Unveiling a New Diagnostic Approach for a Deadly Heart Condition - Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 02, 2024 10 months, 3 weeks, 3 days, 11 hours, 12 minutes ago
Cardiology Updates: Researchers in China have made a significant breakthrough in understanding and diagnosing a dangerous heart condition known as Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC). This disease, which can cause sudden cardiac death and severe heart failure, has been difficult to diagnose and treat due to its complex nature. The team, led by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, has identified a potential new diagnostic method that could save lives. The study findings are covered in this
Cardiology Updates report.
 Unveiling a New Diagnostic Approach for a Deadly Heart Condition - Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
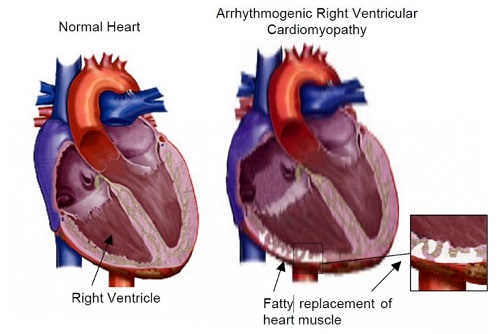
What is ARVC?
Unveiling a New Diagnostic Approach for a Deadly Heart Condition - Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
What is ARVC?
ARVC is a hereditary heart disease that was first discovered in the 1970s. It primarily affects the right ventricle of the heart, causing it to enlarge and be replaced by fatty and fibrous tissue. This condition can lead to serious heart problems, including heart failure and sudden cardiac death. One of the challenges in diagnosing ARVC is its variable clinical symptoms and the many different gene mutations that can cause it.
Traditional diagnostic methods like electrocardiograms and imaging can provide clues, but they are often not definitive. Pathological examination, the gold standard for diagnosis, usually only occurs at an advanced stage of the disease.
A New Approach: The ceRNA Network
The study focused on a new gene regulatory model known as the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network. This network includes various types of RNA, such as mRNA, long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), and micro-RNA (miRNA). These molecules interact in complex ways to regulate gene expression, which can help us understand how diseases develop and progress.
In this study, researchers analyzed RNA data from heart tissue samples to identify differences between ARVC patients and healthy individuals. They constructed a ceRNA network to understand these interactions better. They discovered that certain mRNAs and lncRNAs were differentially expressed in ARVC patients, meaning their levels were significantly different compared to healthy individuals.
Key Findings: The Role of Specific Genes and RNAs
The researchers identified 448 differentially expressed mRNAs (DEM) and 139 differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElnc) in ARVC patients. Also 21 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRs) were found. These RNAs were involved in processes related to the extracellular matrix and fibrosis, which are crucial in ARVC. By examining these differences, they constructed a regulatory network and identified key molecules that could serve as diagnostic markers.
The study highlighted four mRNAs (COL1A1, COL5A1, FBN1, BGN) and two lncRNAs (XIST, LINC00173) as potential biomarkers for ARVC. These molecules were validated using real-time quantitative PCR, a technique that measures RNA levels in tissue samples. The findings were consistent across different datasets, showing the reliability of these biomarkers.
gt;
Diagnostic Potential
To test the diagnostic potential of their findings, the researchers developed a logistic regression model. This model uses the identified RNAs to predict the likelihood of ARVC. Impressively, the model showed high accuracy in distinguishing ARVC patients from healthy individuals, both in initial tests and external validations. This suggests that the identified RNAs could serve as reliable biomarkers for diagnosing ARVC.
Unveiling Key Biological Pathways
The study also shed light on the biological pathways involved in ARVC. Many of the identified genes are linked to extracellular matrix organization and fibrosis. This aligns with ARVC’s hallmark feature of replacing healthy heart tissue with fibrous and fatty deposits. One notable pathway involves the TGF-β/SMAD signaling, known to promote fibrosis and contribute to heart disease.
Understanding these pathways could pave the way for targeted therapies in the future.
Implications for Future Research
While the study’s findings are promising, there are still challenges to overcome. For instance, the lack of comprehensive data combining miRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA from the same samples limits the ability to create a fully integrated diagnostic model. Additionally, further research is needed to validate these findings at the protein level and explore their therapeutic potential.
Conclusion
This study marks a significant step forward in understanding the genetic mechanisms behind ARVC. By identifying key RNAs and constructing a detailed ceRNA network, the researchers have laid the groundwork for more accurate diagnostics and potential treatments for this deadly heart condition. As science continues to unravel the complex web of genetic interactions, there is hope that we can outsmart the silent killer and save more lives.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.
https://www.mdpi.com/2308-3425/11/6/168
For the latest
Cardiology Updates, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-45-percent-of-individuals-who-get-hospitalized-for-heart-arrhythmia-typically-die-within-the-next-ten-years
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/murine-study-reveals-yet-another-way-that-sars-cov-2-causes-heart-damage-targeting-cardiac-pericytes,-causing-heart-s-microvasculature-damage
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/emeritus-professor-in-immunology-warns-in-australian-journal-of-general-practice-that-covid-19-mrna-jabs-possibly-behind-long-covid-heart-issues
