TNF and IFN-Gamma Co-Signaling in COVID-19 Patients Reveals New Insights into Disease Progression
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 29, 2025 2 months, 2 weeks, 1 day, 8 hours, 6 minutes ago
Medical News: The global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 has brought forth a multitude of challenges, not only in managing the virus but also in understanding the factors influencing patient outcomes. A recent groundbreaking study delves into the roles of two critical cytokines, TNF (tumor necrosis factor) and IFN-γ (interferon-gamma), in shaping the immune responses of COVID-19 patients. This
Medical News report aims to break down the findings in an accessible manner for readers of all backgrounds.
 TNF and IFN-Gamma Co-Signaling in COVID-19 Patients Reveals New Insights into Disease Progression
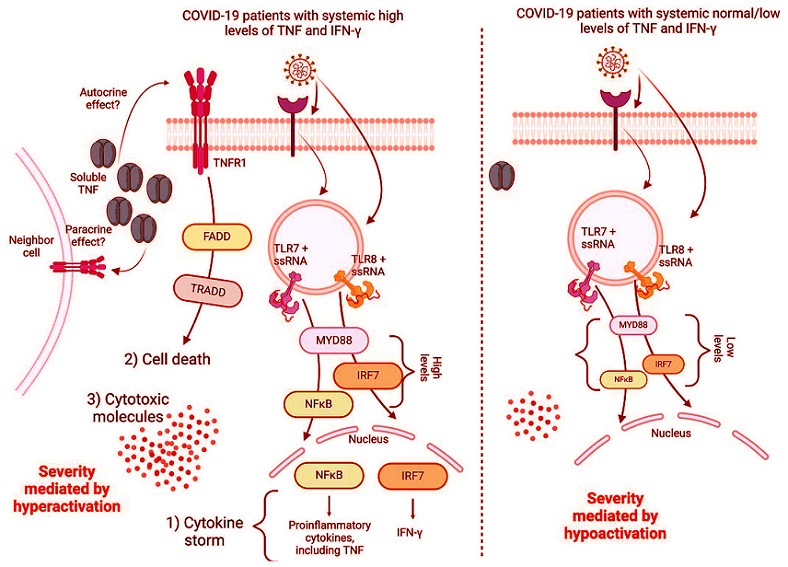
TLR7/TLR8 signaling triggers a proinflammatory response, a cytotoxic profile, and cell death favored by high TNF and IFN-γ levels in COVID-19 patients, causing severe disease mediated through hyperactivation. In contrast, disease severity is also caused by hypoactivation; COVID-19 patients display normal or low TNF and IFN-γ levels and lower expression of molecules related with TLR7/8 signaling and critical molecules involved in cell death.
The Role of TNF and IFN-γ in COVID-19
TNF and IFN-Gamma Co-Signaling in COVID-19 Patients Reveals New Insights into Disease Progression
TLR7/TLR8 signaling triggers a proinflammatory response, a cytotoxic profile, and cell death favored by high TNF and IFN-γ levels in COVID-19 patients, causing severe disease mediated through hyperactivation. In contrast, disease severity is also caused by hypoactivation; COVID-19 patients display normal or low TNF and IFN-γ levels and lower expression of molecules related with TLR7/8 signaling and critical molecules involved in cell death.
The Role of TNF and IFN-γ in COVID-19
TNF and IFN-γ are critical players in the immune system’s response to viral infections. They act as signaling molecules that guide the activation of immune cells to fight pathogens. However, excessive production of these cytokines can lead to a dangerous overreaction known as a cytokine storm. This study aimed to investigate whether TNF and IFN-γ levels influence the severity of COVID-19 and the activation state of immune cells.
What Was the Study About?
Conducted by researchers from the Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias Ismael Cosío Villegas, the Instituto Nacional de Rehabilitación Luis Guillermo Ibarra Ibarra, and the Immunology Laboratory at Escuela Militar de Graduados de Sanidad in Mexico, the study sought to understand how TNF and IFN-γ levels correlate with immune cell activity and patient outcomes. The research provides insights into potential therapeutic strategies by categorizing patients into groups based on cytokine levels.
How Was the Study Conducted?
The research involved 150 COVID-19 patients who were categorized based on their TNF and IFN-γ levels into four distinct groups:
-TNF-high/IFN-γ-high (TNFHIFNγH)
-TNF-high/IFN-γ-normal-low (TNFHIFNγN-L)
-TNF-normal-low/IFN-γ-high (TNFN-LIFNγH)
-TNF-normal-low/IFN-γ-normal-low (TNFN-LIFNγN-L)
The researchers measured cytokine levels, immune cell activity, and genetic variations in genes related to immune responses. They also analyzed patient outcomes, focusing on the need for invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) and other clinical indicators of severe disease.
Key Findings of the Study
The fi
ndings revealed two distinct patterns of immune response among the patients:
1) Hyperactive Immune Response
Patients with high levels of both TNF and IFN-γ (TNFHIFNγH) exhibited:
-Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and IL-6.
-Increased production of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10.
-Higher levels of cytotoxic molecules, including granzymes and perforin, which contribute to cell death.
-A high frequency of immune cells expressing TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), indicating a hyperactive immune state.
These patients were more likely to require invasive mechanical ventilation, highlighting the association between hyperactive immune responses and severe disease outcomes.
2) Hypoactive Immune Response
In contrast, patients with normal-to-low levels of both cytokines (TNFN-LIFNγN-L) displayed:
-Reduced ability to produce inflammatory and cytotoxic molecules.
-Lower activation of molecules involved in TLR7 and TLR8 signaling pathways, such as MYD88 and NFκB.
This hypoactive state suggests an inadequate immune response, which could also lead to severe disease outcomes due to the inability to effectively combat the virus.
Genetic Factors at Play
The study also identified genetic variations that influence cytokine levels and immune responses. Notably:
-The rs3853839 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the TLR7 gene was more frequent in the TNFHIFNγH group.
-The ACA haplotype of the TLR8 gene was dominant in patients with TNFHIFNγN-L profiles.
-Variants in the ACE2 gene, such as the rs2285666 SNP, were associated with higher TNF levels.
These findings underscore the importance of genetic factors in determining individual susceptibility to severe COVID-19.
Implications for Treatment
The study highlights the potential for targeting TNF and IFN-γ signaling pathways as therapeutic strategies. For patients with hyperactive immune responses, therapies aimed at dampening cytokine production could prevent the progression to severe disease. Conversely, patients with hypoactive responses might benefit from treatments that enhance immune activation.
Conclusions
This study sheds light on the complex interplay between TNF and IFN-γ levels, immune cell activity, and COVID-19 severity. The findings suggest that severe COVID-19 can arise from both hyperactive and hypoactive immune states, each requiring different therapeutic approaches. By identifying genetic markers associated with these immune profiles, the research provides a foundation for personalized medicine in managing COVID-19.
In conclusion, understanding the role of TNF and IFN-γ in COVID-19 pathophysiology offers valuable insights into the disease’s mechanisms and potential treatment strategies. The study emphasizes the need for further research to develop targeted therapies that address the diverse immune responses seen in COVID-19 patients. By tailoring treatments to individual immune profiles, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and reduce the burden of severe disease.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/3/1139
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/post-covid-19-depression-and-its-links-to-tnf-alpha
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-the-detrimental-effects-of-tnf%CE%B1-on-liver-during-sars-cov-2-infection-and-its-impact-on-patient-survival
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/interferon-gamma-by-activated-cd4-t-cells-shown-to-inhibit-covid-19-variants-differently
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/persistent-t-cell-dependent-ifn-gamma-release-seen-in-long-covid-individuals
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/coronavirus
