Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 06, 2024 1 year, 7 months, 4 weeks, 2 days, 1 hour, 4 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to light various aspects of viral pathogenesis and its impact on human health. Among the myriad of symptoms and complications associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, neurological manifestations have emerged as a significant concern. This
COVID-19 News report delves into the intricate interplay between the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) within the brain and its influence on the neurological consequences of COVID-19 based on a study review undertaken by researchers from Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences-Iran, Eastern Mediterranean University Famagusta-Turkey, RG University of Health Sciences-Bangalore-India and Tehran University of Medical Sciences-Iran
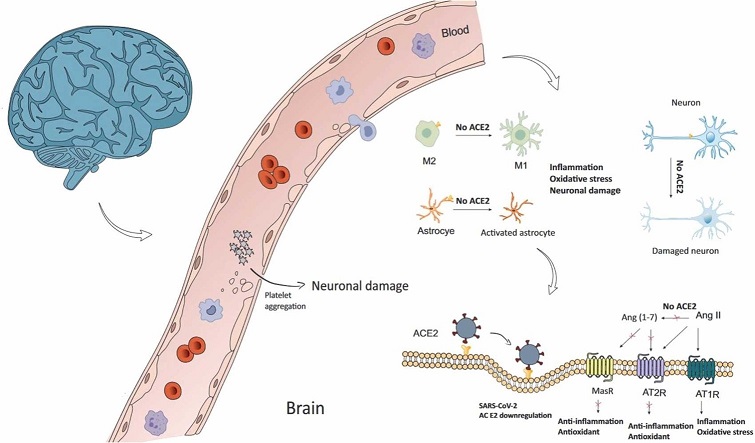 Role Of RAS In COVID-19 Neurological Manifestations - Graphical Abstract
Role Of RAS In COVID-19 Neurological Manifestations - Graphical Abstract
Through a theoretical lens, the study team explored how SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the delicate balance of brain-RAS signaling, leading to a spectrum of neurological complications.
The Renin-Angiotensin System: A Foundation for Brain Function
The Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) serves as a vital regulator of physiological processes, encompassing not only cardiovascular functions but also exerting profound effects on the central nervous system (CNS). Within the brain, the RAS plays a pivotal role in neuroplasticity, immune regulation, and antioxidative mechanisms. Central to this system is the cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (cACE2), which acts as a balancing force by converting Angiotensin II (Ang II) to Angiotensin (1-7), thus modulating neuroinflammation and neuronal protection.
ACE2 in Focus: Linking RAS to COVID-19 Pathogenesis
The ectoenzyme ACE2 emerges as a critical player in the context of COVID-19 pathophysiology. Its presence on cell membranes allows SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, to gain entry into cells, particularly in the respiratory and neurological systems. By downregulating cACE2, the virus disrupts the equilibrium of Ang II and Ang (1-7), tipping the balance towards neuroinflammatory pathways and oxidative stress.
Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19: Insights from RAS Disruption
The neurological repercussions of SARS-CoV-2 infection are diverse and multifaceted. From sensory disturbances such as anosmia and dysgeusia to more severe cerebrovascular disorders and brain stem-related complications, the impact on the CNS is profound. These manifestations are intricately linked to the dysregulation of brain-RAS, highlighting the interconnectedness of viral pathogenesis and neurological outcomes.
Exploring Brain-RAS Modulation: Insights from Studies
Several preclinical studies shed light on the intricate modulation of brain-RAS components and their implications for neuroprotection. Agonists and antagonists targeting Mas receptors (MasR) within the RAS demonstrate the potential to mitigate neuronal damage and promote cellular resilience. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of ta
rgeting RAS components to ameliorate COVID-19-related neurological sequelae.
Pathological Pathways: Unraveling COVID-19 Neurological Complications
The disruption of brain-RAS by SARS-CoV-2 sets off a cascade of pathological events within the CNS. From heightened inflammatory responses to oxidative stress and cytokine release, the milieu created by viral invasion precipitates neuronal injury and neuroinflammation. This intricate interplay underscores the complexity of COVID-19's impact on neurological function.
Case Reports and Meta-Analyses: Clinical Insights into CNS-Related Symptoms
Clinical observations and meta-analyses provide valuable insights into the spectrum of CNS-related symptoms associated with COVID-19. Headache, dizziness, impaired consciousness, and cerebrovascular accidents emerge as prominent features, further highlighting the broad-ranging impact of SARS-CoV-2 on neurological health.
The Crucial Role of RAS Homeostasis in Neurological Integrity
Central to maintaining neurological integrity is the homeostasis of brain-RAS components. Disruptions in this delicate equilibrium, precipitated by SARS-CoV-2, unleash a cascade of events culminating in neuronal injury and functional deficits. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions, cerebrovascular diseases, and brain stem-related disorders stand as testament to the intricate web of interactions within the brain-RAS-COVID-19 axis.
Implications for Future Research and Clinical Practice
The insights garnered from understanding the influence of RAS on COVID-19 neurological manifestations pave the way for future research endeavors and clinical interventions. Targeting specific RAS components, such as ACE2 and Mas receptors, holds promise in mitigating the neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and enhancing patient outcomes. Moreover, a deeper comprehension of the intricate signaling pathways within brain-RAS-COVID-19 nexus is imperative for devising tailored therapeutic strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the influence of the renin–angiotensin system on various processes within the brain underscores its pivotal role in COVID-19 neurological manifestations. By unraveling the complexities of brain-RAS disruption by SARS-CoV-2, we gain valuable insights into the pathogenesis of neurological complications and pave the way for targeted therapeutic interventions. This holistic understanding forms the cornerstone for future research endeavors aimed at mitigating the neurological burden of COVID-19.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S089106182400036X
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
