Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 17, 2025 2 months, 3 weeks, 6 days, 14 hours, 37 minutes ago
Medical News: The glycocalyx is a thin, villus-like structure that forms a protective layer on the inner surface of blood vessels. Composed of various glycoproteins and proteoglycans, this structure serves as a barrier and plays a critical role in regulating vascular functions, maintaining blood vessel integrity, and preventing diseases. Researchers from Nanning Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Zhejiang Chinese Medical University have recently conducted an extensive review to explore factors that degrade this essential structure.
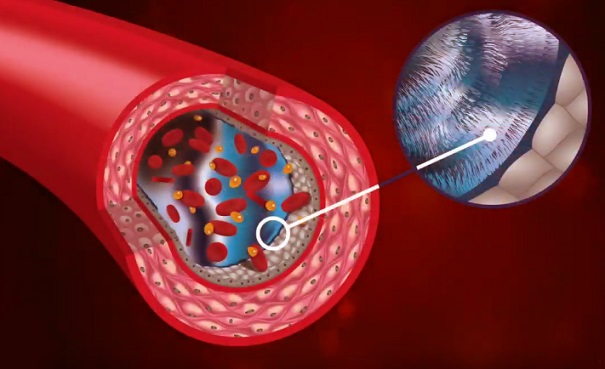 Understanding Factors Leading to Glycocalyx Degradation
Understanding Factors Leading to Glycocalyx Degradation
The glycocalyx is crucial for protecting vascular endothelial cells and ensuring normal blood flow. However, several factors, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and high blood sugar, can damage it. This
Medical News report delves into the key findings and implications of the study, shedding light on why preserving the glycocalyx is vital for human health.
A Historical Perspective
First observed in 1940 by Danielli, the glycocalyx was later characterized in greater detail with the development of advanced imaging techniques. Over the years, it has been found that the glycocalyx serves as a bridge between circulating blood components and endothelial cells. This barrier regulates the selective permeability of vessels and ensures vascular homeostasis. However, damage to the glycocalyx can result in several pathological conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes-related complications.
Key Factors Influencing Glycocalyx Degradation
The researchers highlighted several factors contributing to the degradation of the glycocalyx. These include:
-Inflammation: Inflammatory responses can lead to glycocalyx damage by upregulating enzymes like heparanase and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). These enzymes break down glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) within the glycocalyx. Studies have shown that inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), can disrupt the structure and stability of the glycocalyx. This degradation can trigger a cascade of events leading to vascular inflammation and increased permeability.
-Oxidative Stress: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during oxidative stress can attack the glycocalyx. These molecules degrade key components such as hyaluronan (HA) and heparan sulfate (HS), resulting in endothelial dysfunction. The study suggests that antioxidants like superoxide dismutase can mitigate this damage by neutralizing ROS.
-High Blood Sugar: Hyperglycemia, a hallmark of diabetes, has been closely associated with glycocalyx degradation. Elevated glucose levels can activate oxidative stress pathways and increase the expression of degrading enzymes. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) formed in hyperglycemia further exacerbate this process by activating receptors that promote inflammation.
-High Sodium Levels: High dietary salt intake was identified
as another factor contributing to glycocalyx damage. Sodium overload destabilizes the glycocalyx, resulting in increased endothelial stiffness and reduced vascular barrier function.
-Hormonal Influences: Female sex hormones, particularly during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, were found to impact glycocalyx integrity. Progesterone, in particular, was identified as a potential contributor to glycocalyx degradation through its effects on inflammation.
Mechanisms Behind Glycocalyx Degradation
The study provided insights into the biochemical and molecular pathways underlying glycocalyx damage. For instance, the activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway plays a pivotal role in inflammation-induced degradation. Similarly, ROS-mediated damage is facilitated by enzymes such as NADPH oxidase, which increases oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells.
The researchers also emphasized the role of MMPs in cleaving proteoglycans and GAGs, while heparanase specifically targets heparan sulfate chains. Together, these enzymes contribute to the thinning and loss of the glycocalyx, making blood vessels more susceptible to injury.
Clinical Implications
Damage to the glycocalyx has far-reaching implications for human health. Conditions such as atherosclerosis, diabetes, and ischemia-reperfusion injuries are closely linked to glycocalyx degradation. Understanding these mechanisms opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at protecting or restoring the glycocalyx.
Potential treatments include the use of antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and glycocalyx mimetics. For example, exogenous heparan sulfate has shown promise in experimental models of kidney diseases by reducing protein leakage and inflammation. Similarly, dietary modifications, such as reducing sodium intake and managing blood sugar levels, can help maintain glycocalyx integrity.
Future Directions
Despite the progress made, much remains to be understood about the glycocalyx. The researchers called for the development of more advanced imaging and diagnostic techniques to study this structure in real-time. Such tools could help monitor glycocalyx health and guide the development of targeted therapies.
Additionally, exploring the role of the glycocalyx in other diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, could yield valuable insights. Collaborative efforts among researchers from various fields will be essential to fully unravel the complexities of this vital structure.
Conclusions
Preserving the glycocalyx is crucial for maintaining vascular health and preventing chronic diseases. The study highlights the importance of understanding the factors and mechanisms that lead to glycocalyx degradation. By addressing these factors, it is possible to develop effective strategies to protect the glycocalyx and improve overall health outcomes.
The findings of this review were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Frontiers in Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1490395/full
For the latest Glycocalyx Health, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/australian-study-uncovers-covid-19-s-impact-on-the-endothelial-glycocalyx
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/peer-reviewed-study-warns-that-covid-19-vaccines-are-causing-endotheliopathy-or-glycocalyx-degradation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-clotting-caused-by-damage-of-small-vessels-and-glycocalyx-which-releases-hyaluronic-acid,-syndecan-1,-p-selectin-that-promotes-agrregation
