Taiwanese Study Discovers That SARS-CoV-2 Gains Entry Into Cells With Low ACE2 Expression Via A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase Domain 9 (ADAM9)
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Sep 17, 2023 1 year, 7 months, 3 days, 16 hours, 54 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has left an indelible mark on global public health and the economy. The emergence of various variants of concern that possess increased transmissibility and enhanced immune evasiveness with some, according to studies and
COVID-19 News reports possessing changes in pathogenesis and tropism…have complicated the outbreak possibly ending. To combat the virus effectively, a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind SARS-CoV-2's entry into host cells is crucial.
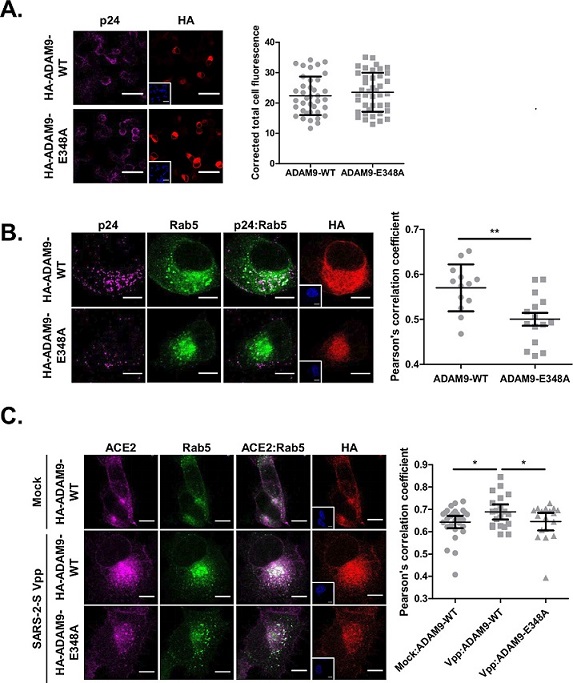 The catalytic activity of ADAM9 plays a role in endocytosis. (A) Spike Vpps were bound to the plasmid-transfected H1650-ACE2 cells for 2 h at 4°C and then fixed for immunofluorescence staining against anti-HIV p24 antibody (magenta), anti-HA antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 µM. (B) H1650-ACE2 cells were transfected with equal amounts of eGFP-Rab5 and either HA-tagged ADAM9-WT or ADAM9-E348A. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 Vpp for 1 h at 37°C and subsequently fixed for immunofluorescence staining against anti-HIV p24 antibody (magenta), anti-HA antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). (C) The transfection and infection were done the same way as in (B). (B and C) Co-localized signals are presented as white points. (A–C) Co-localization and corrected total cell fluorescence were analyzed using ImageJ. Scale bar = 25 µM. Results are presented as the mean ± SD.
The catalytic activity of ADAM9 plays a role in endocytosis. (A) Spike Vpps were bound to the plasmid-transfected H1650-ACE2 cells for 2 h at 4°C and then fixed for immunofluorescence staining against anti-HIV p24 antibody (magenta), anti-HA antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 µM. (B) H1650-ACE2 cells were transfected with equal amounts of eGFP-Rab5 and either HA-tagged ADAM9-WT or ADAM9-E348A. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 Vpp for 1 h at 37°C and subsequently fixed for immunofluorescence staining against anti-HIV p24 antibody (magenta), anti-HA antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). (C) The transfection and infection were done the same way as in (B). (B and C) Co-localized signals are presented as white points. (A–C) Co-localization and corrected total cell fluorescence were analyzed using ImageJ. Scale bar = 25 µM. Results are presented as the mean ± SD.
Recent research conducted by scientists from China Medical University in Taichung and Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan, has shed light on a pivotal host protein, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 9 (ADAM9), which facilitates the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into cells with low ACE2 expression levels. This discovery opens up new avenues for the development of antiviral strategies against COVID-19.
SARS-CoV-2 Entry and the Role of ACE2
SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a receptor found on the surface of target cells. The viral Spike protein, consisting of the S1 receptor-binding subunit and the S2 membrane-fusion subunit, engages with ACE2 to initiate the infection process. After binding, SARS-CoV-2 can enter cells through either the cell surface or endocytic pathways. In the cell surface pathway, viral entry is initiated when the Spike protein is cleaved by enzymes like furin and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2), leading to the fusion of viral and cellular membranes and the release of viral RNA into the cell's cytoplasm. In the endocytic pathway, the virus is internalized into the cytoplasm through endocytosis, followed by further membrane fusion and RNA release.
Challenges with ACE2 Expression
While ACE2 is the primary receptor for SARS-CoV-2, recent studies have highlighted discrepancies in ACE2 expression patterns compared to the virus's tissue tropism. Notably, the highest levels of ACE2 expression are found in tissues like the small intestine, testis, kidney, heart muscle, and colo
n. In contrast, ACE2 expression in the lung, a major target organ for SARS-CoV-2 infection, is relatively low and primarily limited to type II alveolar cells. This disparity suggests that additional host factors may be involved in facilitating viral entry into certain cell types, especially those with low ACE2 expression.
The Discovery of ADAM9 as a Host Factor
To uncover potential host factors aiding SARS-CoV-2 entry, researchers conducted an arrayed shRNA screen in H1650 and HEK293T cells. Through this screening process, they identified ADAM9, a member of the ADAM family of transmembrane proteins, as a critical host factor for SARS-CoV-2 entry. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that silencing ADAM9 reduced virus entry, while its overexpression enhanced infection, highlighting the essential role of ADAM9 in the viral entry process.
ADAM9's Role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
ADAM9's involvement in SARS-CoV-2 infection extends beyond its facilitation of virus entry. The study revealed that ADAM9 is implicated in the binding and endocytosis stages of SARS-CoV-2 entry. Through immunoprecipitation experiments, researchers demonstrated that ADAM9 directly binds to the S1 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. Furthermore, ADAM9 can interact with ACE2, and co-expression of both proteins significantly enhances virus infection. Importantly, the enzymatic activity of ADAM9 was found to facilitate virus entry, indicating its multifaceted role in the infection process.
ADAM9 as a Potential Therapeutic Target
The identification of ADAM9 as a crucial co-factor for SARS-CoV-2 entry offers promising prospects for the development of antiviral strategies against COVID-19.
Given the ubiquity of ADAM9 expression in human tissues and its upregulation in various cancers, understanding its role in viral infection becomes even more significant. Interestingly, recent multi-omics analyses of COVID-19 patients without comorbidities identified ADAM9 as a key driver of disease severity. Higher ADAM9 RNA expression levels were detected in the serum of critically ill COVID-19 patients, suggesting a potential link between ADAM9 expression and disease severity.
ADAM9's Potential Implications for COVID-19 Severity
Cancer patients, who often exhibit elevated ADAM9 expression, have been shown to have a higher risk of severe COVID-19 and increased mortality rates. This observation raises intriguing questions about the relationship between ADAM9 expression and COVID-19 severity, which warrants further investigation. While the study demonstrated that ADAM9 knockdown significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection, it's worth noting that the effect was modest. Future research may explore the impact of ADAM9 knockout, potentially revealing even more significant effects on viral entry.
Conclusion
The research conducted by scientists in Taiwan has uncovered a pivotal host factor, ADAM9, which plays a crucial role in facilitating SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells with low ACE2 expression. This discovery offers valuable insights into the mechanisms behind COVID-19 infection and opens new doors for the development of antiviral strategies.
As the pandemic continues to evolve with the emergence of new variants, understanding the complex interplay between host factors and the virus is essential for devising effective countermeasures. ADAM9's multifaceted involvement in viral entry and its potential links to disease severity highlight its significance as a potential therapeutic target in the ongoing battle against COVID-19. Further research in this field promises to deepen our understanding of virus-host interactions and pave the way for innovative approaches to combat this global health crisis.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Microbiology Spectrum.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.03854-22
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
