Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 29, 2024 10 months, 4 weeks, 17 hours, 55 minutes ago
Medical News: Acrolein, a highly reactive aldehyde, is found abundantly in polluted air and cigarette smoke, posing a significant health risk. This compound, also known as 2-propenal, is not only an environmental contaminant but is also produced endogenously within the human body. Its high reactivity towards amino acids' thiol and amino groups can lead to significant cellular damage. This
Medical News report explores how acrolein affects erythrocytes (red blood cells), focusing on its impact on cell membrane and cytosol proteins.
 The Hidden Danger in Our Air and Cigarettes: Acrolein's Impact on Erythrocytes
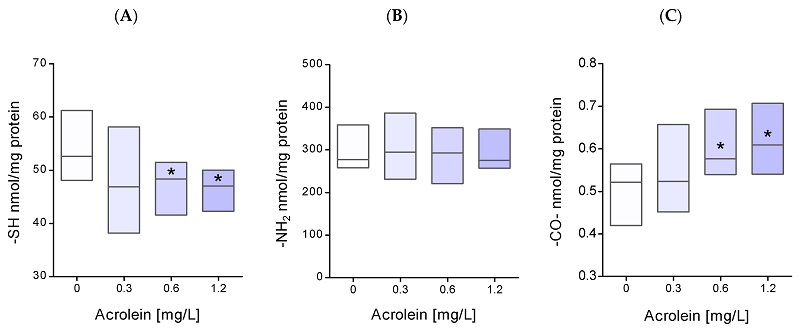
The level of (A) thiol, (B) amino, and (C) carbonyl groups in erythrocyte plasma membrane proteins after incubation of whole erythrocytes with acrolein. Data were presented as mean with a box plot of minimum and maximum values, n = 9, * p < 0.05—ACR (0.6 mg/L) and ACR (1.2 mg/L) versus control.
What is Acrolein?
The Hidden Danger in Our Air and Cigarettes: Acrolein's Impact on Erythrocytes
The level of (A) thiol, (B) amino, and (C) carbonyl groups in erythrocyte plasma membrane proteins after incubation of whole erythrocytes with acrolein. Data were presented as mean with a box plot of minimum and maximum values, n = 9, * p < 0.05—ACR (0.6 mg/L) and ACR (1.2 mg/L) versus control.
What is Acrolein?
Acrolein is a toxic chemical commonly found in cigarette smoke and polluted air. It is also produced within the body during the breakdown of certain fats and the metabolism of amino acids. This compound is known to induce and accelerate various diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and certain cancers. The high reactivity of acrolein with cellular proteins makes it particularly harmful.
Mechanism of Acrolein's Damage
Acrolein's interaction with cysteine thiol groups, which are highly reactive, leads to the formation of acrolein-cysteine adducts through a process known as the Michael addition reaction. Although these adducts reduce acrolein's cytotoxicity, they remain harmful to cells. Studies have shown that both acrolein and its conjugates with cysteine induce oxidative stress and apoptosis (programmed cell death) in various cell types.
Acrolein and Oxidative Stress
One of the critical pathways through which acrolein exerts its harmful effects is by inducing oxidative stress. This compound can cause oxidative damage to cell membranes, DNA, and mitochondria. The increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells exposed to acrolein lead to a reduction in intracellular antioxidants like glutathione. This imbalance can disrupt cellular functions and contribute to the progression of various diseases.
The Study: Acrolein's Impact on Erythrocytes
Researchers from the University of Lodz conducted a study to explore how acrolein affects erythrocytes. They hypothesized that acrolein might contribute to protein damage in these cells, disrupting the cell membrane structure. The study involved incubating erythrocytes with different concentrations of acrolein and analyzing changes in cell membrane fluidity, membrane cytoskeleton, and osmotic fragility.
Key Findings
-Changes in Membrane Fluidity
The researchers found that acrolein exposure led to significant changes in the fluidity of erythrocyte membranes. Using specific spin labels to measure membrane fluidity, they observed no changes in the lipid fluidity of the outer monolayer. However, significant differences were noted at deeper levels of the membrane, indicating that acrolein affects the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer.
-Protein Modifications
The study also revealed significant changes in the conformational state of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Acrolein exposure caused a notable increase in the mobility of membrane cytoskeletal proteins, particularly in the spectrin-actin complex. These changes likely contribute to the increased osmotic sensitivity of erythrocytes treated with acrolein.
-Reduced Antioxidant Potential
The non-enzymatic antioxidant potential of erythrocytes was significantly reduced following acrolein exposure. This reduction is attributed to the high reactivity of acrolein with thiol groups and the resulting oxidative stress. The decrease in antioxidant potential suggests that acrolein disrupts the balance of oxidative and antioxidative processes within cells.
-Osmotic Fragility
Erythrocytes exposed to higher concentrations of acrolein showed increased sensitivity to hemolysis (cell rupture) in response to osmotic stress. This heightened fragility is likely due to the stiffening of cell membranes and changes in membrane protein structure induced by acrolein.
Implications for Health
The findings of this study highlight the harmful effects of acrolein on erythrocytes, which could have broader implications for human health. The disruption of erythrocyte function can lead to impaired oxygen transport and increased susceptibility to various diseases. The induction of oxidative stress and protein damage by acrolein underscores the importance of minimizing exposure to this toxic compound.
Conclusion
Acrolein, a common pollutant found in cigarette smoke and polluted air, poses a significant threat to cellular health. Its high reactivity towards cellular proteins leads to oxidative stress, membrane stiffening, and increased cell fragility. This study provides crucial insights into the mechanisms by which acrolein damages erythrocytes, emphasizing the need for measures to reduce exposure to this harmful compound. By understanding the detrimental effects of acrolein, we can better appreciate the importance of air quality and smoking cessation efforts in protecting our health.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Molecules.
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/29/11/2519
For the latest on Air Pollutants, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/thailand-medical-experts-warn-air-pollution-crisis-in-chiangmai-is-causing-alarming-rise-in-lung-fibrosis-lung-cancer-and-deaths
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/u-s-study-shows-that-exposure-to-air-pollutants-can-exacerbate-the-effects-of-a-covid-19-infection
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/brain-health-researchers-from-university-of-california-claim-that-traffic-related-air-pollution-affects-early-brain-development
