Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Dec 07, 2024 4 months, 6 days, 3 hours, 44 minutes ago
Medical News: Researchers from the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and University of Tartu in Estonia have unveiled pivotal insights into how SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, manipulates human cellular mechanisms to replicate efficiently. The study provides a deep dive into the interaction between the virus's nucleocapsid (N) protein and a host protein called G3BP (Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein). This groundbreaking research could open doors to new antiviral therapies and strategies for vaccine development.
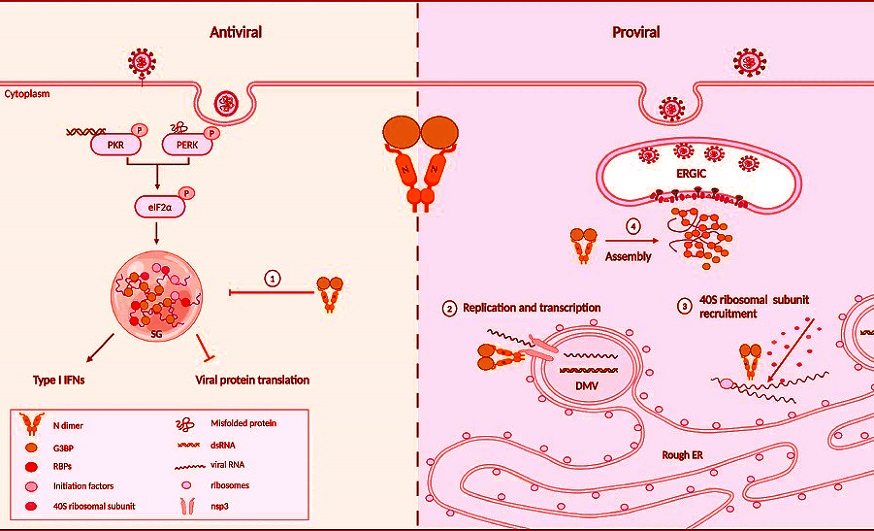 The antiviral and proviral roles of G3BP in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells.
SARS-CoV-2 infection activated PKR/PERK-eIF2α serves as a protective mechanism in host cells, leading to the G3BP dependent SGs assembly. However, SARS-CoV-2 N protein hijacks G3BP, contributing to the enhancement of SARS-CoV-2 replication across multiple stages of the replication cycle: (1) G3BP-N interaction mediates the disassembly of SGs. (2) Early in infection, the N protein recruits G3BP to nsp3 at the RTC, potentially aiding in viral RNA synthesis and transcription; (3) The G3BP-N complex recruits 40S ribosomal subunits to viral factories for efficient viral protein translation; (4) G3BP promote the LLPS of N, facilitating SARS-CoV-2 virus assembly.
The Critical Role of G3BP in Viral Replication
The antiviral and proviral roles of G3BP in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells.
SARS-CoV-2 infection activated PKR/PERK-eIF2α serves as a protective mechanism in host cells, leading to the G3BP dependent SGs assembly. However, SARS-CoV-2 N protein hijacks G3BP, contributing to the enhancement of SARS-CoV-2 replication across multiple stages of the replication cycle: (1) G3BP-N interaction mediates the disassembly of SGs. (2) Early in infection, the N protein recruits G3BP to nsp3 at the RTC, potentially aiding in viral RNA synthesis and transcription; (3) The G3BP-N complex recruits 40S ribosomal subunits to viral factories for efficient viral protein translation; (4) G3BP promote the LLPS of N, facilitating SARS-CoV-2 virus assembly.
The Critical Role of G3BP in Viral Replication
G3BP is a multifunctional RNA-binding protein central to the formation of stress granules (SGs). These granules act as part of a cell's defense mechanism against stress, including viral infections. Many viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, target G3BP to evade host defenses and enhance their replication.
This study revealed that the SARS-CoV-2 N protein binds to G3BP with high affinity, inhibiting the formation of stress granules. This action not only helps the virus escape host antiviral mechanisms but also repurposes G3BP to aid the virus in its replication process. The research focused on understanding the importance of this interaction, particularly how the N protein uses G3BP to increase viral RNA translation near double-membrane vesicles (DMVs). These vesicles are specialized structures where viral RNA synthesis occurs.
What Happens Without G3BP Interaction
To investigate further, researchers developed a mutant version of SARS-CoV-2, termed RATA, which lacks the ability to bind G3BP. The results were striking. Without this interaction, the RATA mutant virus triggered a robust and prolonged stress granule response in infected cells. Its replication was significantly reduced across various cell types, and its ability to cause disease was notably weakened in mouse models.
This
Medical News report outlines how these findings highlight the central role of the G3BP-N interaction in ensuring efficient viral replication and severe pathogenesis. By disrupting this interaction, the researchers effectively weakened the virus’s ability to propagate and cause dis
ease.
Localized Translation of Viral mRNAs: A Key Insight
The study uncovered a critical mechanism where G3BP, once hijacked by the viral N protein, is recruited to DMVs early in the infection process. DMVs are sites where viral RNA is synthesized, and the presence of G3BP at these locations facilitates the localized translation of viral mRNAs. This ensures the production of viral proteins essential for the virus's replication cycle.
Using advanced imaging techniques, researchers observed that in the absence of G3BP (as with the RATA mutant), the translation of viral mRNAs near DMVs was significantly impaired. As a result, viral protein production dropped, leading to reduced viral replication. This impairment underscores the importance of the G3BP-N interaction in sustaining SARS-CoV-2’s life cycle.
Impact on Mouse Models: Reduced Pathogenicity
The study extended its analysis to in vivo models. Using K18-hACE2 mice, a model for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, researchers compared the effects of wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the RATA mutant. Mice infected with the wild-type virus experienced significant weight loss and severe lung damage, while those infected with the RATA mutant showed no such symptoms.
Additionally, mice initially infected with the RATA mutant were later exposed to a high dose of the wild-type virus. Remarkably, these mice exhibited strong immunity, showing no signs of weight loss or severe lung pathology. This finding indicates that the RATA mutant not only causes reduced disease but also triggers robust immune protection against subsequent infections.
Broader Implications for Vaccine Development
The attenuation of the RATA mutant virus presents an exciting opportunity for vaccine research. By engineering a live-attenuated vaccine that disrupts the G3BP-N interaction, it may be possible to elicit strong immune responses without causing severe disease. Such a vaccine could provide broad protection against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants while ensuring safety for recipients.
The ability of the RATA mutant to induce protective immunity without causing disease makes it a strong candidate for further research as a live-attenuated vaccine. This approach could potentially revolutionize vaccine strategies, not only for SARS-CoV-2 but also for other viruses that exploit similar host-pathogen interactions.
Detailed Conclusions and Future Directions
This comprehensive study sheds light on the dual role of G3BP in SARS-CoV-2 infection. On one hand, G3BP is a key player in the host's antiviral stress response through its involvement in stress granules. On the other hand, SARS-CoV-2 cleverly hijacks this protein to enhance its replication efficiency. By binding to the viral N protein, G3BP is redirected from its antiviral role to a proviral function, aiding in the production of viral proteins near DMVs.
The findings have several important implications. First, they provide a deeper understanding of the molecular interactions that drive SARS-CoV-2 replication. Second, they identify the G3BP-N interaction as a potential therapeutic target. Drugs designed to disrupt this interaction could hinder the virus’s ability to replicate, providing a novel antiviral strategy.
Finally, the study emphasizes the feasibility of using engineered mutants like RATA as a basis for live-attenuated vaccines. By targeting specific host-virus interactions, such vaccines could offer robust protection while minimizing risks.
Future research should focus on further exploring the therapeutic potential of targeting the G3BP-N interaction. Additionally, the development of live-attenuated vaccines based on similar principles could benefit from continued study of the RATA mutant’s behavior in different models and its efficacy against various viral strains.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Nature Communications.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1038/s41467-024-54996-3
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-french-study-shows-that-host-proteins-g3bp-plays-a-key-proviral-role-in-sars-cov-2-viral-assembly
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-scientists-discover-blocking-protein-interactions-between-human-g3bp1-2-proteins-and-sars-cov-2-xfg-peptide-motif-inhibits-infection
