Unveiling The Intriguing Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2's Most Toxic Accessory Protein: ORF6 Sheds Light On COVID-19 Pathogenesis
COVID-19 News - SARS-CoV-2 - ORF6 Jun 10, 2023 1 year, 10 months, 2 weeks, 2 days, 1 hour, 38 minutes ago
Bulgarian Scientists Make Groundbreaking Discoveries That Could Revolutionize COVID-19 Treatment Strategies
COVID-19 News: The world is still grappling with the devastating impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has wreaked havoc on global health systems and economies. Scientists and researchers have been working tirelessly to unravel the mysteries surrounding SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for this unprecedented crisis. Among its arsenal of proteins, ORF6 stands out as the most toxic and enigmatic, holding the key to understanding the virus's pathogenicity.
A team of scientists from the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences and Sofia University has recently made groundbreaking discoveries that shed light on the mechanism of action of ORF6, offering crucial insights into COVID-19 pathogenesis.
ORF6's Role in Immune Suppression
ORF6, an accessory protein unique to the Sarbecovirus subgenus of the Betacoronaviruses, including SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, plays a crucial role in suppressing the host cell's immune response to the viral infection as covered in various past studies and
COVID-19 News reports.
While its precise mechanism has remained elusive, the Bulgarian research team harnessed the power of in silico and in vitro experiments to delve into the intricate workings of ORF6.
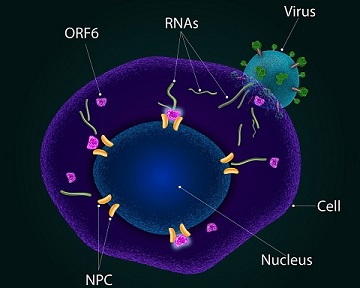
Through computational modeling and experimental investigations, the study team discovered that ORF6, embedded in the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, interacts with a protein called RAE1. This interaction leads to the sequestration of RAE1 in the cytoplasm, resulting in a depletion of this critical protein in the nucleus. Consequently, the transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the host cells are impaired, negatively impacting cellular genome stability. These disruptions compromise the cell cycle's progression into the S-phase and promote the accumulation of RNA-DNA hybrids, contributing to the virus's pathogenicity.
ORF6's Impact on Host Cell Proliferation and Genome Integrity
The study's implications go beyond immune suppression. The researchers discovered that ORF6's toxicity, which surpasses that of all other SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins, extends to its impact on cell proliferation and genome integrity. By inhibiting the transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, ORF6 disrupts the delicate balance required for proper cell cycle progression. This disruption leads to a slowdown in cell division and proliferation, ultimately impairing the host's ability to mount an effective immune response against the virus.
Furthermore, the accumulation of RNA-DNA hybrids resulting from ORF6's interference with genome stability has profound implications for the virus's pathogenesis. RNA-DNA hybrids are known to trigger an immune response and promote DNA damage. The presence of these hybrids in infected cells can activate innate immune sensors, such as cGAS-STING, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and exacerbat
ing the inflammatory response associated with severe COVID-19 cases.
Implications for COVID-19 Treatment and Challenges in Drug Design
The findings of this groundbreaking study hold immense promise for combating the detrimental effects of SARS-CoV-2 on host cells. Understanding the various ways in which ORF6 interferes with DNA replication and compromises cellular functions paves the way for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies. By identifying ORF6 as an excellent target for drug design, researchers can work towards mitigating the pathogenic effects of the virus and potentially revolutionize COVID-19 treatment.
Despite the urgent need for effective treatments, ORF6 remains one of the few proteins of SARS-CoV-2 with an unresolved 3D structure. This lack of structural information hinders the development of specific inhibitors. However, the Bulgarian research team has made significant strides in overcoming this obstacle by constructing a full-length structural model of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 protein embedded in an endoplasmic reticulum membrane. This innovative approach provides a foundation for rational drug design and brings us one step closer to finding potential therapeutic interventions.
Additionally, the structural model of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 protein constructed by the Bulgarian research team provides a foundation for rational drug design. With a better understanding of ORF6's molecular structure and its interactions with RAE1, researchers can explore small molecule inhibitors or therapeutic antibodies that can effectively disrupt these interactions and neutralize ORF6's toxic effects.
In-depth investigations using molecular dynamics simulations and experimental validation have revealed the interactions between ORF6 and RAE1. The team confirmed the formation of a stable ORF6-RAE1 protein complex, sequestering RAE1 primarily in the cytoplasm, away from its crucial nuclear functions. These findings shed light on the molecular basis of their binding, aligning perfectly with available experimental data.
The discovery of ORF6's crucial role in COVID-19 pathogenesis opens up new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Developing drugs or treatments that specifically target ORF6 could help mitigate the harmful effects of the virus on host cells. By disrupting the ORF6-RAE1 interaction or interfering with ORF6's ability to sequester RAE1 in the cytoplasm, it may be possible to restore normal cellular functions and enhance the immune response against the virus.
Conclusion
The recent discoveries by the Bulgarian research team have uncovered the fascinating mechanism of action of ORF6, the most toxic protein of SARS-CoV-2. By elucidating its role in immune suppression, cell proliferation, and genome integrity, these findings offer crucial insights into COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Moreover, the identification of ORF6 as a potential target for therapeutic interventions brings hope for the development of novel treatments to mitigate the harmful effects of the virus on the human body.
The study findings were published on a preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202306.0648/v1
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
