Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 13, 2024 5 months, 17 hours, 25 minutes ago
Medical News: Transfer RNA Fragments and Inflammation: A New Avenue for Disease Insights
In recent years, scientists have increasingly focused on a surprising player in human biology - small fragments of transfer RNA (tRNA), known as tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs). These tiny RNA segments, discovered through advancements in high-throughput sequencing technology, are now understood to be instrumental in managing inflammation, which is the body’s natural defense against infection and injury. Although traditionally associated with immune response, recent studies show tsRNAs hold potential as key regulators in various diseases.
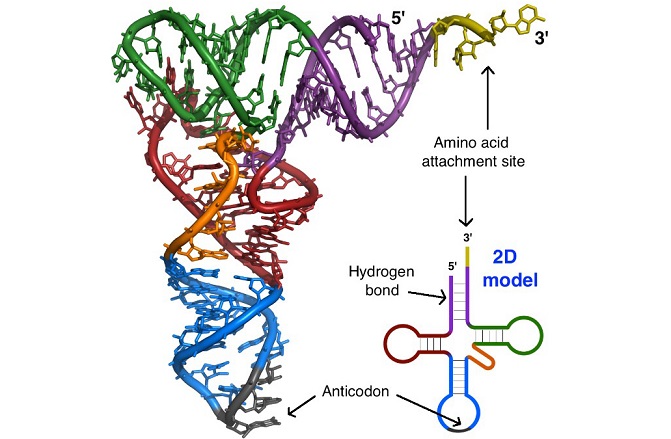 3D Model of tRNA versus a 2D model
3D Model of tRNA versus a 2D model
This
Medical News report explores tsRNAs and their functions in the inflammatory process, discussing the implications for diagnosing and treating inflammation-related diseases. Researchers from Ningbo University’s Health Science Center and affiliated medical institutions in China have found that tsRNAs play critical roles in several stages of inflammation, including managing inducers, cells, and mediators in inflammatory responses.
tsRNAs and Inflammatory Inducers
Inflammation can be triggered by various factors, such as pathogens and tissue damage. tsRNAs have been shown to be heavily involved in the inflammatory responses that occur during microbial infections. For example, a specific tsRNA fragment from the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa reduces inflammation by inhibiting the secretion of interleukin-8 (IL-8), a chemical signal involved in the body’s inflammatory response. This fragment also decreases inflammation by reducing immune cell infiltration in lung tissues, providing relief from infection-induced symptoms.
tsRNAs’ Interaction with Inflammatory Cells
Inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils, macrophages, and endothelial cells, play essential roles in controlling the intensity and spread of inflammation in the body. Among these, macrophages are known to play dual roles depending on the stage of inflammation. At the onset, M1 macrophages promote inflammation by releasing proinflammatory substances. Later, M2 macrophages release anti-inflammatory signals to restore tissue balance.
Research shows tsRNAs regulate the function of these macrophages. One tsRNA fragment, tsRNA-21109, has been identified as a suppressor of M1 macrophage activity, potentially reducing inflammation in diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus. Additionally, some tsRNAs influence the activity of endothelial cells, the primary cells responsible for forming new blood vessels during chronic inflammation. When new vessels form, they sustain inflammatory cells in the tissue. Specific tsRNAs regulate this process, demonstrating anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting blood vessel formation, as observed in age-related macular degeneration cases.
tsRNAs and Inflammatory Mediators
Inflammatory mediators - substances like cytokines and chemokines - are vital in controlling both the start and end of inflammation. tsRNAs interact clos
ely with these mediators, acting as either suppressors or enhancers. For instance, in high glucose environments, a tsRNA fragment boosts the production of two inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-18, which play crucial roles in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Other tsRNAs act oppositely, suppressing cytokine production and potentially reducing inflammation. One fragment, tDR-56:71-Ala-CGC-1-M4, lowers the levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and TNF-α, thereby reducing cell death in damaged tissues.
tsRNAs and Inflammation-Related Signaling Pathways
The process of inflammation is regulated by intricate signaling pathways. These pathways transmit signals within cells to initiate or suppress inflammation. tsRNAs have shown significant effects on pathways like NF-κB, JAK/STAT, and TLR, all of which are integral to the body’s inflammatory response. In one study, a specific tsRNA fragment triggered the production of proinflammatory cytokines by activating toll-like receptor 7, a pathway that plays a vital role in the body’s reaction to pathogens. Meanwhile, another fragment blocks the JAK3 pathway, which can decrease inflammation in patients with osteoarthritis, suggesting its use in therapeutic applications.
The Role of tsRNAs in Disease-Associated Inflammation
tsRNAs are associated with various diseases, with recent studies finding their presence in diseases like cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic kidney disease. Research reveals that in some cancers, tsRNAs contribute to the tumor’s ability to evade the immune system, while in other cases, they suppress tumor growth. For example, one tsRNA fragment identified in colorectal cancer tissue suppresses the immune-inhibiting M2 macrophages, enhancing the immune system’s ability to attack tumor cells. In gastric cancer, specific tsRNAs directly impact inflammatory pathways, offering potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for the disease.
Potential of tsRNAs in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications
Beyond their roles in disease management, tsRNAs show promise as early indicators of tissue damage. Unlike other biomarkers, tsRNAs remain stable in the bloodstream, making them suitable for noninvasive diagnostic tests. This stability, combined with their ability to indicate the degree of tissue damage, positions tsRNAs as excellent biomarkers for conditions that typically require early intervention, such as organ damage, ischemia, or radiation exposure. Moreover, as tsRNAs can indicate specific inflammation types and stages, they could help tailor treatments more precisely to individual patients.
Conclusions
The study of tsRNAs is rapidly expanding our understanding of inflammation and its role in diseases. These small RNA fragments influence every aspect of inflammation, from initial triggers to complex signaling networks. By regulating inflammatory inducers, cells, mediators, and pathways, tsRNAs play vital roles in both promoting and resolving inflammation. This research opens up new possibilities for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of inflammation-related diseases. Scientists are hopeful that understanding tsRNAs will eventually lead to breakthrough treatments for chronic conditions associated with inflammation, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Inflammation.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12950-024-00418-6
For the latest on tRNAs, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/trna-thiouridine-modification-reprogramming-behind-parasite-plasmodium-falciparum-developing-antimalarial-drug-resistance
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/coronavirus-s-protein-alters-dsrna-accumulation-and-stress-granule-formation-by-regulating-adari1
