Study Involving 29 Wildtype SARS-CoV-2 Proteins, 15 Variant S Proteins And Various Human Cells Identified 745,163 Viral & Host Protein-Protein Interactions!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Apr 24, 2024 11 months, 2 weeks, 2 days, 18 hours, 59 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, understanding the intricate mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 interactions within human cells becomes increasingly crucial. Recent studies conducted by Westlake University, Fudan University, and Shandong University that is covered in this
COVID-19 News report have delved deep into the viral-host protein-protein interactions, shedding light on the functional evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variants across various susceptible human organs.
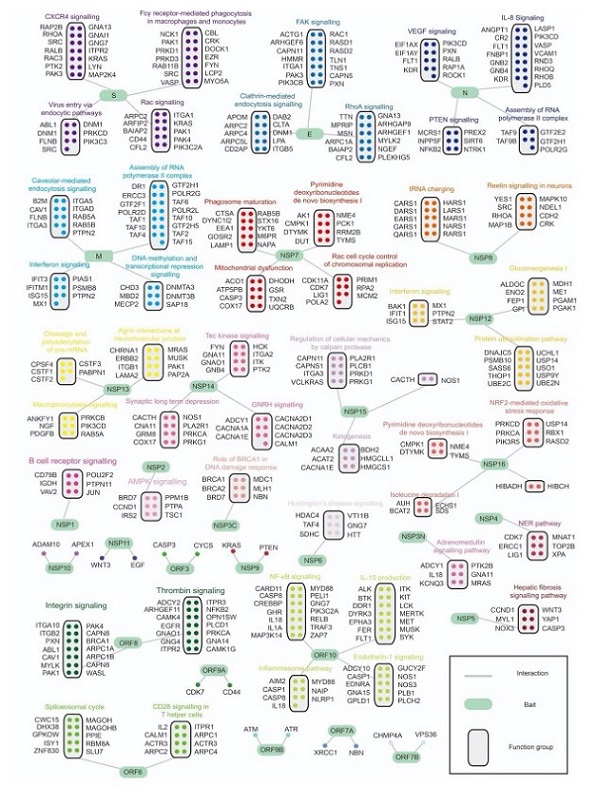 Spectrum of protein interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and humans.
A protein‒protein interaction network between 29 SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human proteins is shown for host‒virus interactions. The green ovals indicate viral proteins, iridescent circles indicate the HCIPs identified from SFB tandem affinity purification experiments, and gray rounded rectangles indicate groups of proteins belonging to the same protein complex or from the same pathway. Iridescent text indicates the functional signaling pathways enriched.
The Scope of the Study
Spectrum of protein interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and humans.
A protein‒protein interaction network between 29 SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human proteins is shown for host‒virus interactions. The green ovals indicate viral proteins, iridescent circles indicate the HCIPs identified from SFB tandem affinity purification experiments, and gray rounded rectangles indicate groups of proteins belonging to the same protein complex or from the same pathway. Iridescent text indicates the functional signaling pathways enriched.
The Scope of the Study
The study involved a meticulous examination of 29 wildtype SARS-CoV-2 proteins and 15 SARS-CoV-2 variant S proteins across different human cell types, including lung, bronchus, neuron, liver, and kidney-derived cells. The primary objective was to identify viral-host protein interactions and establish phylointeractomics of SARS-CoV-2 variants across susceptible human organs.
Significance of the Research
The significance of this research lies in its potential to unravel critical insights into viral infection, replication, and immune evasion mechanisms. By identifying specific host proteins involved in these processes, the study paves the way for developing targeted therapeutic strategies to combat COVID-19 and its associated complications.
Current State of COVID-19 Evolution
Over the past four years since its emergence, SARS-CoV-2 has undergone significant mutations, leading to the emergence of various variants. These mutations not only pose challenges for global epidemic prevention but also complicate interactions with host proteins, impacting vaccine efficacy and antibody neutralization.
Cellular Context and Viral Infection
SARS-CoV-2 primarily targets tissues in the respiratory, nervous, digestive, and urinary systems. However, its ability to infect other organs like the heart, liver, brain, and kidneys underscores the necessity of studying viral-host interactions across diverse cellular contexts.
Methodology and Data Collection
The study employed TAP-MS (tandem affinity purification coupled with mass spectrometry) to establish viral-host interaction networks for 29 SARS-CoV-2 proteins and 15 variant S proteins across different human cell lines.
This comprehensive approach expanded the understanding of binary interactions and identified 745,163 viral-host protein-protein interactions.
Key Findings
The research identified several critical findings:
-Host Cell Receptors: Confirmation of host cell receptors like ACE2, AXL, and TMEM106B, which play pivotal roles in viral attachment and entry.
-Interaction Networks: Establishment of tissue context-dependent interaction networks, highlighting distinct patterns of viral protein interactions in various organs.
-Functional Clustering: Clustering of viral proteins based on their interactions with host proteins involved in viral assembly, replication, and immune modulation.
Phylointeractomics: Phylogenetic analysis revealed how mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants influence viral tropism and disease progression.
-Drug Targets: Identification of potential drug targets among host proteins involved in viral lifecycle processes.
Insights into Cellular Pathways
The study uncovered enrichments in pathways related to viral infection, inflammation, immune response, thrombosis, blood coagulation, phagocytosis, lactate metabolism, reactive oxygen species, vesicle transport, ferroptosis, DNA repair, and more. These pathways provide crucial insights into how SARS-CoV-2 manipulates host cellular machinery for its benefit and contributes to COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Implications for Treatment Strategies
The identification of tissue-specific viral-host interaction networks and key host factors opens avenues for developing targeted therapies. By disrupting crucial interactions involved in viral replication and immune evasion, potential drugs could mitigate COVID-19 severity and reduce associated complications.
Understanding Viral Evolution and Clinical Implications
Phylointeractomics analysis revealed how mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants alter viral-host interactions, influencing viral tropism and clinical manifestations. For instance, variants like Beta, Delta, and Omicron showed distinct interaction patterns, correlating with their transmission dynamics and disease severity.
Validation and Future Prospects
The study's findings were validated through experimental assays and computational modeling, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the identified interactions. Future research directions may include integrating omics data, single-cell analyses, and correlation network studies to further elucidate viral tropism and facilitate drug screening and repurposing efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comprehensive analysis of SARS-CoV-2 interactions across human cells provides a detailed roadmap of viral-host protein-protein interactions, cellular pathways involved in infection and replication, and insights into variant-specific behavior. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of COVID-19 pathogenesis but also offers promising avenues for developing effective therapeutic interventions tailored to different organs and viral variants.
The study findings were published on a preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed for publication into the Nature Journals.
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4254091/v1
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
