysfunction. The induction of oxidative stress by the SARS-CoV-2 virus contributes to the development of thrombosis and other neurological complications observed in COVID-19 patients. This discovery not only deepens our understanding of the disease but also provides potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Efforts to combat COVID-19 should not only focus on controlling viral replication and the immune response but also consider the management of oxidative stress. Strategies aimed at reducing oxidative stress and restoring the balance between antioxidants and RONS could help mitigate the neurological impact of the disease. This may involve the use of antioxidant compounds, such as vitamins C and E, N-acetylcysteine, melatonin, and natural polyphenols, which have shown promise in reducing oxidative stress in other conditions.
Additionally, targeting the signaling pathways involved in oxidative stress, such as toll-like receptors and NF-κB, could be a viable approach to modulating the inflammatory response and reducing neuronal dysfunction. Therapeutic agents that inhibit these pathways or regulate their activity may hold potential for preventing or ameliorating the neurological complications associated with COVID-19.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.
https://www.sciengine.com/ABBS/doi/10.3724/abbs.2023085;JSESSIONID=e2c12f56-933e-4467-8db8-875182188245
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
