For All The Latest Medical News, Health News, Research News, COVID-19 News, Dengue News, Glaucoma News, Diabetes News, Herb News, Phytochemical News, Cardiology News, Epigenetic News, Cancer News, Doctor News, Hospital News
A thrush infection of the breast can cause pain and difficulty when breastfeeding. Thrush is caused by infection with the fungus Candida albicans, which often happens after a baby or mother has taken a course of antibiotics.
Antibiotics can decrease the number of “good” bacteria in the body that usually keep harmful microbes in check, thereby allowing Candida albicans to flourish. This may permit Candida infection to take hold. A thrush infection may also occur as the result of cracking of or damage to the nipples, allowing the fungus to spread into the nipple and the breast tissue.
Women who experience the following may have a thrush infection of the breast:
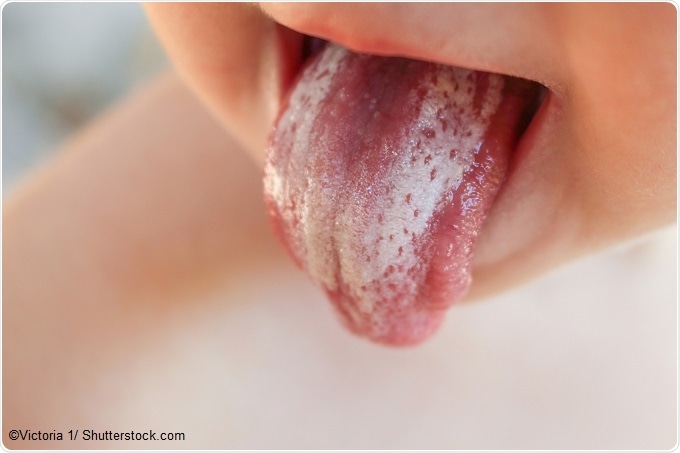
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of oral thrush in a breastfed baby
A doctor can diagnose a thrush infection in a baby or mother by taking swabs from the mother’s nipples and from the baby’s mouth, which are then sent for laboratory analysis. The mother and baby are both treated, even when the baby has no signs of infection in the mouth, because the baby could have a latent infection which could re-infect the mother during breastfeeding. The main medication used to treat a thrush infection of the breast is miconazole, an antifungal cream that is applied to and around the nipple after the baby is fed. The main treatment for a baby with a thrush infection is a liquid suspension of nystatin which is gently applied around and inside the baby’s mouth.