Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 20, 2024 9 months, 3 weeks, 21 hours, 33 minutes ago
Anti-Aging News: As we age, our skin naturally begins to show signs of wear and tear. Factors like UV exposure and environmental pollutants can accelerate this process, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and age spots. But what if there was a way to slow down these effects? Recent research by scientists from Switzerland that is covered in this
Anti-Aging News report, has shed light on a promising pathway that could revolutionize anti-aging skincare.
 Anti-Aging Power of Plasmin Inhibitors
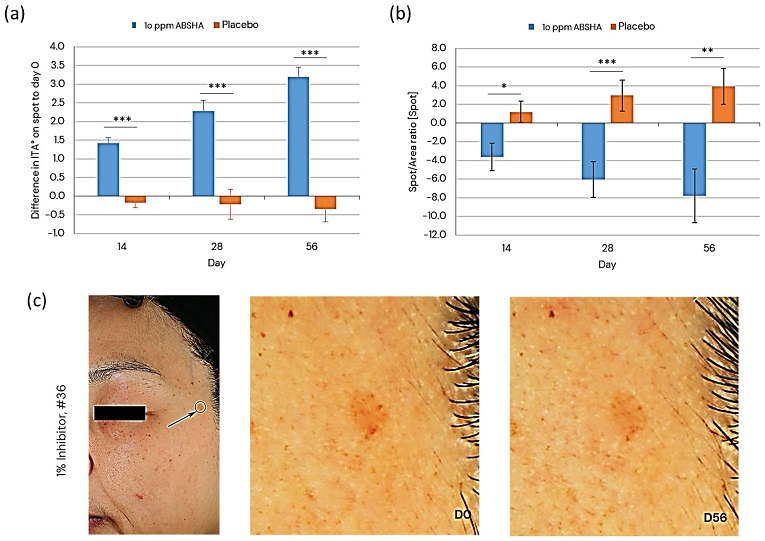
Evolution of (a) age spot color and (b) age spot size. Images in (c) show the location of a particular age spot and its color evolution from the baseline (D0) to the end of the study (D56) when treated with the 10 ppm ABSHA formulation. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by Mann–Whitney U test.
Plasmin: The Enzyme Behind Skin Aging
Anti-Aging Power of Plasmin Inhibitors
Evolution of (a) age spot color and (b) age spot size. Images in (c) show the location of a particular age spot and its color evolution from the baseline (D0) to the end of the study (D56) when treated with the 10 ppm ABSHA formulation. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by Mann–Whitney U test.
Plasmin: The Enzyme Behind Skin Aging
Plasmin is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in inflammation and skin barrier integrity. When our skin is exposed to UV rays, plasmin levels increase, leading to higher transepidermal water loss (TEWL). This process not only causes inflammation but also activates other harmful enzymes that degrade essential skin proteins like collagen and elastin.
The Power of Plasmin Inhibitors
Researchers at DSM-Firmenich and Curio Biotech in Switzerland have discovered that inhibiting plasmin can significantly reduce these negative effects. They developed a dual inhibitor called Amidinobenzyl Benzylsulfonyl D-Seryl Homophenylalaninamide Acetate (ABSHA), which targets both plasmin and its activator urokinase (uPA). This inhibitor has shown remarkable results in both laboratory and human studies.
Laboratory Findings: A Promising Start
In the lab, scientists conducted various tests to observe the effects of ABSHA on skin cells. They found that ABSHA significantly reduced the expression of harmful enzymes like MMP-9, which are responsible for degrading collagen IV, a key structural protein in the skin. This inhibition helps maintain the integrity of the skin's extracellular matrix, keeping it firm and elastic.
Real-World Results: A Two-Month Study
To validate their findings, researchers conducted a two-month study involving female volunteers in Guangzhou, China. Participants applied a skincare formulation containing 10 parts per million (ppm) of ABSHA twice daily. The results were astounding.
Improved Skin Hydration
One of the key measurements was TEWL, which indicates how well the skin retains moisture. The group using the ABSHA formulation saw a significant reduction in TEWL, indicating better skin barrier function and hydration.
Increased Collagen Density and Elasticity
Using ultrasound, researchers measured an increase in dermal density, suggesting that the skin had more co
llagen and elastin. This was further supported by improved elasticity measurements, which showed that the skin became more resilient and less prone to wrinkles.
Reduction in Wrinkles and Age Spots
Participants also experienced a noticeable reduction in wrinkle volume, particularly on the forehead and around the eyes. Additionally, age spots became lighter and smaller, enhancing the overall appearance of the skin.
Self-Assessment: Visible Improvements
At the end of the study, participants filled out a self-assessment questionnaire. The majority reported significant improvements in their skin's appearance, including reduced wrinkles and age spots. This subjective feedback confirmed the objective measurements, showcasing the potential of ABSHA as a powerful anti-aging ingredient.
Conclusion: A New Era in Skincare
The study firmly establishes plasmin as a key player in skin aging. By inhibiting this enzyme, ABSHA not only reduces inflammation and prevents collagen degradation but also promotes overall skin health. This dual-action approach targets both "plasminflammation" and "plasminaging," offering a comprehensive solution to combat the signs of aging.
As researchers continue to explore the full potential of plasmin inhibitors, ABSHA stands out as a groundbreaking discovery in the field of anti-aging skincare. For those looking to maintain youthful, radiant skin, products containing this innovative ingredient could be a game-changer.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Cosmetics.
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/11/3/103
For the latest
Anti-Aging News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/korean-murine-study-shows-that-thymus-quinquecostatus-celakovski-can-possibly-enhance-testosterone-levels-in-aging-men
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/anti-aging-news-study-by-massachusetts-general-hospital-shows-that-cocoa-extract-supplements-help-in-promoting-cognitive-prowess-in-the-elderly
