Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 22, 2024 10 months, 4 days, 18 hours, 29 minutes ago
Immunology Updates: Understanding Tregitopes: The Immune System’s New Ally.
In recent years, a promising strategy has emerged for managing autoimmune diseases, allergies, and transplant rejection. This approach revolves around Tregitopes, a class of peptides that have the potential to revolutionize immune system treatments. By activating regulatory T cells (Tregs), Tregitopes can reduce inflammation and promote immune tolerance, offering hope for various immunological disorders. This
Immunology Updates news report is based on a white paper by researchers from Iran.
 Tregitopes: A Revolutionary Approach to Treating Immune Disorders
What are Tregitopes?
Tregitopes: A Revolutionary Approach to Treating Immune Disorders
What are Tregitopes?
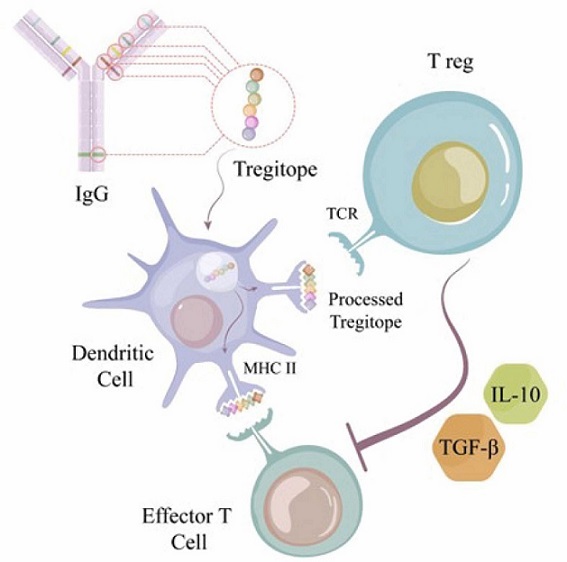
Tregitopes, short for "T regulatory epitopes," are peptides that can activate regulatory T cells (Tregs). Tregs are crucial in maintaining immune balance by preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own cells. Tregitopes work by binding to MHC II molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which then present these peptides to Tregs, promoting their proliferation and activation. This activation results in the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β, which help in maintaining immune tolerance.
How Tregitopes Work
Tregitopes influence the immune system in several ways. They reduce the expression of molecules like CD80, CD86, and MHC class II on APCs while enhancing the expression of ILT3, a molecule that inhibits immune responses. This leads to the suppression of inflammatory pathways, particularly the NF-kappa B signaling pathways, which are often overactive in autoimmune diseases. The dual action of Tregitopes, by both activating Tregs and modulating APCs, creates a more tolerant immune environment.
Applications in Autoimmune Diseases
Tregitopes have shown promise in managing various autoimmune conditions. For example, in diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes (T1D), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Tregitopes can induce specific Tregs that target disease-related antigens, reducing harmful immune responses. In experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model for MS, Tregitopes have demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects. They help in reducing the severity of the disease by decreasing the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the central nervous system and lowering the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Enhancing Vaccine Design
Beyond treating autoimmune diseases, Tregitopes are being explored to improve vaccine efficacy. By modulating the immune response, Tregitopes can enhance the body’s ability to generate a protective response to vaccines while minimizing potential side effects. This has significant implications for the development of more effective and safer vaccines. For instance, in the context of influenza vaccines, researchers are looking into modifying the vaccine components to include Tregitopes, which can potentially lead to stronger and more long-lasting immunity.
Addressing Pregnancy Complications
Tregitopes also play a vital role in reproductive immunology. They help maintain immune tolerance during pregnancy, reducing the risk of complications such as spontaneous abortion and preterm birth. By promoting the expansion of Tregs, Tregitopes ensure the immune system accepts the fetus, which is crucial for a successful pregnancy. Studies have shown that Tregitope-derived therapies can help in reducing the incidence of pregnancy-related complications by enhancing the body's natural tolerance mechanisms.
Managing Metabolic Disorders
In metabolic disorders like infantile-onset Pompe disease (IOPD), Tregitopes offer a novel treatment approach. IOPD patients often develop antibodies against enzyme replacement therapy, reducing its effectiveness. Tregitopes can induce tolerance to these therapeutic enzymes, improving treatment outcomes and patient survival. This approach is particularly promising for patients who have developed resistance to standard treatments, as Tregitopes can help in resetting the immune system's response to the therapeutic enzymes.
The Future of Tregitopes in Clinical Applications
Research into Tregitopes is ongoing, with scientists exploring their potential in various clinical settings. The ability of Tregitopes to induce antigen-specific tolerance makes them a promising candidate for treating a wide range of immunological disorders. However, challenges remain, including optimizing the design of Tregitope-based therapies and conducting extensive clinical trials to establish their safety and efficacy. Future studies will need to address these challenges to fully realize the potential of Tregitopes in clinical practice.
Conclusion
Tregitopes represent a significant advancement in immunotherapy. By harnessing the power of regulatory T cells, these peptides offer a targeted approach to restoring immune balance. As research progresses, Tregitopes could become a cornerstone in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, allergies, transplant rejection, and more, providing hope for patients worldwide. The future looks promising for Tregitopes as they continue to be explored for their wide-ranging applications and potential to improve the quality of life for many individuals suffering from immune-related disorders.
The white paper on Tregitopes was published in the peer reviewed journal: Biomedicine and Pharmacotheraphy (Elsevier).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332224008679
For the latest
Immunology Updates, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/immunology-updates-newly-discovered-role-of-dot1l-in-shaping-the-defense-system
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/meet-the-hidden-hero-in-our-immune-system-socs1
