U.S. Medical News: Researchers Warn That Incidence Of Syphilitic Uveitis Is Rising In America At An Alarming Rate!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 26, 2023 1 year, 4 months, 3 weeks, 1 day, 10 hours, 15 minutes ago
U.S. Medical News: In recent years, a concerning trend has emerged in the United States, signaling a substantial increase in the incidence of syphilitic uveitis. A retrospective cross-sectional study conducted from 2010 to 2019 has revealed alarming statistics, indicating a nearly threefold rise in serious cases of syphilitic uveitis requiring hospitalization during this period. This surge comes at a time when the nation is grappling with a shortage of the gold-standard treatment, injectable penicillin G, further complicating the management of this vision-threatening condition.
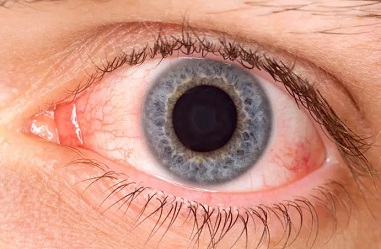 Syphilitic Uveitis
Understanding Syphilitic Uveitis
Syphilitic Uveitis
Understanding Syphilitic Uveitis
Syphilitic uveitis is a manifestation of ocular syphilis, presenting as an infectious type of uveitis that warrants consideration in the differential diagnosis of any ocular inflammation. This condition can occur at any stage of acquired syphilis, posing a significant risk of visual loss if left unrecognized or misdiagnosed as a noninfectious ocular inflammation. Ocular syphilis can affect various eye structures, with posterior uveitis and panuveitis being the most common, potentially leading to severe consequences such as decreased visual acuity and even permanent blindness.
Clinical Manifestations and Demographic Trends
Common signs and symptoms associated with syphilitic uveitis include red eyes, eye floaters, eye pain, sensitivity to light (photophobia), abnormal eye movements, and the Argyll Robertson pupil - a phenomenon where pupils constrict when focusing on a near object but not in response to bright light.
https://eyewiki.aao.org/Ophthalmologic_Manifestations_of_Syphilis
The retrospective study found that the incidence of syphilitic uveitis disproportionately affected certain demographic groups, including men (78.9%), Black adults (32%), residents of the Southern United States (42.1%), and those in the lowest median household income quartile (38.8%).
National Incidence Trends
Analyzing data from inpatient admissions between 2010 and 2019, the study covered in this
U.S. Medical News report, indicated a national incidence rate of 0.15 per 100,000 population. The incidence exhibited an escalating trend over the study period, with the lowest rate recorded in 2011 (0.08 per 100,000 population) and the highest in 2019 (0.23 per 100,000 population). This upward trajectory raises concerns among researchers and clinicians, emphasizing the urgent need for increased awareness and vigilance in identifying and treating syphilitic uveitis.
Clinical Experience and Shortage of Treatment
Dr Tahreem A. Mir, a researcher from Vanderbilt University Medical Center, highlighted that the study's findings align with the clinical experience of healthcare professionals. Dr Mir initiated the study due to a noticeable uptick in patients presenting with syphilitic uveitis - a conditio
n often diagnosed by ophthalmologists when patients experience visual changes without realizing they have syphilis.
The shortage of injectable penicillin G further complicates the situation, as it remains the gold-standard treatment for syphilitic uveitis, emphasizing the need for alternative strategies in the face of ongoing supply challenges.
https://www.ashp.org/drug-shortages/current-shortages/drug-shortage-detail.aspx?id=909&loginreturnUrl=SSOCheckOnly
https://www.vdh.virginia.gov/clinicians/shortage-of-penicillin-g-benzathine-bicillin-l-a/
Treatment Challenges and Recommendations
Neuro-ophthalmologists stress that intravenous penicillin is highly effective when administered promptly; however, due to the rarity of the condition, many ophthalmologists may not immediately consider syphilis in their differential diagnoses. Delayed diagnosis can have severe consequences, as evidenced by research indicating that poor visual acuity at the time of presentation is a strong predictor of poor vision outcomes. With the shortage of injectable penicillin showing no signs of resolution, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend an alternative treatment option - 10 to 14 days of ceftriaxone delivered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Study Insights and Implications
The retrospective study, utilizing the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, included data from 444,674 patients over the ten-year period. Among the 5,581 syphilitic uveitis-related hospitalizations, the median age was 45, and 23% had comorbid HIV. Patients with syphilitic uveitis typically required hospitalization for the placement of peripherally inserted central catheter lines to facilitate treatment delivery, with a median hospitalization period of six days. The median inflation-adjusted hospitalization charge in 2019 was US$39,464.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rising incidence of syphilitic uveitis in the United States poses a significant public health concern, particularly considering the challenges posed by the shortage of the gold-standard treatment, injectable penicillin G. The study's findings underscore the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for syphilis when evaluating patients with intraocular inflammation. Timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent devastating visual outcomes, and clinicians must consider alternative treatment options in the face of ongoing supply constraints. The medical community, along with public health agencies, must work collaboratively to address this emerging healthcare issue and develop strategies to mitigate the impact of syphilitic uveitis on individuals and communities across the nation.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: JAMA Ophthalmology.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/2812271
For the latest
U.S. Medical News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
