For All The Latest Medical News, Health News, Research News, COVID-19 News, Dengue News, Glaucoma News, Diabetes News, Herb News, Phytochemical News, Cardiology News, Epigenetic News, Cancer News, Doctor News, Hospital News
Oral thrush refers to the infection of the mouth with the fungus Candida albicans. The condition, which is also referred to as oral candidiasis, causes white plaques that resemble cottage cheese to form on the tongue, on the inside of the cheeks and sometimes on the tonsils, gums and the back of the throat. In some cases, oral thrush can spread down into the esophagus which can cause difficulty eating and swallowing.
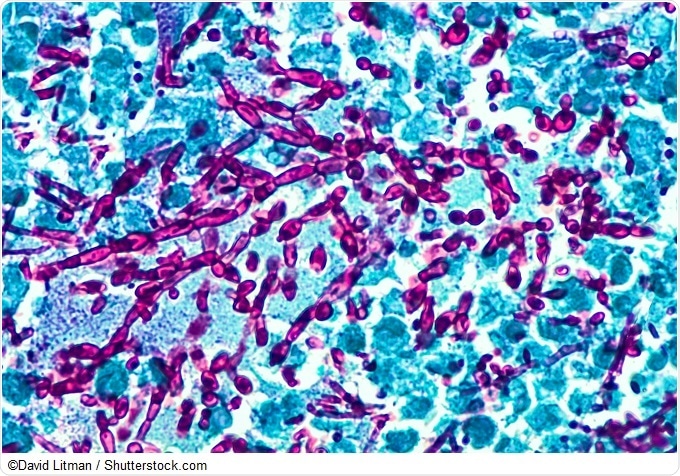
Image: Budding yeast and pseudohyphae of Candida albicans, stained with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain.
Low levels of Candida albicans are present naturally in the mouth of healthy individuals, but they are usually kept in check by the immune system, which maintains a healthy balance of good and bad microbes in the body. However, certain factors such as illness, the use of certain medications, stress or poor oral hygiene can disrupt this microbial balance and lead to overgrowth of the fungus, in which case, symptoms may develop.
The condition is not contagious and can usually be treated with antifungal medication, taken over the course of 10 to 14 days. Depending on the patient’s age and the underlying cause, medication may take the form of liquids or gels (topical medications) that can be applied to the inside of the mouth or, in some cases, tablets or capsules may be prescribed. These medications do not usually cause side effects, although some people may experience nausea, diarrhea, abdominal bloating and pain.
Taking the following measures can help reduce the risk of oral thrush developing: