Source: Thailand Medical New Dec 13, 2019 6 years, 1 month, 3 weeks, 6 hours, 2 minutes ago
A type of artificial intelligence
, deep learning, can boost the power of
MRI in predicting
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (
ADHD), according to a study published in the journal Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. Researchers said the approach could also have applications for other neurological conditions.
Human brains are basically complex sets of networks. Advances in functional
MRI, a type of imaging that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, have helped with the mapping of connections within and between brain networks. This comprehensive brain map is referred to as the
connectome.
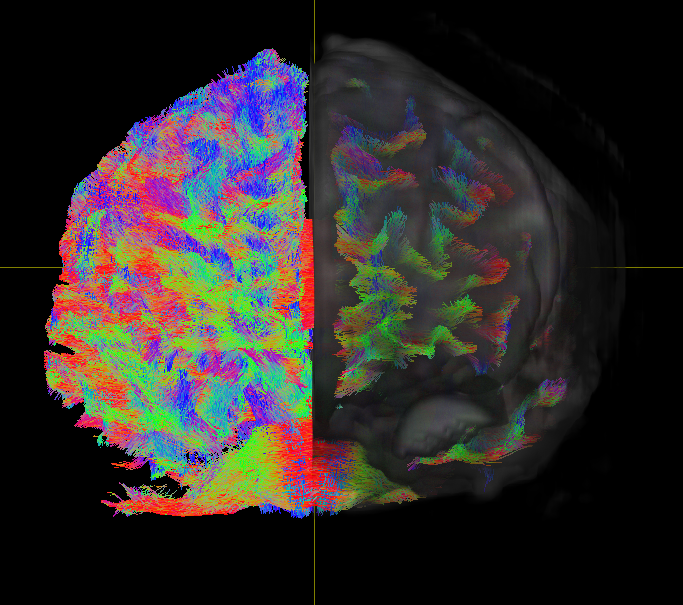
These days, the
connectome is regarded as key to understanding brain disorders like
ADHD, a condition that makes it difficult for a person to pay attention and control restless behavior.
Approximately 9.4% of U.S. children, ages 2 to 17 years (6.1 million) in 2016 have been diagnosed with
ADHD, according to the National Survey of Children's Health The disorder cannot yet be definitively diagnosed in an individual child with a single test or medical imaging exam. Instead,
ADHD diagnosis is based on a series of symptoms and behavior-based tests.
It is regarded that
Brain MRI has a potential role in diagnosis, as research suggests that
ADHD results from some type of breakdown or disruption in the
connectome. The
connectome is constructed from spatial regions across the
MR image known as parcellations. Brain parcellations can be defined based on anatomical criteria, functional criteria, or both. The brain can be studied at different scales based on different brain parcellations.
Past studies have focused on the so-called single-scale approach, where the
connectome is constructed based on only one parcellation. For the new study, researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center took a more comprehensive view. They developed a multi-scale method, which used multiple
connectome maps based on multiple parcellations.
To develop the deep learning model, the researchers used data from the NeuroBureau
ADHD-200 dataset. The model used the multi-scale brain
connectome data from the project's 973 participants along with relevant personal characteristics, such as gender and IQ.
This new multi-scale approach improved
ADHD detection performance significantly over the use of a single-scale method.
Dr Lili He, Ph.D., from the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and senior author of the study told
Thailand Medical News, "Our results emphasize the predictive power of the brain
connectome. The constructed brain functional
connectome that spans multiple sca
les provides supplementary information for the depicting of networks across the entire brain."
By further improving diagnostic accuracy,
deep-learning-aided
MRI-based diagnosis could be critical in implementing early interventions for
ADHD patients. Approximately 5% of American pre-school and school-aged children have been diagnosed with
ADHD. These children and adolescents face a high risk of failing in academic study and building social relationships, which can result in financial hardship for families and create a tremendous burden on society. The approach also has potential beyond
ADHD, according to Dr. He.
Dr He added, "This model can be generalized to other neurological deficiencies. We already use it to predict cognitive deficiency in pre-term infants. We scan them soon after birth to predict neurodevelopmental outcomes at two years of age."
The researchers expect to see the
deep learning model improve as it is exposed to larger neuroimaging datasets. They also hope to better understand the specific breakdowns or disruptions in the
connectome identified by the model that are associated with
ADHD.
Reference: Chen, M., Li, H., Wang, J., Dillman, J. R., Parikh, N. A., & He, L. (2019). A Multichannel Deep Neural Network Model Analyzing Multiscale Functional Brain Connectome Data for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Detection. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, 2(1), e190012. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2019190012 